Rabies human diploid-cell vaccine (Imovax Rabies by Merieux and Wyvac by Wyeth) were licensed
On Jun. 9, 1980, the rabies human diploid-cell vaccine (Imovax Rabies by Merieux, now Sanofi, and Wyvac by…
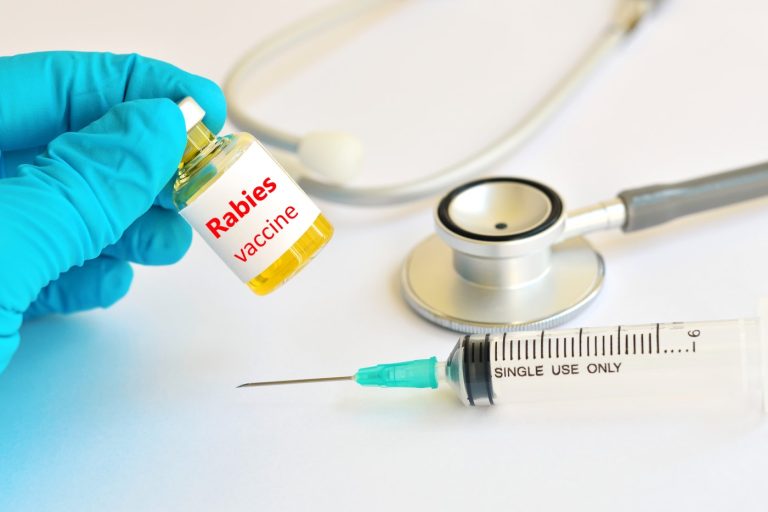
On Jun. 9, 1980, the rabies human diploid-cell vaccine (Imovax Rabies by Merieux, now Sanofi, and Wyvac by…

