The CDC activated its Emergency Operations Center for Tropical Storm Ernesto
Aug. 24, 2024, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) activated its Emergency Operations Center (EOC)…
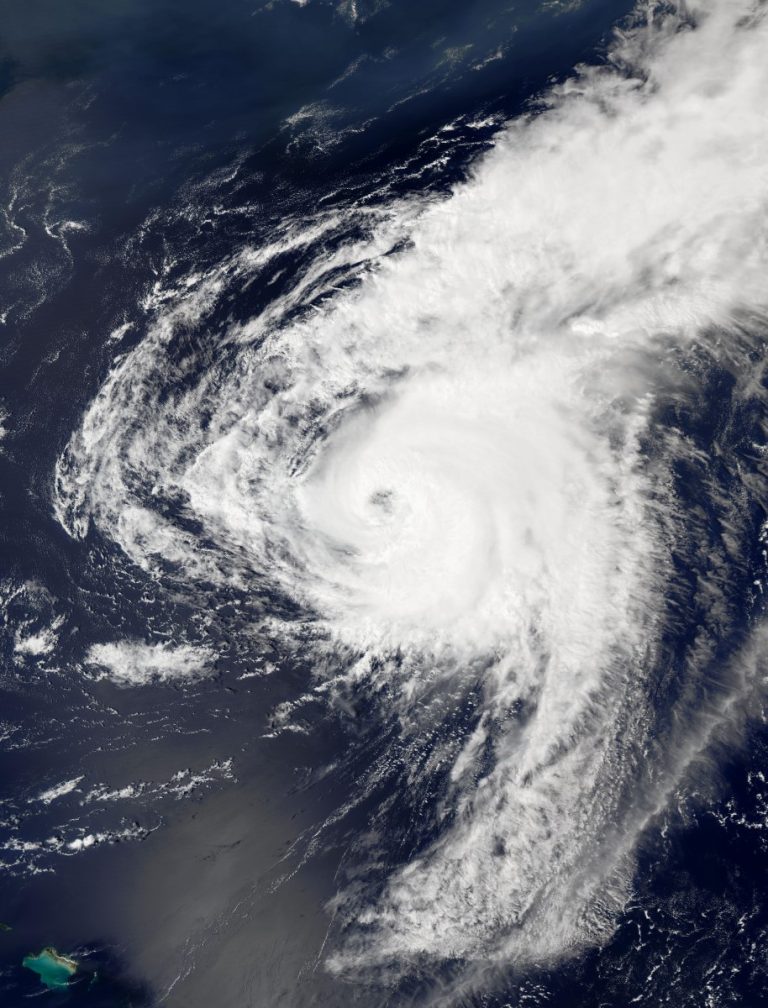

Aug. 24, 2024, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) activated its Emergency Operations Center (EOC)…

In 2006, the Kansas State University Biosecurity Research Institute dedicated the Biosecurity Research Institute (BRI) that was designed…
On Dec. 23, 2005, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices…
On Dec. 19, 2005, in a 2-year legal battle over the U.S. military’s anthrax vaccination program, the Food…
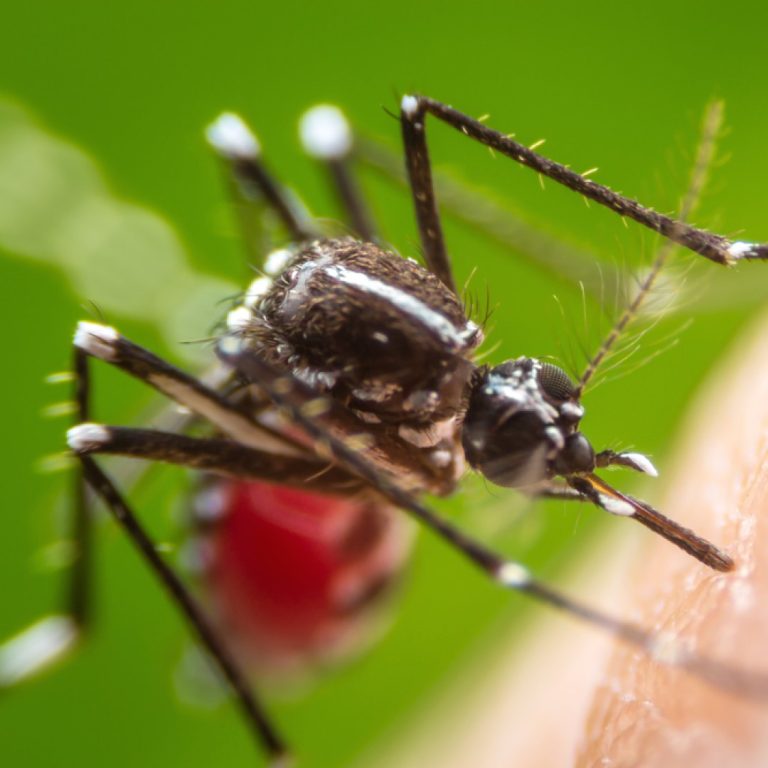

