The CDC began a national rubella immunization campaign
In 1969, live, attenuated rubella vaccines were first licensed in the U.S., and a vaccination program was established…
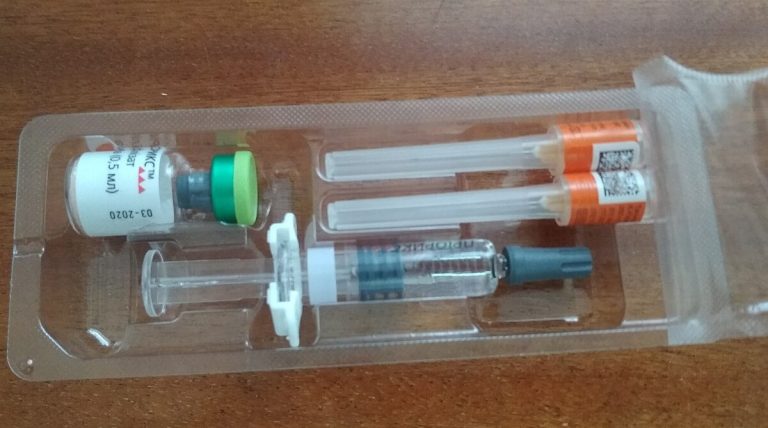
In 1969, live, attenuated rubella vaccines were first licensed in the U.S., and a vaccination program was established…
On Nov. 26, 1968, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed a second live, further attenuated measles…
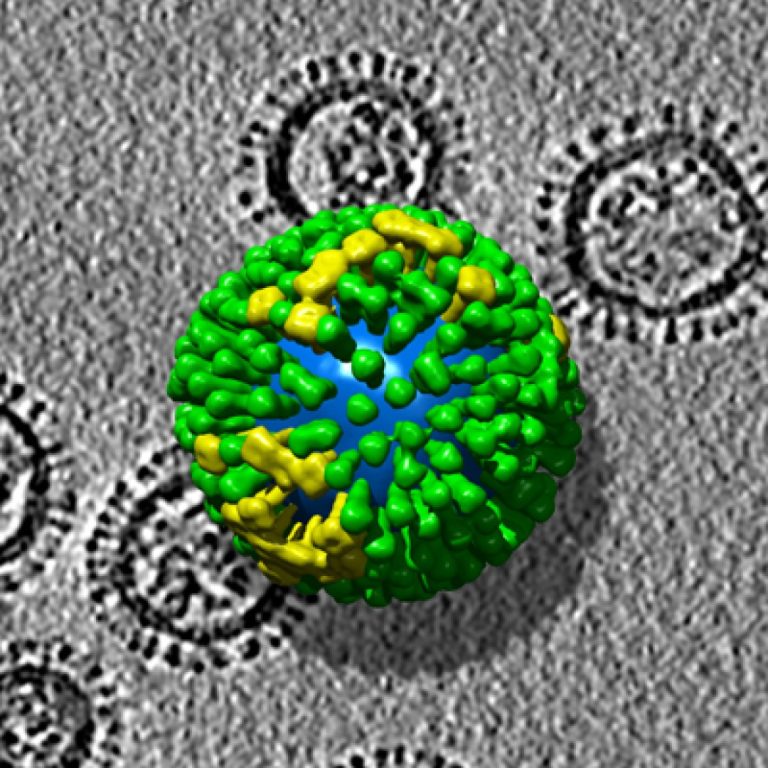
The 1968 pandemic, also known as the Hong Kong flu, was caused by an influenza A (H3N2) virus…
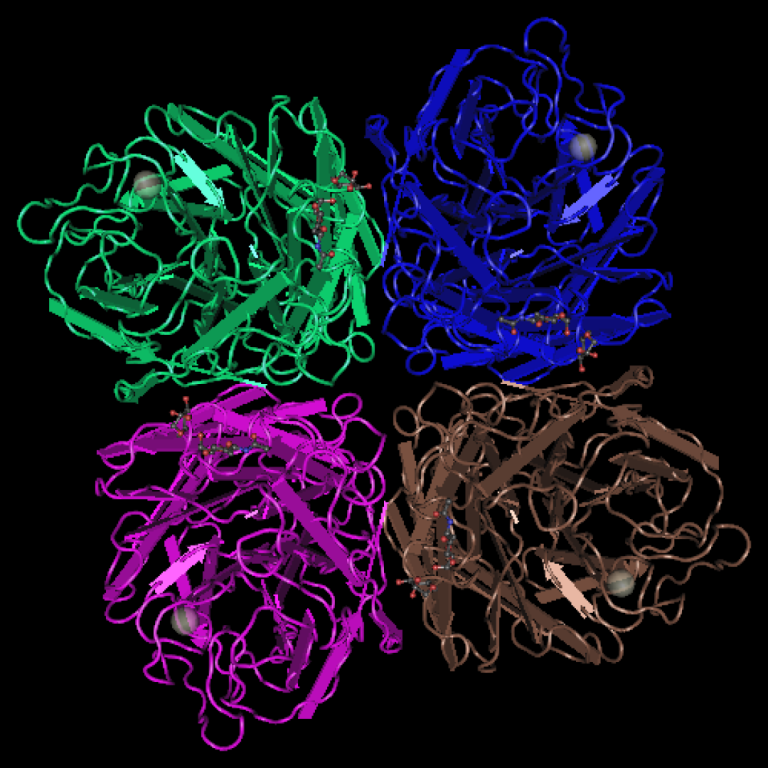
In 1968, a pandemic was caused by an influenza A (H3N2) virus comprised of two genes from an…
On Dec. 28, 1967, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Mercks mumps virus vaccine live (MumpsVax)….