On May 8, 1980, members of the World Heath Organization (WHO) in Geneva announced that “smallpox had been…
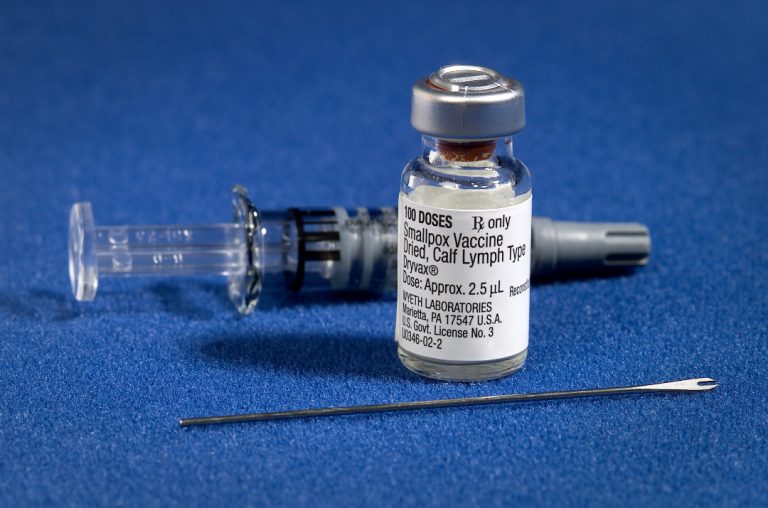
On May 8, 1980, the World Health Assembly certified the world free of naturally-occurring smallpox. Smallpox is an…
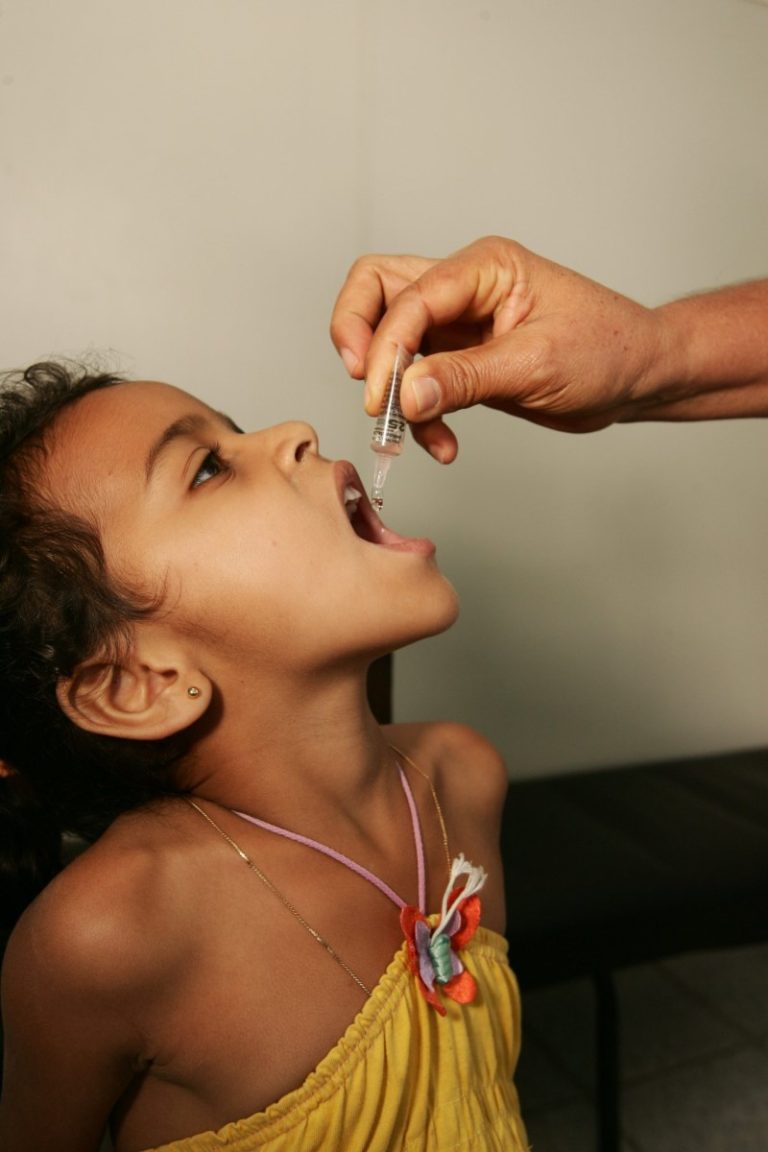
On Jul. 27, 1979, the last cases of wild type 1 poliovirus occurred in the U.S. among unvaccinated…
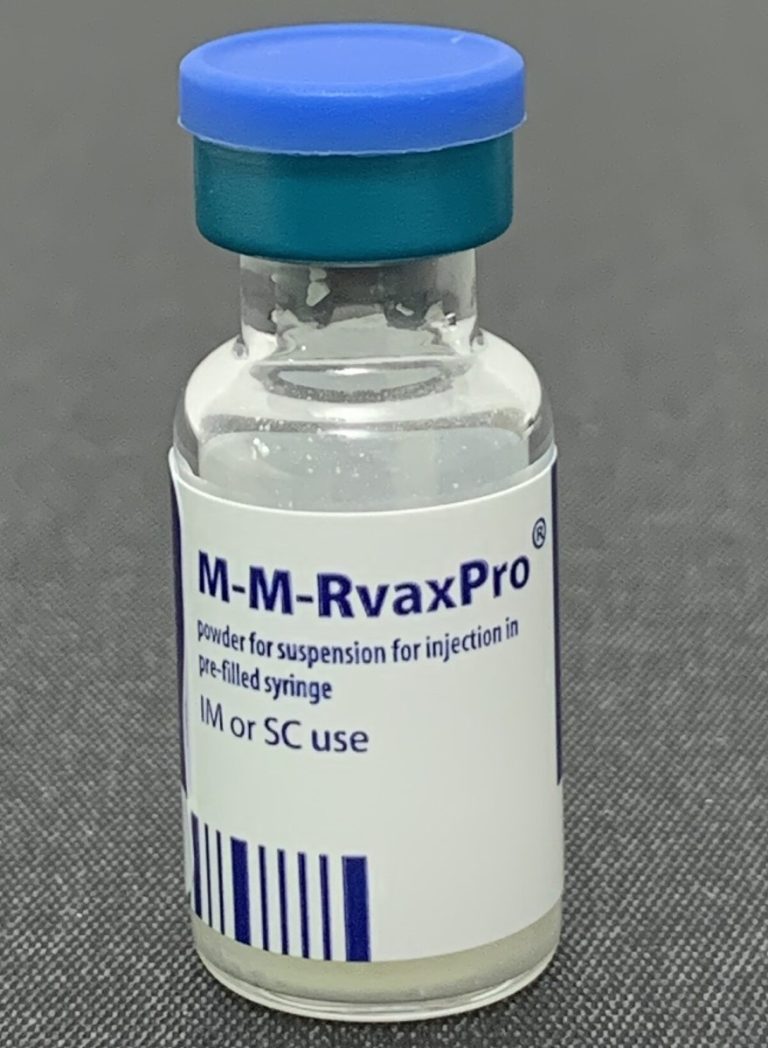
In 1979, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed the RA 27/3 (human diploid fibroblast) strain of…
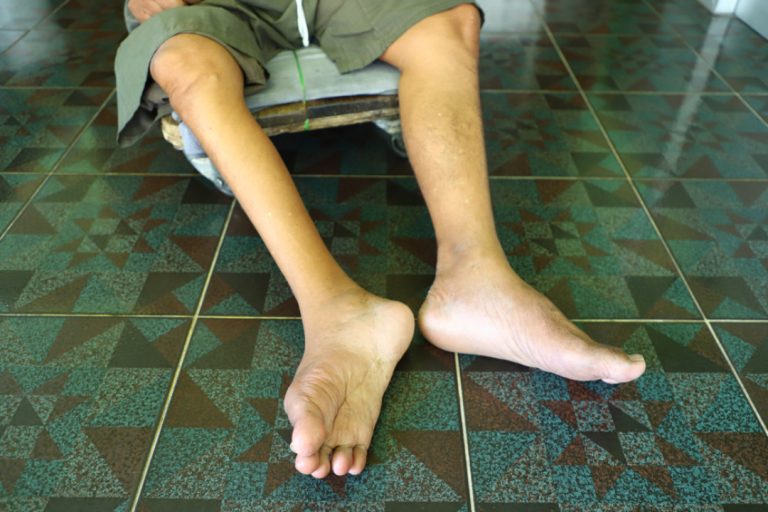
In 1979, the last wild case of polio was recorded in the U.S. However, in 1993, the virus…

