The McArdle Laboratory was founded in Madison
In 1940, the McArdle Memorial Laboratory was founded in Madison. McArdle Lab was one of the first basic…

In 1940, the McArdle Memorial Laboratory was founded in Madison. McArdle Lab was one of the first basic…
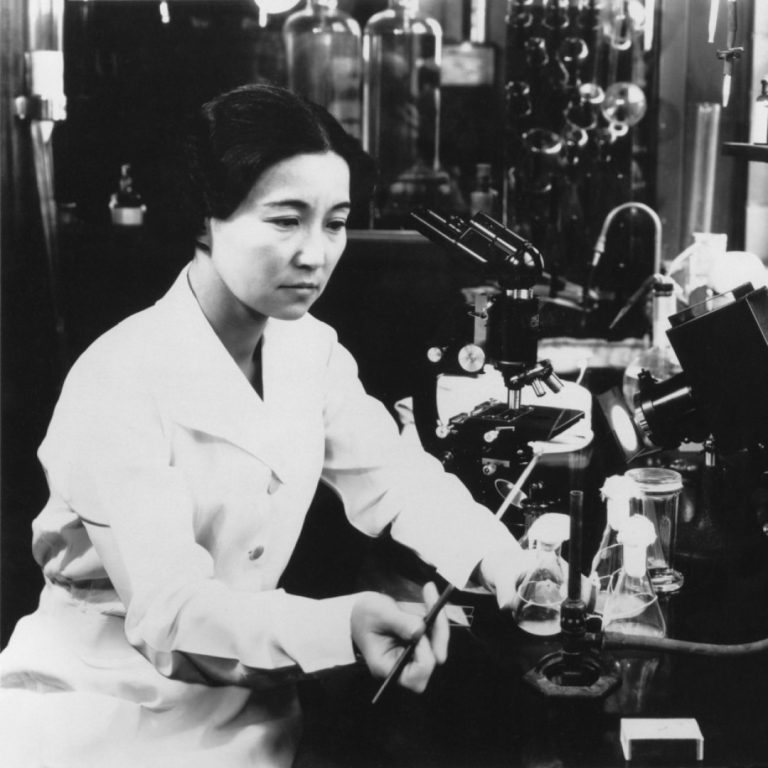