On Jun. 12, 1966, the Serum Institute of India was founded in 1966 by Dr. Cyrus Poonawalla with…
In 1965,tThe bifurcated needle for smallpox vaccine was introduced. In 1961 the bifurcated needle was developed as a…
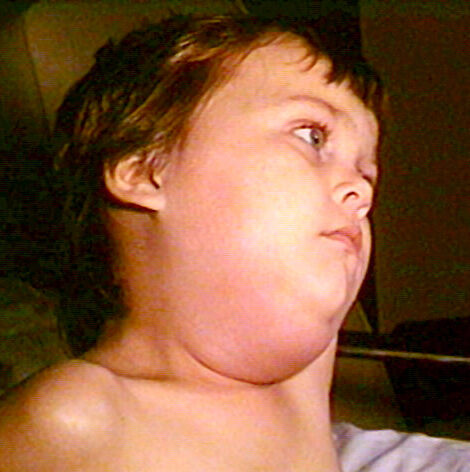
In 1965, the rubella virus was attenuated by a NIH research team lead by Paul Parkman and Harry…

In March 1964, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) to the U.S. Public Health Service was formed to…
In 1964, live, further attenuated measles virus vaccine (Lirugen by Pitman Moore-Dow based on the Schwarz strain, derived…

On Jun. 25, 1963, the Trivalent oral polio vaccine was licensed. The vaccine development began in 1957 by…

On Mar. 21, 1963, the first live virus measles vaccine (Rubeovax by Merck) was licensed. Other live virus…

In 1963, the U.S. Congress established the Immunization Grant Program; polio incidence plummeted to only 396 reported cases…

In 1963, the first measles vaccines were licensed in 1963. Both vaccines were an inactivated (モkilledヤ) and a…

On Mar. 27, 1962, the Sabin oral polio vaccine (OPV) type 3 MOPV was licensed in the U.S.,…

In 1962, oral polio vaccine types 1 and 2, developed by Dr. Albert Sabin and grown in monkey…

In 1961, oral polio vaccine, developed by Dr. Albert Sabin, was licensed for use in the U.S. In…
In 1960, the U.S. Surgeon General, in response to substantial morbidity and mortality during the 1957-58 pandemic, recommends…

In 1959, the Salk Institute was initially envisioned by Jonas Salk, M.D., the developer of the polio vaccine,…

In 1958, mpox (MPVX) was first discovered when two nonfatal outbreaks of a pox-like disease were reported in…

In 1958, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) sent a team of EIS officers to…

In 1958, Hollister-Stier Laboratories became a subsidiary of Cutter Laboratories. Hollister-Stier Laboratories, located in Spokane, was founded by…
In Feb. 1957, a new influenza A (H2N2) virus emerged in East Asia, triggering a pandemic (‘Asian Flu’)….