On Jan. 3, 1978, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed the Monovalent group A (Menomune-A by…
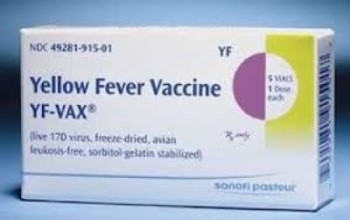
On Jan. 3, 1978, the Yellow fever vaccine (YF-Vax by Connaught) was licensed in the U.S. The Yellow…

In 1978, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) completed construction of a new hot lab…
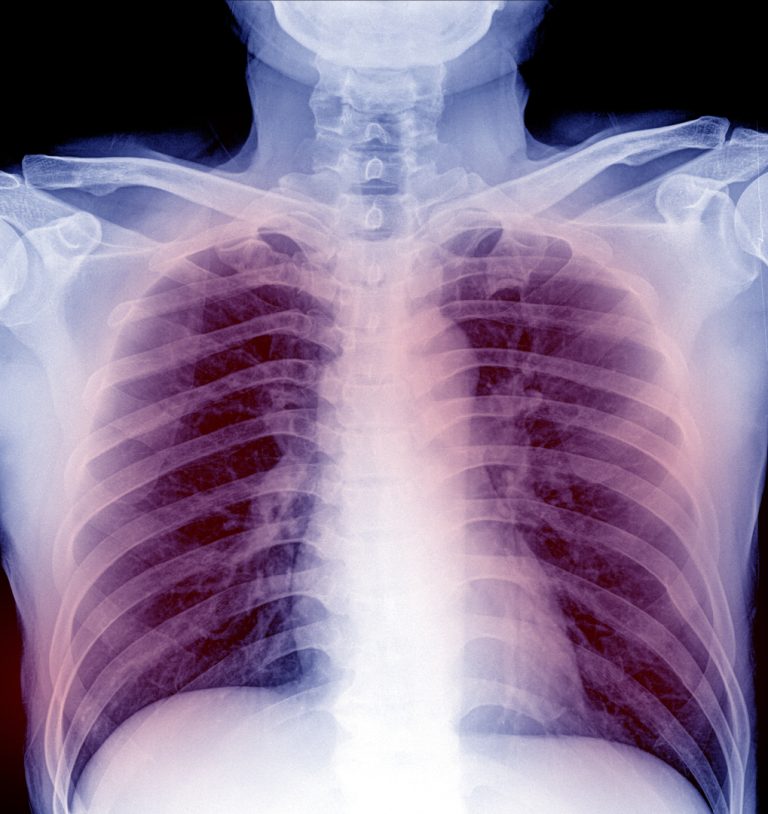
On Nov. 21, 1977, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed the first pneumococcal vaccine containing 14…