In 1940, biochemist and bacteriologist Ruby Hirose was recognized by the American Chemical Society for accomplishments in chemistry….
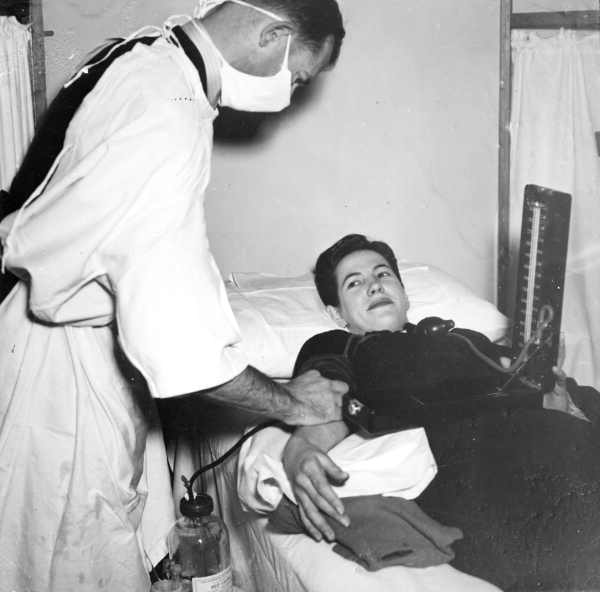
In 1940, the U.S. government established a national blood collection program. That same year the National Research Council…
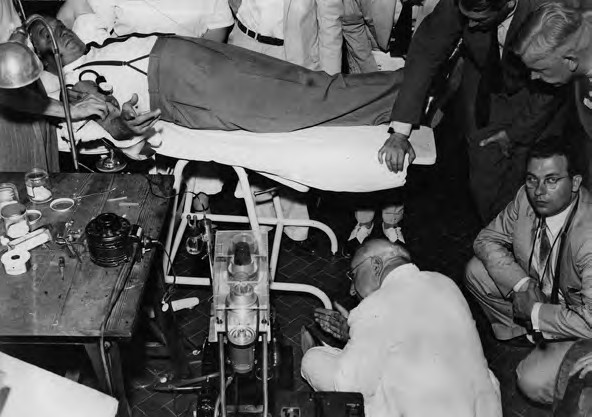
In 1940, Edwin Cohn, a professor of biological chemistry at Harvard Medical School, developed cold ethanol fractionation, the…
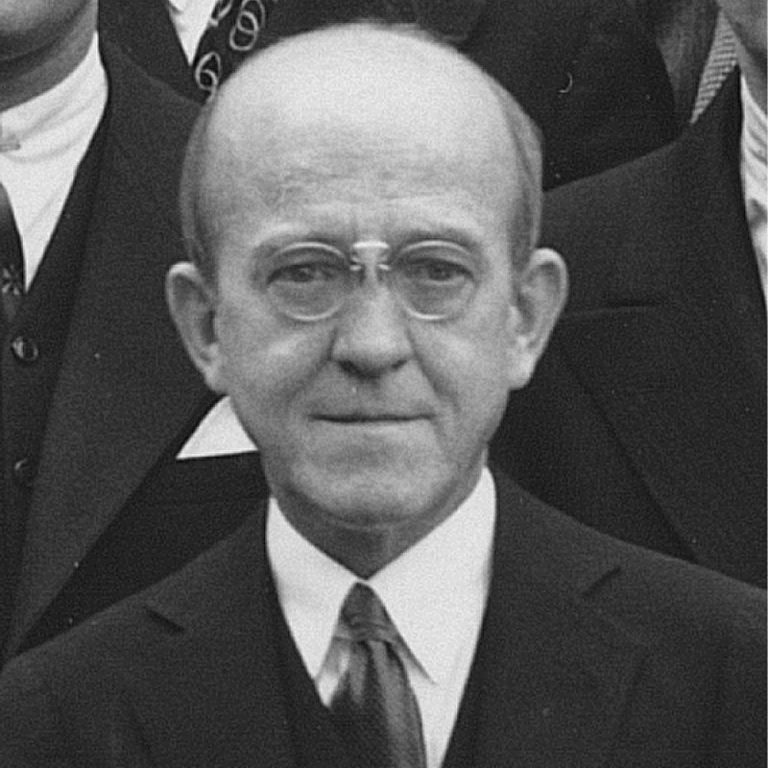

In 1940, American Oswald Avery precipitates a pure sample of what he calls the transforming factor; he has…
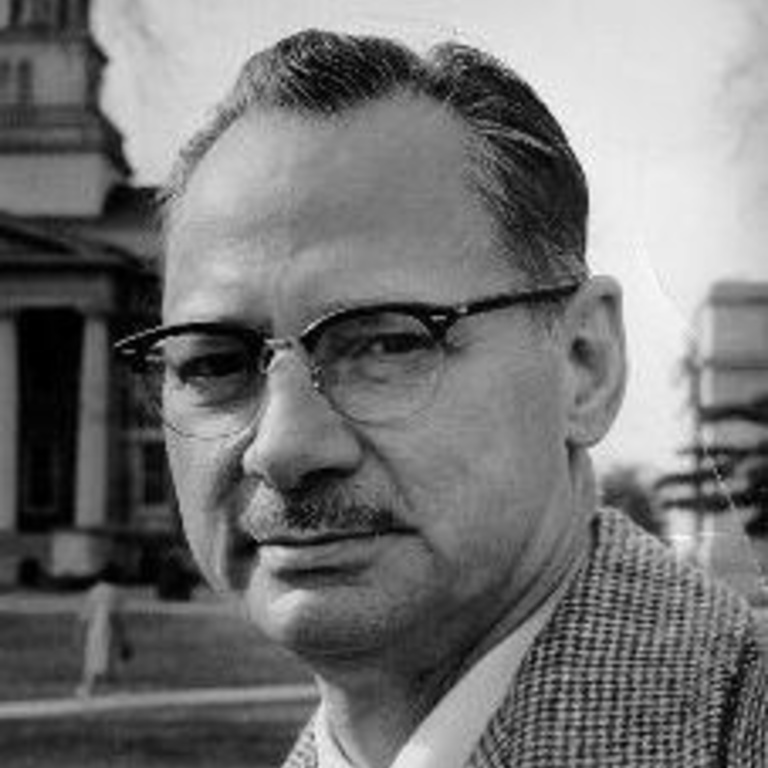