On Oct. 30, 2005, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation announced three grants totaling $258.3 million for advanced…

On Sept. 6, 2005, the vaccine that combined the measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella antigens (Proquad by Merck)…
On Aug. 31, 2005, the inactivated, injectable influenza vaccine (Fluarix) by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) was licensed. The vaccine was…
On Aug. 11, 2005, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved an application of a pediatric/adolescent formulation of…
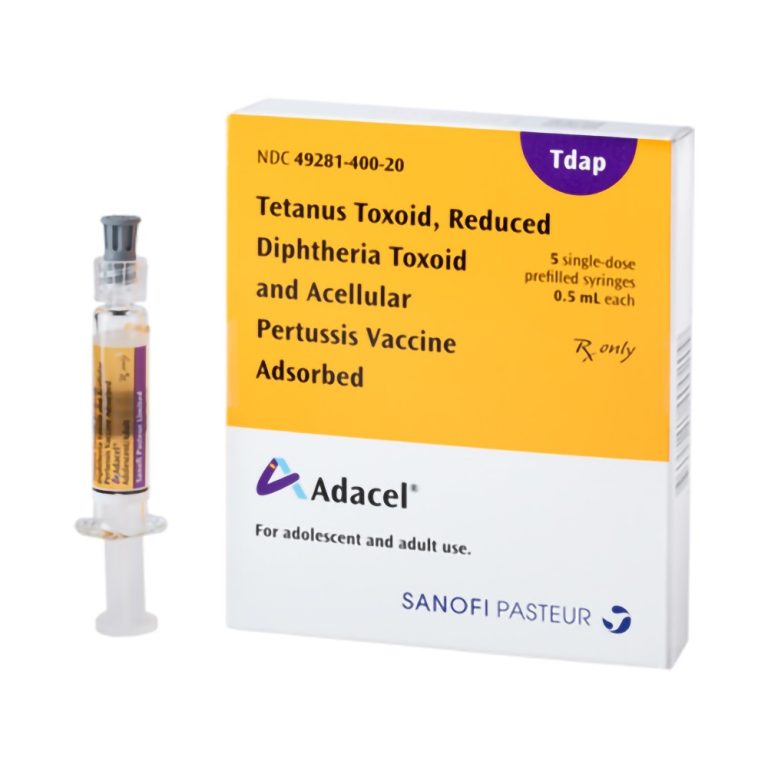
On Jun. 9, 2005, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed a 2nd Tdap vaccine (Adacel by…
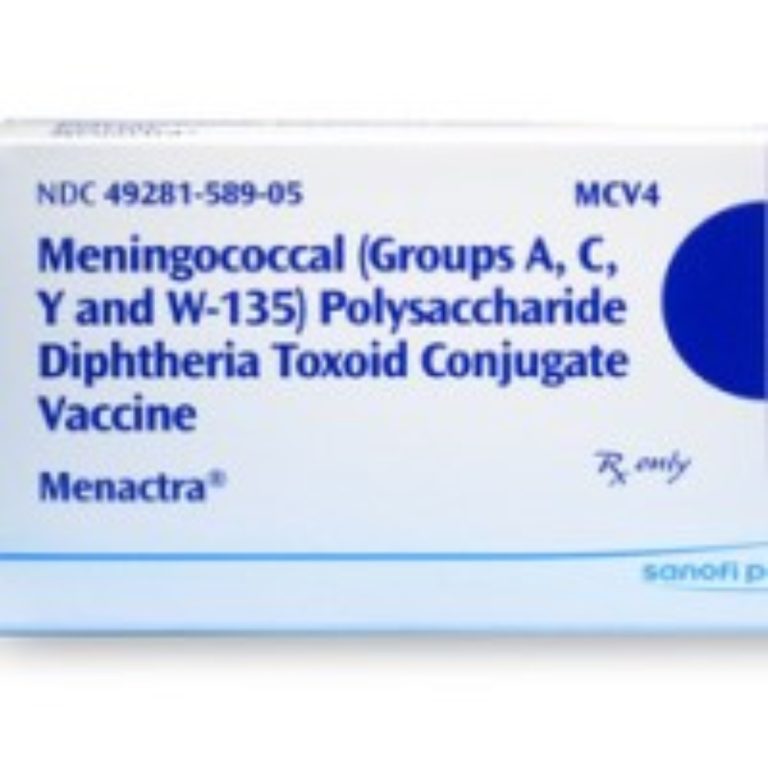
On Apr. 22, 2005, Sanofi Pasteur announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted licensure to…
On Apr. 1, 2005, Sanofi pasteur was awarded a five-year $97 million contract from the U.S. Department of…
On Mar. 21, 2005, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that a major public…
On Mar. 16, 2005, University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) officials announced the formation of the Institute for…

