OHSU and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory team up to accelerate biomedical discovery
On May 6, 2015, Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU and the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National…

On May 6, 2015, Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU and the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National…

On May 5, 2015, Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey was one of seven international sites to offer…

On May 4, 2015, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) dedicated Building 4 in honor of Lowell P….

On May 1, 2015, Wei Yang, Ph.D, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, received the…
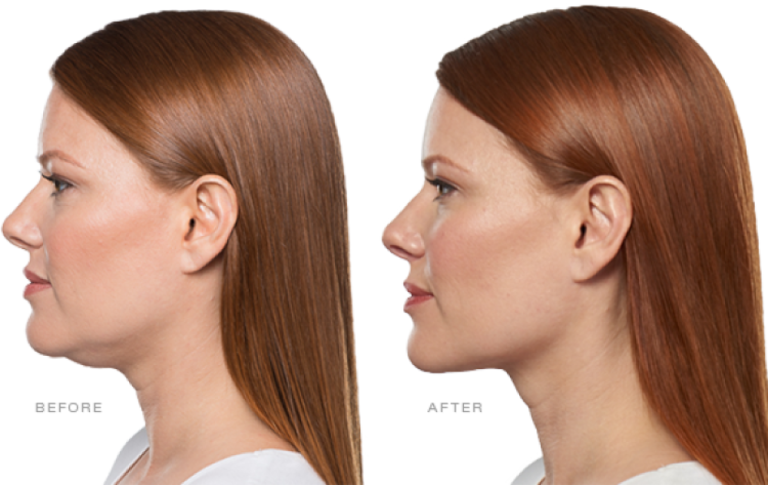

On Apr. 29, 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had approved Kybella, an injection…
On Apr. 29, 2015, the Pan American Health Organization ᅠdeclared that the Americas region has become the first…

On Apr. 24, 2015, researchers led by David Huang, M.D., Ph.D. at Oregon Health Sciences University’s (OHSU) Casey…

On Apr. 23, 2015, an international collaboration that involved researchers from Sweden, the United States, Canada, and Russia…
On Mar. 27, 2015, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published new Immunization Practices Advisory…
On Mar. 27, 2015, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee…

On Mar. 26, 2015, Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, announced plans to invest more than $125…

On Mar. 25, 2015, deCODE genetics published four landmark papers built on whole-genome sequence data from more than…

On Mar. 25, 2015, longtime University of Southern California (USC) benefactors Mark and Mary Stevens donated $50 million…

On Mar. 25, 2015, the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center was designated a Cancer Center of Excellence by the…
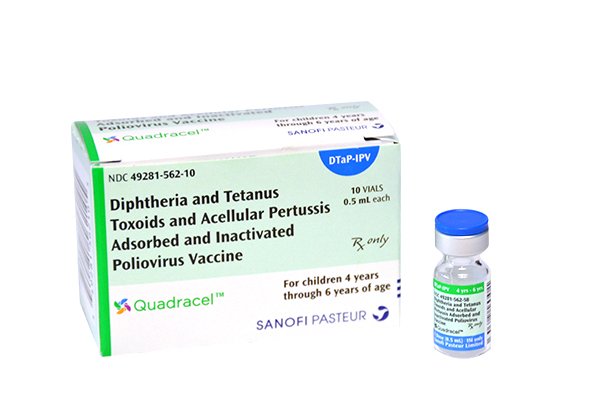
On Mar. 24, 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Sanofi’s Quadracel, a newᅠcombinationᅠDTaP+IPVᅠ vaccine for…

On Mar. 23, 2015, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI), Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and the Simons…

On Mar. 23, 2015, the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to Jacqueline K. Barton “to recognize…

On Mar. 2, 2015, Dr. Helen Wallace, a world-renowned professor, mentor and advocate known for her passion for…

On Feb. 23, 2015, a bankruptcy judge approved the sale of the assets of Dendreon Corp., a Seattle-based…

On Jan. 29, 2015, a Rutgers University study suggests that pregnant women and young children are more susceptible…

On Jan. 23, 2015, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Health Alert Network issued a…

On Jan. 23, 2015, Novartis announced the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted accelerated approval of…