On Oct. 30, 1977, Ali Maow Maalin, a hospital cook in Merca, Somalia, was diagnosed with smallpox by…

On May 12, 1977, the Program for the Introduction and Adaptation of Contraceptive Technology (PIACT) was founded by…

On Apr. 6, 1977, the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (now Department of Health and Human Services)…

On Oct. 13, 1976, the swine flu vaccination program in the U.S. was suspended following reports of paralysis. …

In 1976, Influenza A/Victoria-like strains had been identified in New Jersey as early as January 21. The novel…
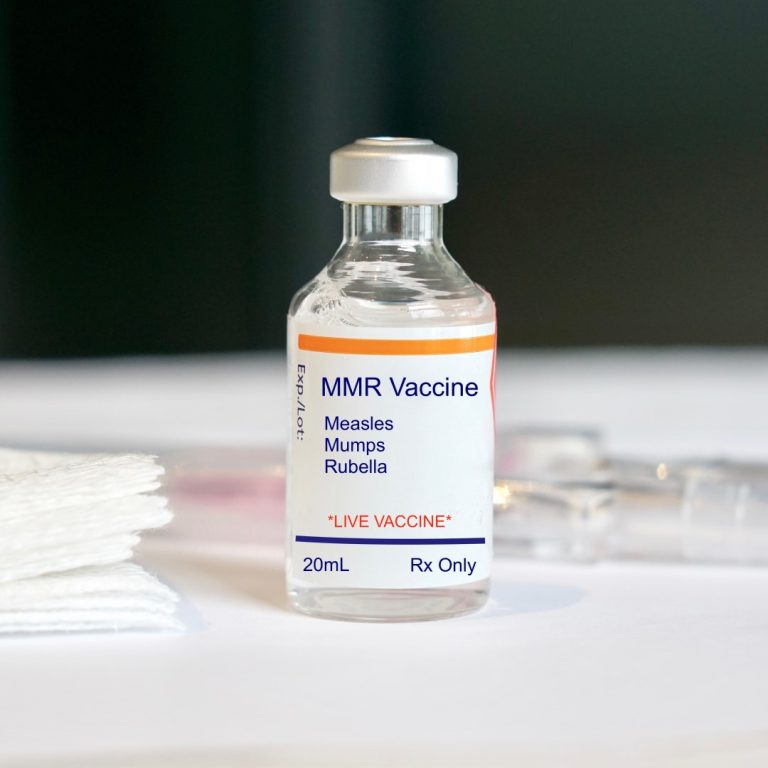
In 1976, because of evidence of increased vaccine efficacy at older ages, the recommended age for vaccination was…

In 1976, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) was involved in a national immunization program…
In 1975, The World Health Assembly passed a resolution to create the Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI) to…
On Apr. 2, 1974, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed the first monovalent (group C) meningococcal…
In 1974, the Expanded Programme on Immunization was created within World Health Organization (WHO) in response to poor…
On Apr. 22, 1971, the measles, mumps, and rubella virus (M-M-R II) vaccine Live developed by Maurice Hilleman was…

In 1973, the publication “Biohazards in Biological Research,” was edited by S. Hellman, M. Oxman, and R. Pollack. …

On Apr. 10, 1972, the United States, the Soviet Union and 70 other nations signed an agreement that…

On Apr. 22, 1971, Combined measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR by Merck) as well as combined measles…