In 1940, Wendell Johnson at the University of Iowa pioneers the fields of speech pathology and audiology. Throughout…
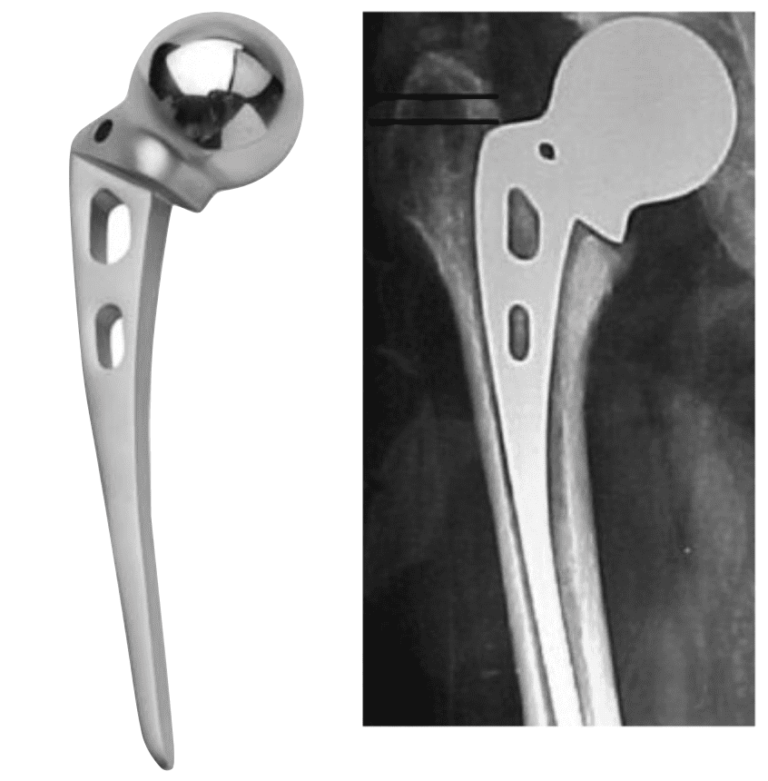
On Sept. 28, 1940, Dr. Austin T. Moore, an American surgeon at Johns Hopkins hospital, and Harold Ray…

In 1939, Hugh G. Grady and Harold L. Stewart first identified the type II cell of the pulmonary…
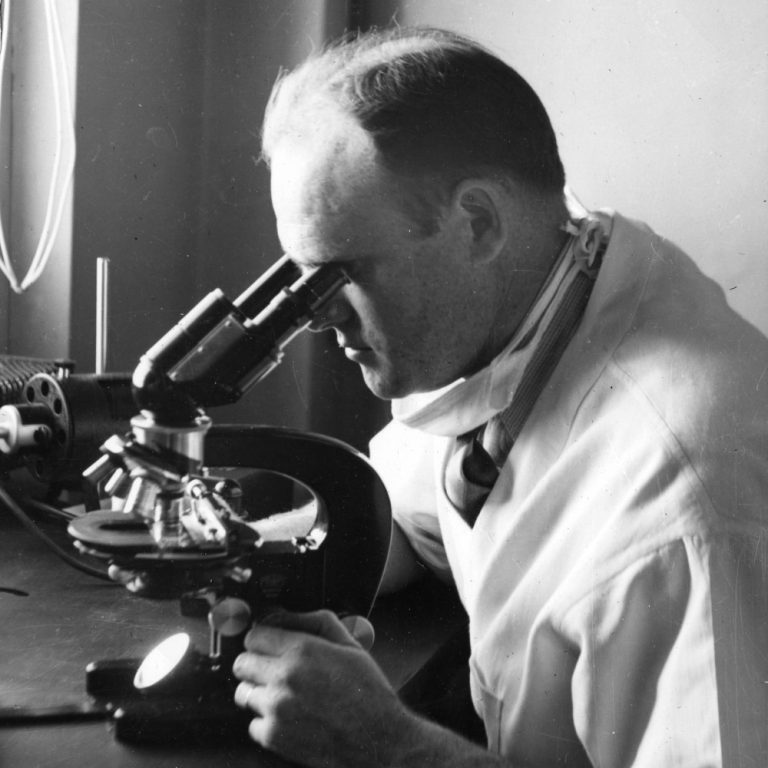