On Jan. 12, 2015, The Albert Einstein Cancer Center became the only medical institution in New York City,…
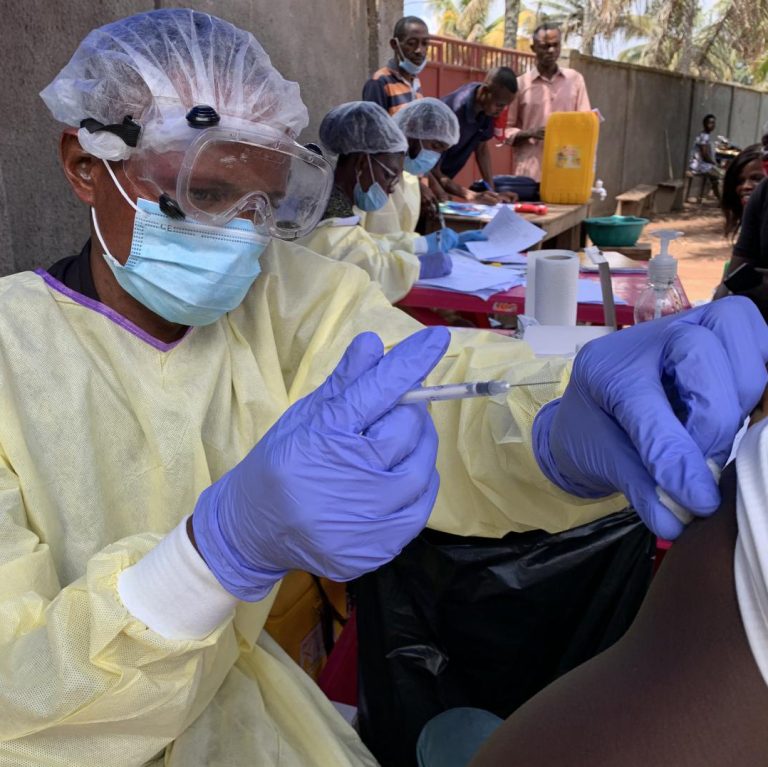
On Feb. 27, 2015, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) responded to the West Africa…
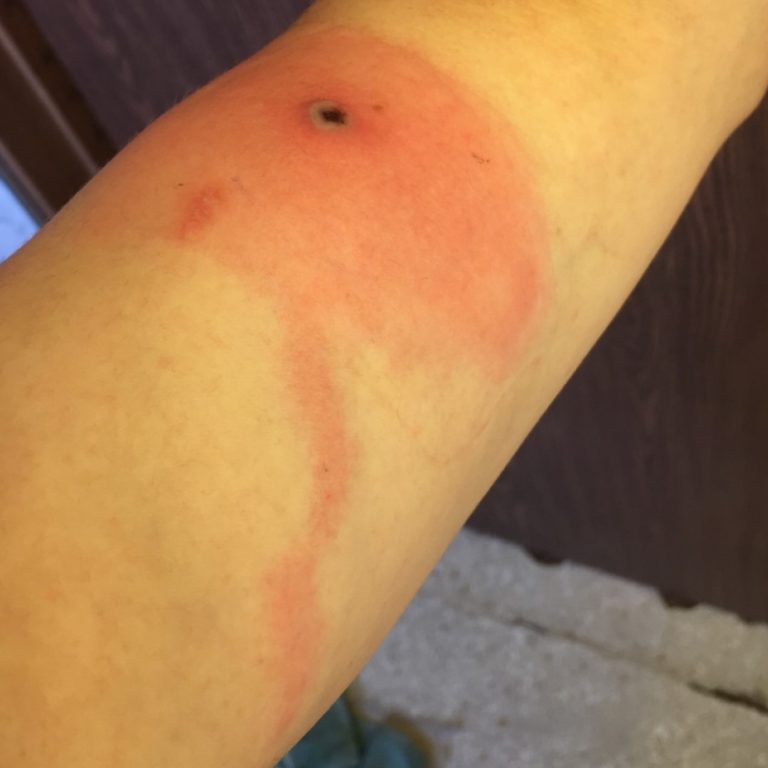

In 2015, the state of Alaska Department of Health announced they had identified Alaskapox virus in a patient…

In 2015, Dr. Horace H. Loh received the Society of Chinese Bioscientists in America (SCBA) Lifetime Achievement Award…

In 2015, the California Life Sciences Association was founded. (CLSA) was founded when the Bay Area Bioscience Association…
In 2015, Yale Cancer Center was awarded a SPORE (Specialized Programs of Research Excellence) grant for translational research…

On Dec. 23, 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a formulation of Novo Nordisk’s diabetes drug, liraglutide,…

On Dec. 23, 2014, Juno Therapeutics announced the closing of its initial public offering of 12.7 million shares…