In 1971, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended discontinuation of routine immunization and vaccination…
In 1971, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) discovered that hepatitis B is sexually transmitted….
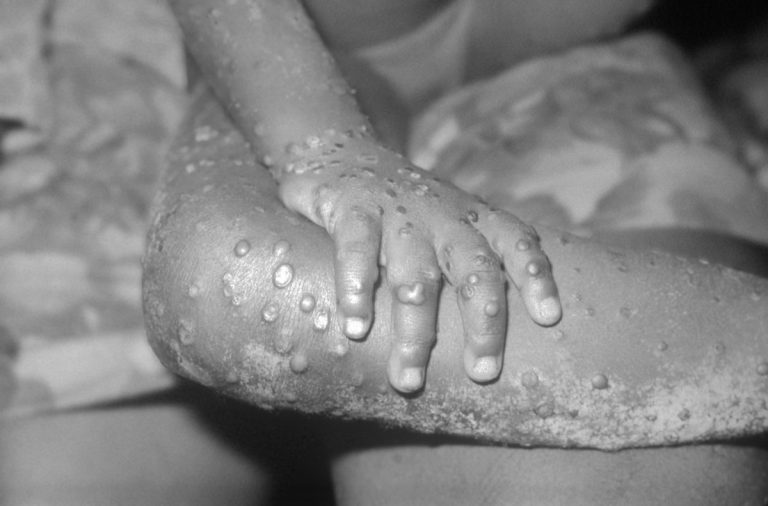
In 1970, the first human case of mpox was reported in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)…

In 1970, influenza H3N2 viruses were first identified in swine during an influenza surveillance study in Taiwan. This…
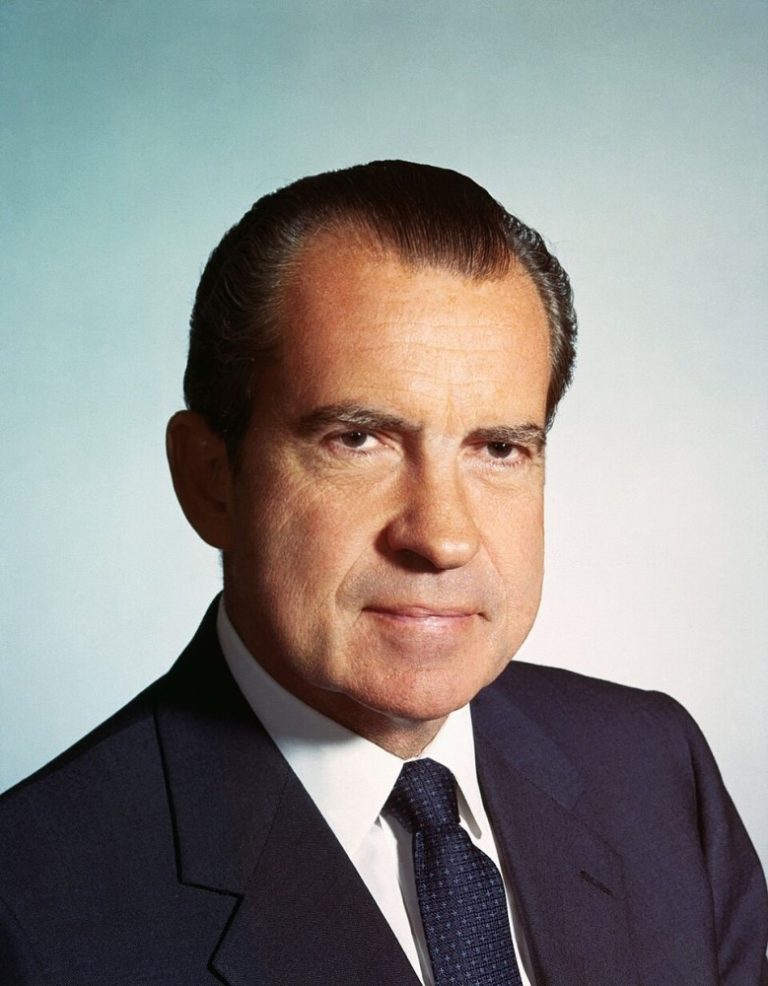

On Nov. 25, 1969, President Richard Nixon issued his “Statement on Chemical and Biological Defense Policies and Programs”…

In 1969, Max Delbruck of the California Institute of Technology was awarded the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physiology…