On Dec. 23, 1938, Herald R. Cox published: Use of Yolk Sac of Developing Chick Embryo as Medium…

On Nov. 11, 1938, Mary Mallon, also known as Typhoid Mary and the first person in the U.S.,…

On Nov. 5, 1938, the British Columbia Cancer Institute, BC Cancer’s first cancer treatment centre officially opened in…
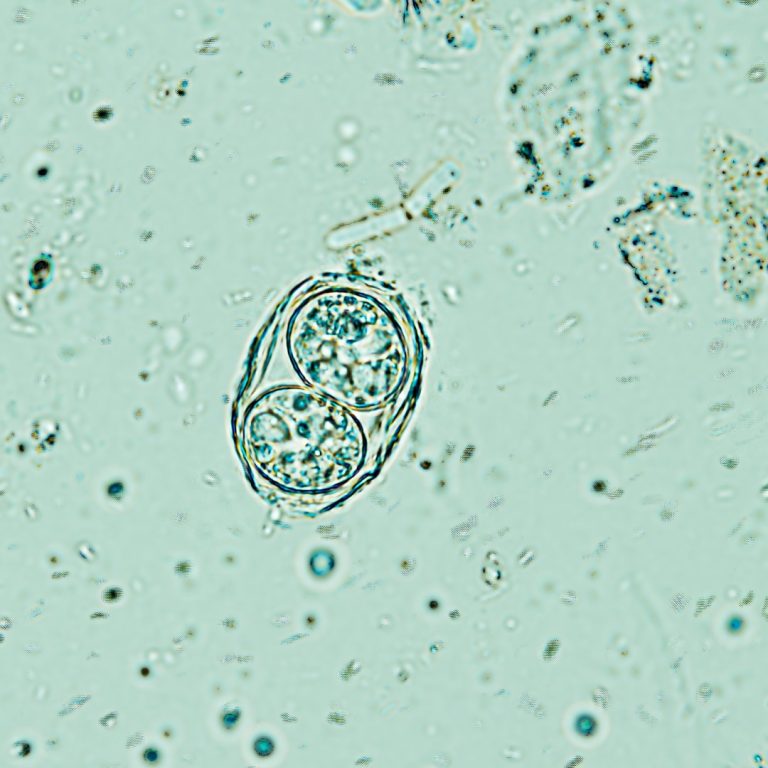
On May 23, 1938, Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondi) was identified in humans gondii was identified in an infant…