On Dec. 26, 2004, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) assisted with an earthquake measuring…
On Nov. 1, 2004, an Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) research team announced that it was one…

On Sept. 14, 2004, researchers at OHSU and OHSU’s Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute announced a collaboration with…
On Aug. 25, 2004, a significant shortage of influenza vaccine occurred in the U.S. as a result of…

On Jul. 21, 2004, Project BioShield Act of 2004 was signed by President George W. Bush. The Act…
On May 25, 2004, researchers at the Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute (VGTI) and the Oregon National Primate…

On May 10, 2004, an international call-to-action has been issued by more than one hundred lupus organizations based…
On Mar. 24, 2004, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed tetanus and diphtheria toxoids adsorbed for…

On Mar. 1, 2004, the National incident Management System (NIMS), developed by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS),…

In 2004, The Division of Global Migration and Quarantine, part of the CDC’s National Center for Infectious Diseases,…

On Oct. 16, 2003, scientists from the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation (OMRF) and the University of Oklahoma Health…
On Sept. 29, 2003, $81 million was awarded by National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) through…
On Aug. 17, 2003, Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) announced the final results of a smallpox vaccine…
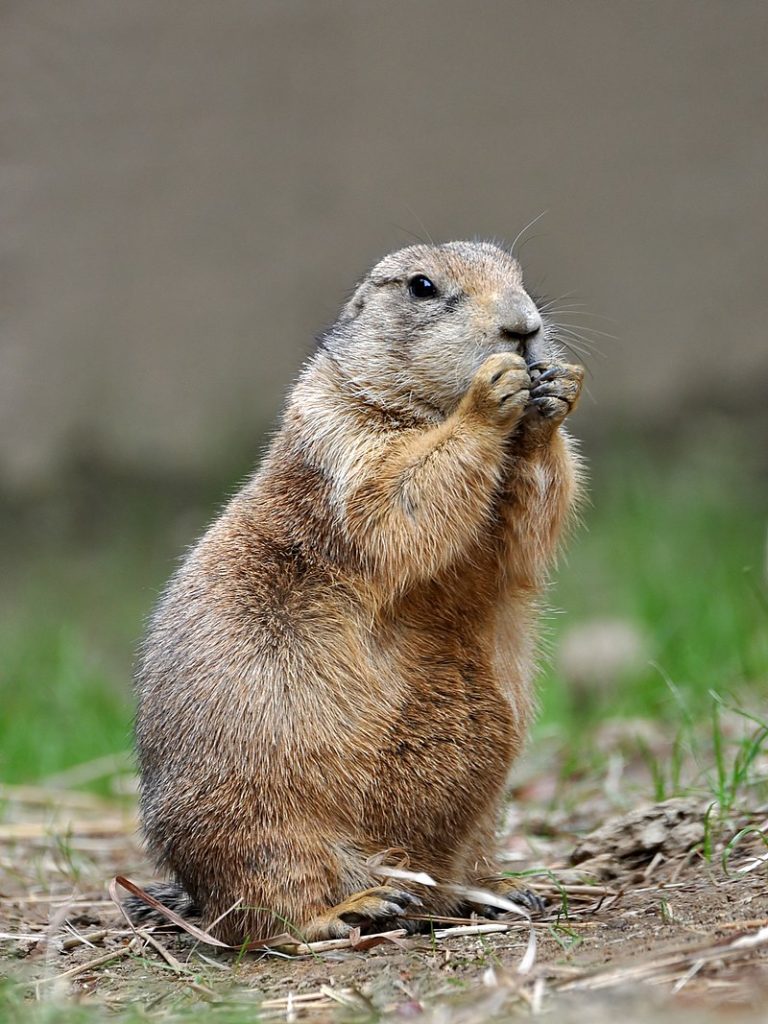

On Jul. 8, 2003, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) responded to U.S. outbreak of…

On Apr. 14, 2003, researchers at Canada’s Michael Smith Genome Science Centre in Vancouver announced they had sequenced…

On Mar. 18, 2003, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) was placed on U.S. quarantine list. Persons under quarantine…
On Mar. 6, 2003, the Singapore Ministry of Health (MOH) and the World Health Organization (WHO), announced they…