Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments was awarded the 2000 Nobel Prize in Physics for his invention of the integrated circuit
In 1958, the Integrated circuit was invented by Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments (TI). Kilby was awarded the…
In 1958, the Integrated circuit was invented by Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments (TI). Kilby was awarded the…

On Aug. 12, 1957, Dr. David Hume performed the first kidney transplant at the Medical College of Virginia.
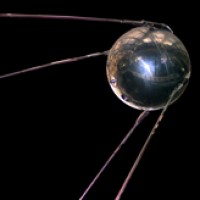
On Oct. 4, 1957, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik I, the first satellite in space.

On Sept. 10, 1957, the first Nevada Southern (University of Nevada, Las Vegas, aka UNLV) classes were held…

In 1957, the University of Washington’s (UW) Division of Medical Genetics was established in the Department of Medicine…
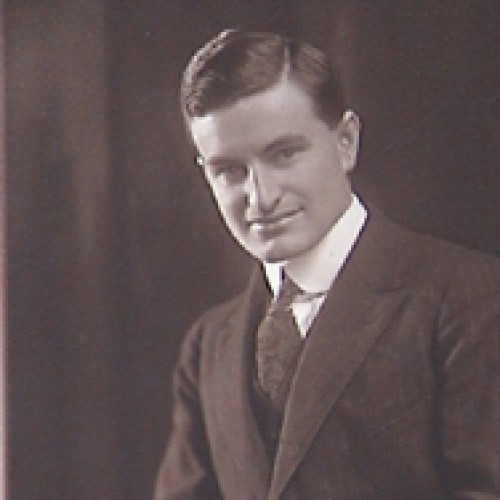

In April 1957, the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to Farrington Daniels “to recognize distinguished services…
In Feb. 1957, a new influenza A (H2N2) virus emerged in East Asia, triggering a pandemic (‘Asian Flu’)….

In Feb. 1957, a new influenza A (H2N2) virus emerged in East Asia, triggering a pandemic (“Asian Flu”)….

In 1957, vancomycin was isolated by Dr. E.C. Kornfield, an organic chemist with Eli Lilly in the deep…

In 1957, The Venereal Disease Division was transferred from the U.S. Public Health Service to CDC. It brought…
In 1957, McLean Hospital researchers developed a procedure for extracting and identifying brain lipids, paving the way toward…

In 1957, The University of Missouri School of Medicine was transformed into a four-year program. As a result,…
In 1957, Johnsonᅠ&ᅠJohnson established operations in India.

In 1957, Frederic N. Schwartz became president and CEO of Bristol-Myers when Henry Bristol, approaching 70, chose to…

In 1957, the term agribusiness was coined by Harvard Business School’s Ray Goldberg.

In 1957, The Medical College of Virginia School of Graduate Studies was organized with Dr. Ebbe C. Hoff…

In 1957, the American Association of Blood Banks formed a committee on Inspection and Accreditation to monitor the…

In 1957, Gilson was founded in in Middleton by Dr. Warren Gilson, a faculty member at the University…

In 1957, Alick Isaacs from Great Britain and Jean Lindenmann from Switzerland identified the interferons in 1957 and…
In 1957, Charles Heidelberger introduces 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a new type of anticancer drug that resulted from rational design.
In 1957, Roy Hertz and Min Chiu Li achieve the first completed cure of a human solid tumor…
In 1957, the Mexican Agriculture Program (MAP) was the The Rockefeller Foundationメs first intensive agricultural endeavor begun in…

In 1957, the FAO published its first Plant Introduction Newsletter, a periodical summary of who has what germplasm…

In 1957, the ‘Asian flu’ influenza pandemic emerged, resulting in the CDC setting up an influenza surveillance unit,…
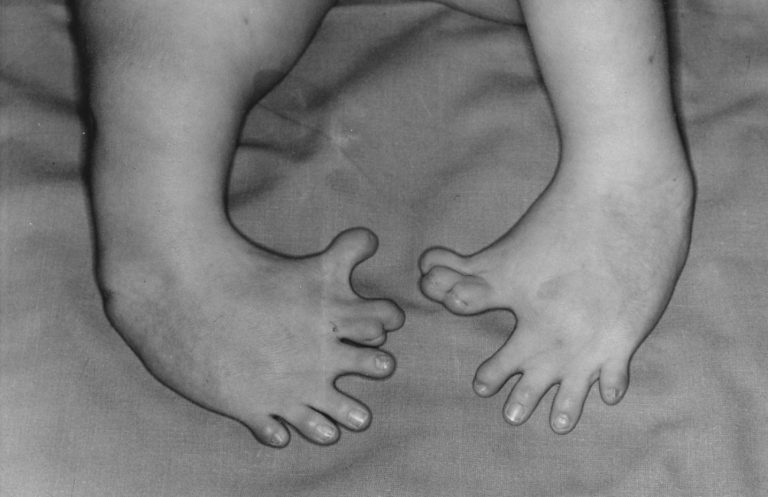
On Dec. 25, 1956, the first Thalidomide birth occurred in Germany. Thalidomide, a new sleeping pill developed by…