On Jan. 3, 1938, President Roosevelt founded the National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis (NFIP) known today as the…
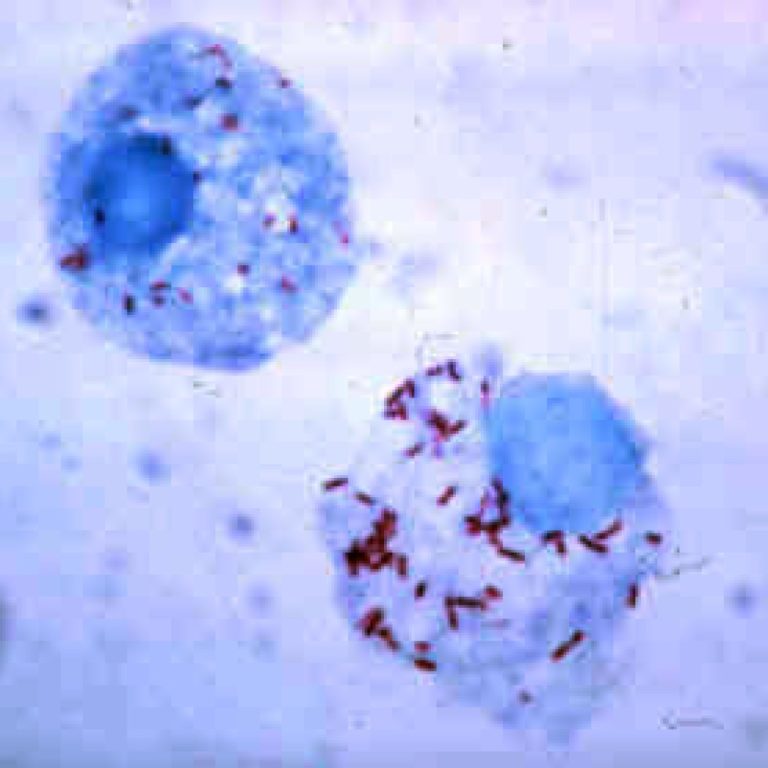
In 1938, Gordon E. Davis and Herald R. Cox identified a new rickettsial disease, which they called Nine…
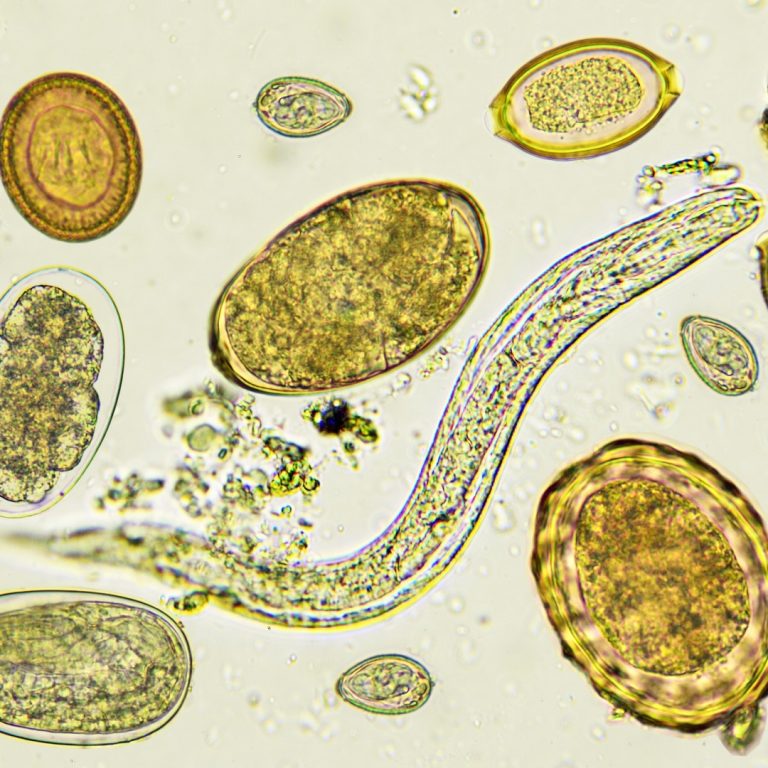
In 1938, John Bozicevich developed immunological methods for the diagnosis of helminth parasitic infections. Helminthiasis, also known as…
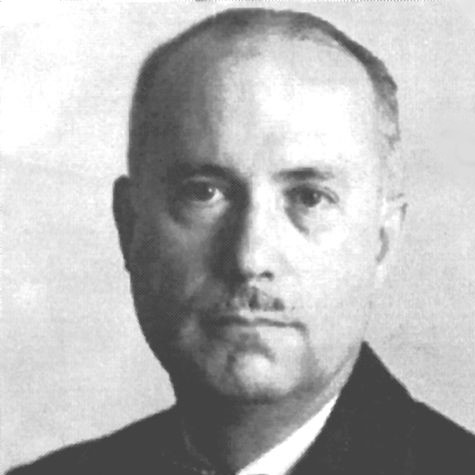

In 1938, Murray J. Shear from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) reported that a basic fraction of creosote…

In 1938, a small scale test of formulated Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) for corn borer control begins in Europe….

In 1938, The Medical College of Virginia opened a new laboratory and outpatient clinic (A. D. Williams Memorial…

In 1938, Rolla Neil Harger of Indiana University School of Medicine collaborated with Robert Borkenstein of the Indiana…

On Nov. 16, 1937, the U.S. Congress directed the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to give a full…
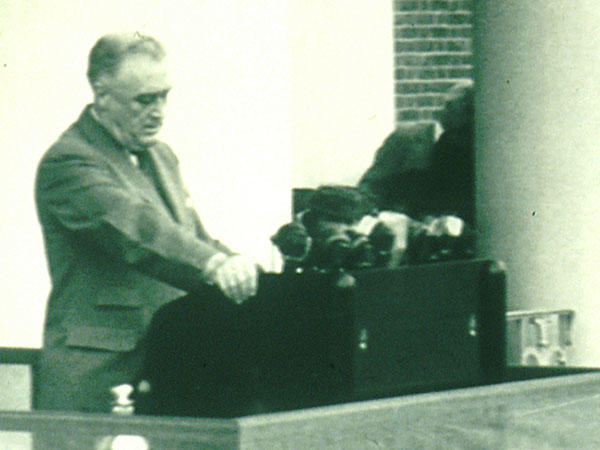