In Feb. 1957, a new influenza A (H2N2) virus emerged in East Asia, triggering a pandemic (“Asian Flu”)….
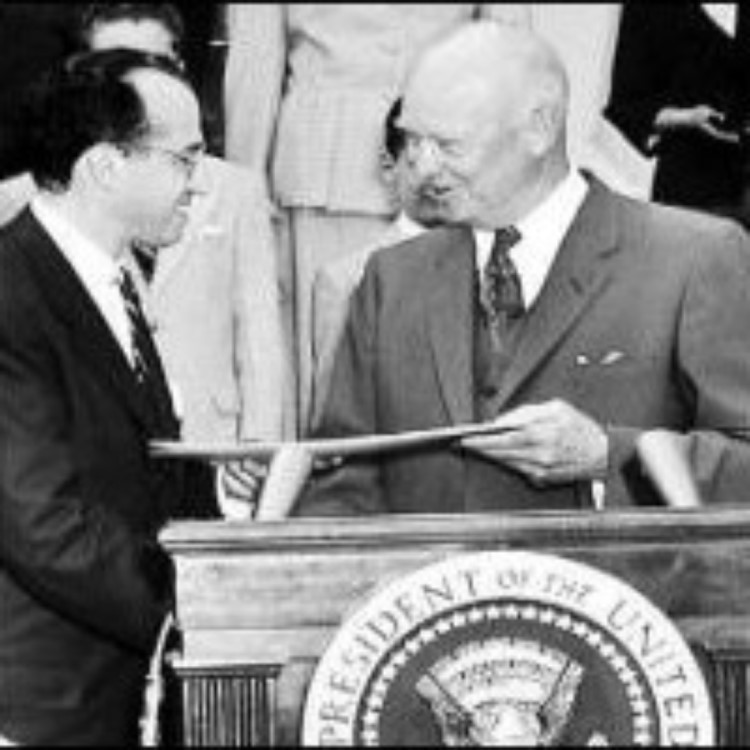

On Jan. 27, 1956, Dr. Jonas Salk, developer of the Polio vaccine released in 1955, received a special…
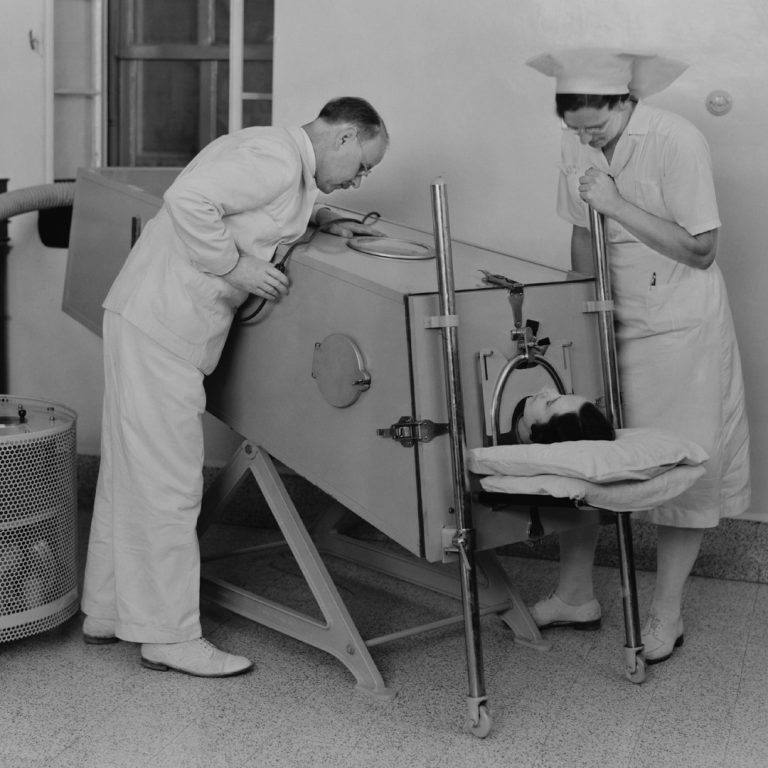