On Oct. 19, 1956, the Pacific Northwest Diabetes Research Institute (PNDRI) was founded by William B. Hutchinson, Sr.,…
On Aug. 8, 1956, President Dwight D. Eisenhower swore in Leroy E.Burney as U.S. Surgeon General. Eisenhower nominated…
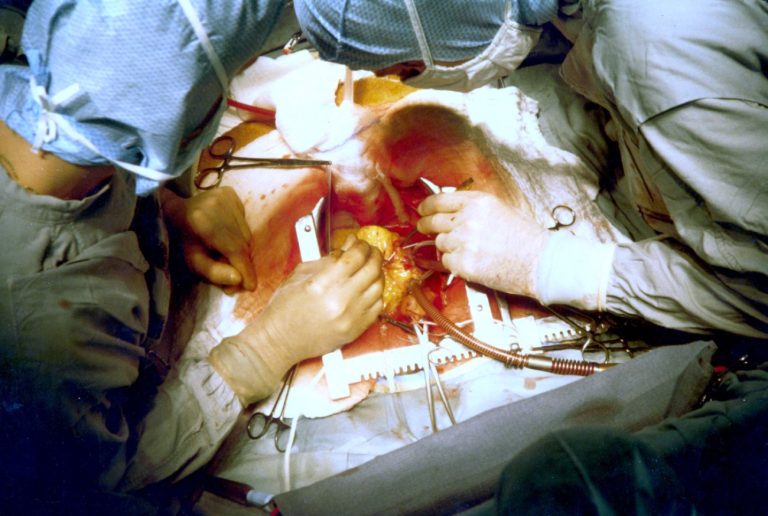
On Aug. 1, 1956, Dr. K. Alvin Merendino at the University of Washington in Seattle performed the first successful…
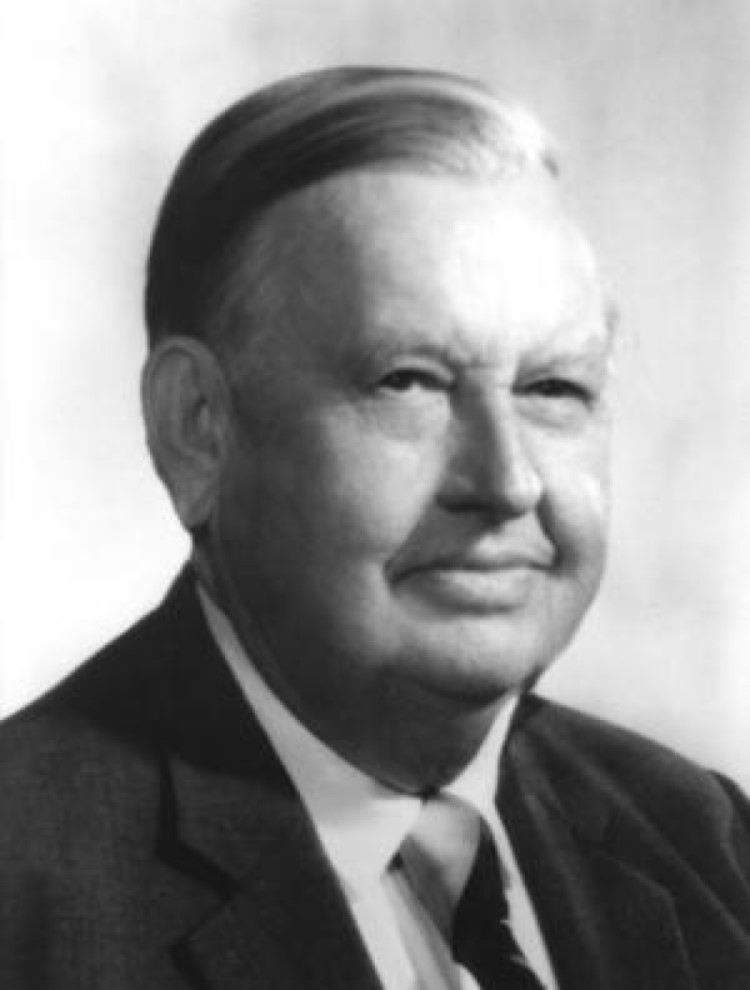

In 1956, the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to Carl S. Marvel “to recognize distinguished services…
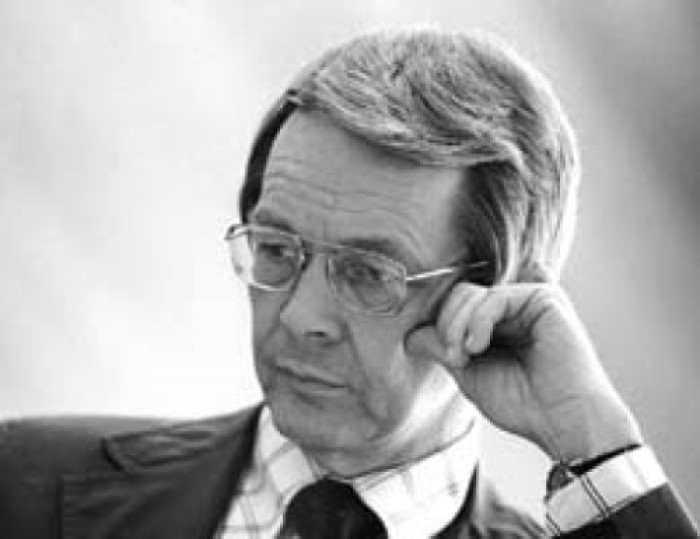

On May 29, 1956, Physio-Control was incorporated by Dr. K. William Edmark, a Seattle cardiovascular surgeon, who was…