On Aug. 5, 1937, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Act, P.L. 244, 75th U.S. Congress, was signed by…

On Apr. 19, 1937, Perkin-Elmer was founded by Richard Perkin, a banker and Charles Elmer, a court reporter…
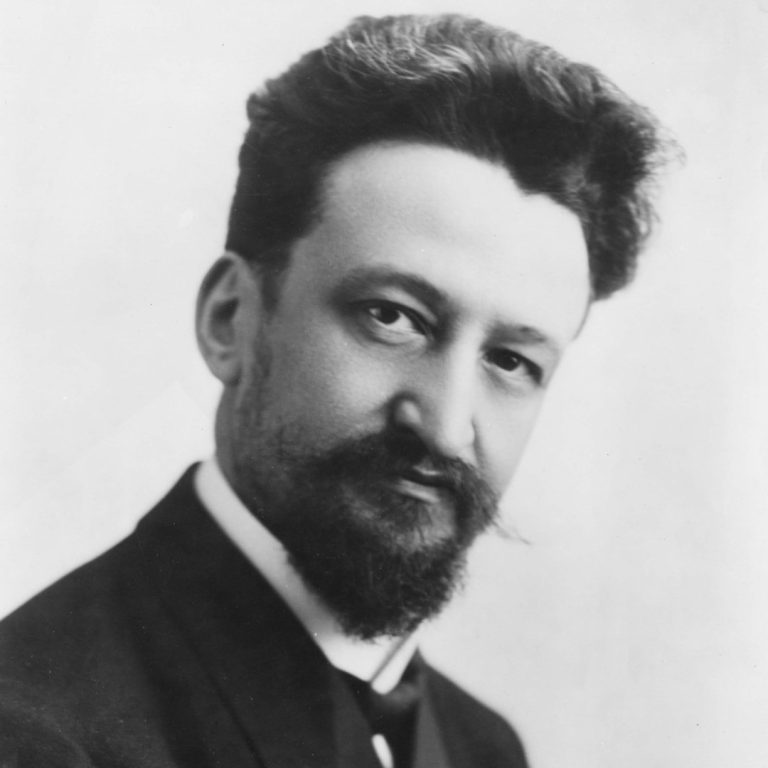

On Mar. 15, 1937, the world’s first blood bank was opened at Cook County Hospital in Chicago by…
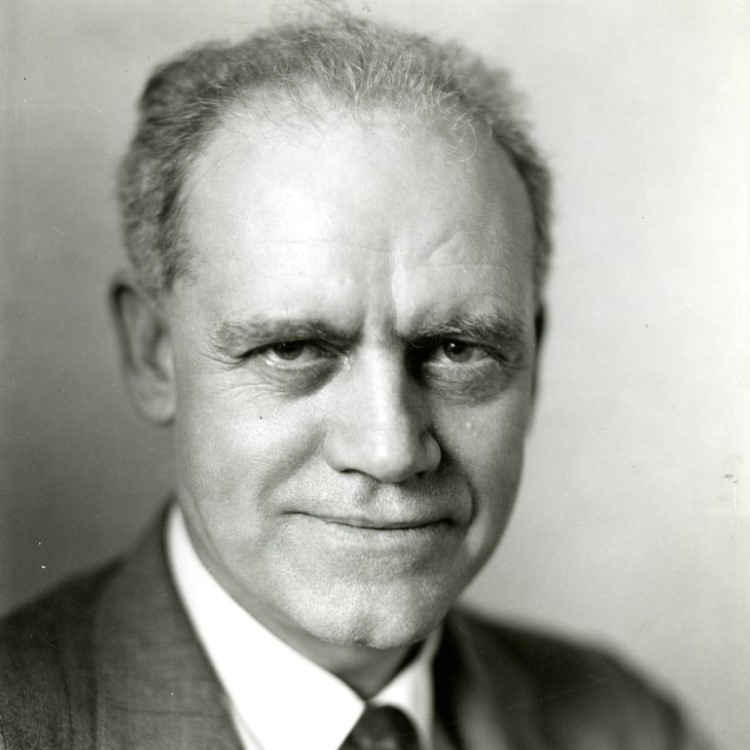