On Aug. 17, 1955, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced the hiring of 48 temporary investigators…
On Apr. 26, 1955, Officials first noticed an increase in reported polio cases in California. Soon it was…
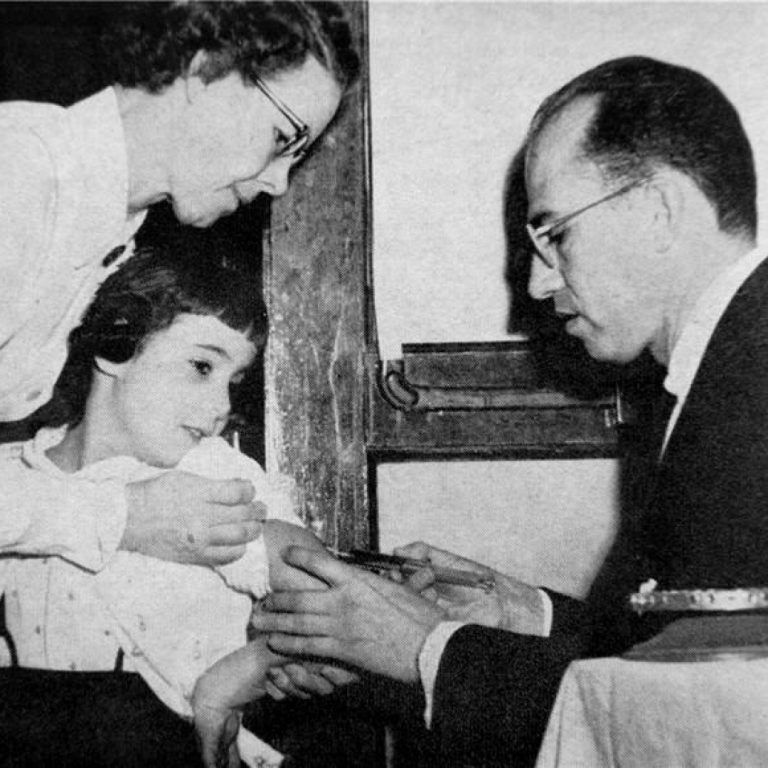
On Apr. 12, 1955, the polio vaccine developed by Dr. Jonas Salk at the University of Pittsburgh was…
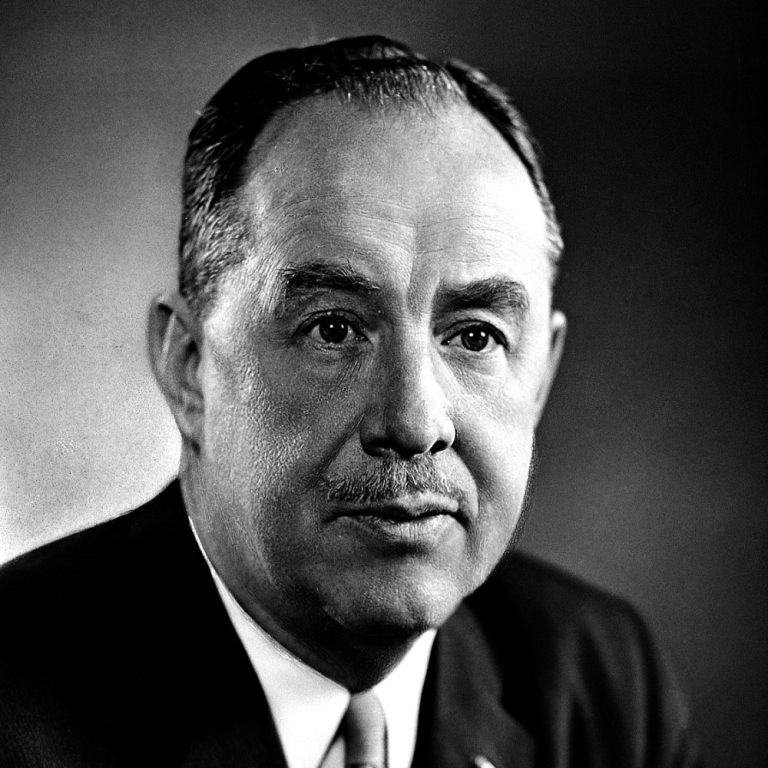

On Apr. 12, 1955, a convocation was held at the University of Michigan (UM), where Dr. Thomas Francis…
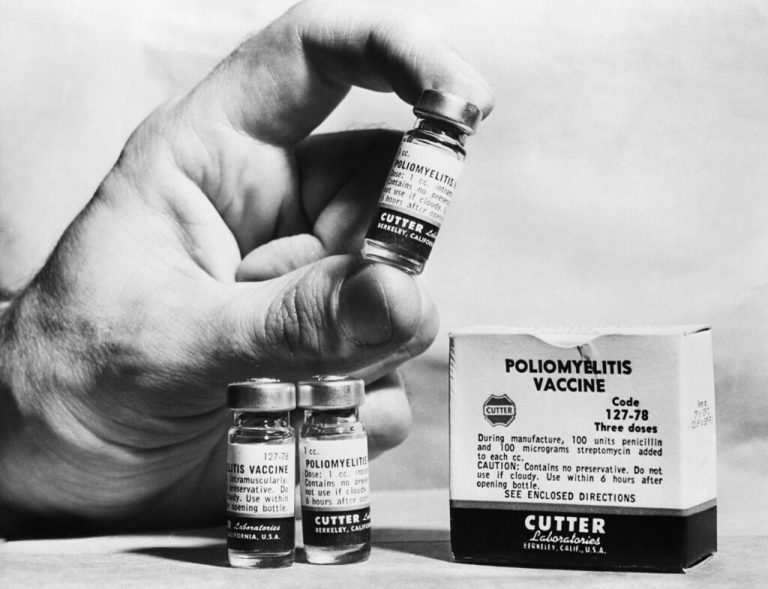
In April 1955, Cutter Laboratories, located in Berkeley, California and one of several companies licensed by the U.S….