In 1937, Maurice C. Hall developed a technique, known as the “NIH swab,” to diagnose enterobiasis; it is…
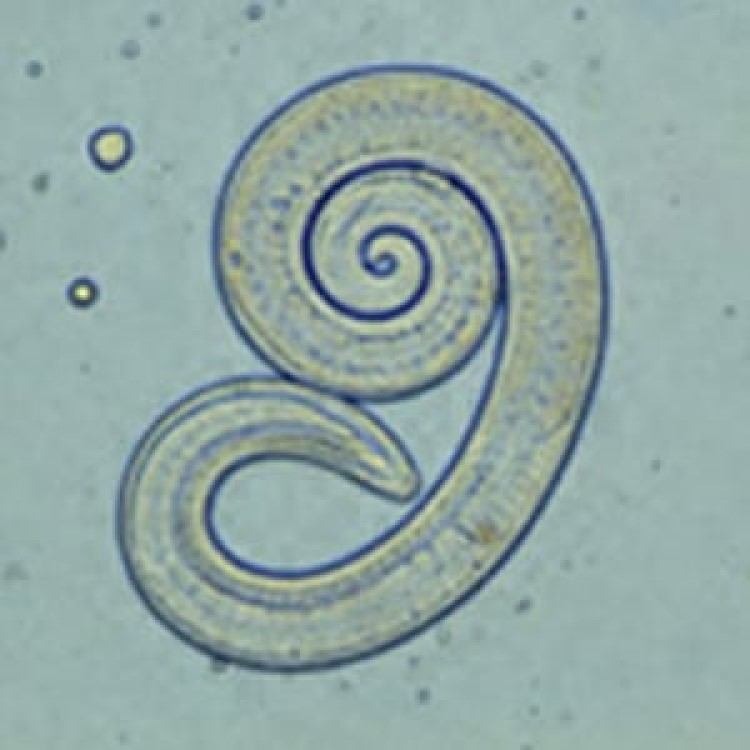
On Aug. 19, 1938, Maurice C. Hall, Willard H. Wright and colleagues published Studies in Trichinoisis that demonstrated…
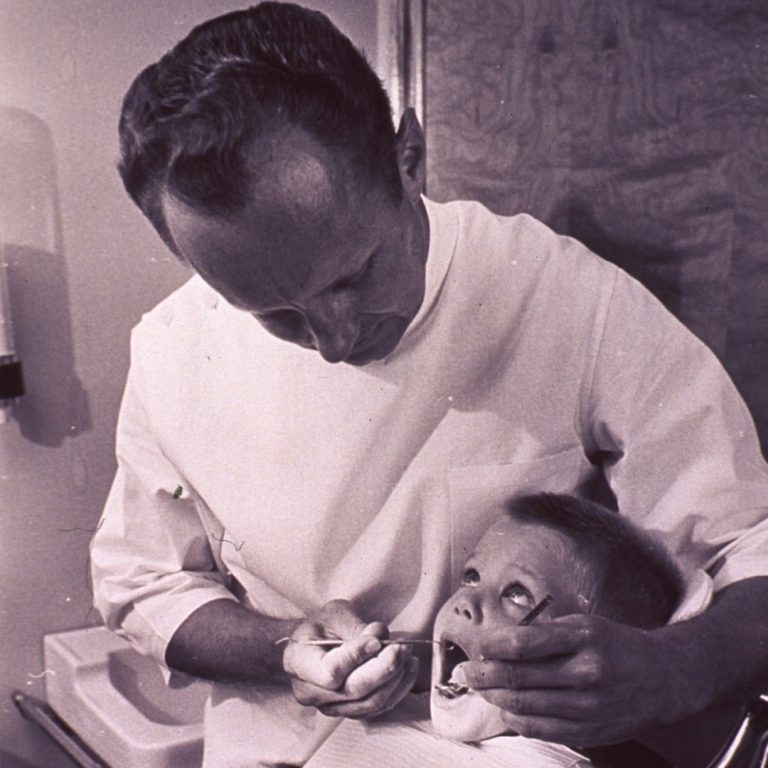
In 1937, Henry Klein, Carroll E. Palmer, John W. Knutson devised a Decayed Missing Filled (DMF) Index guide…

In May 1935, Kenneth Lynch and William Atmar Smith from the Medical College of South Carolina published an…
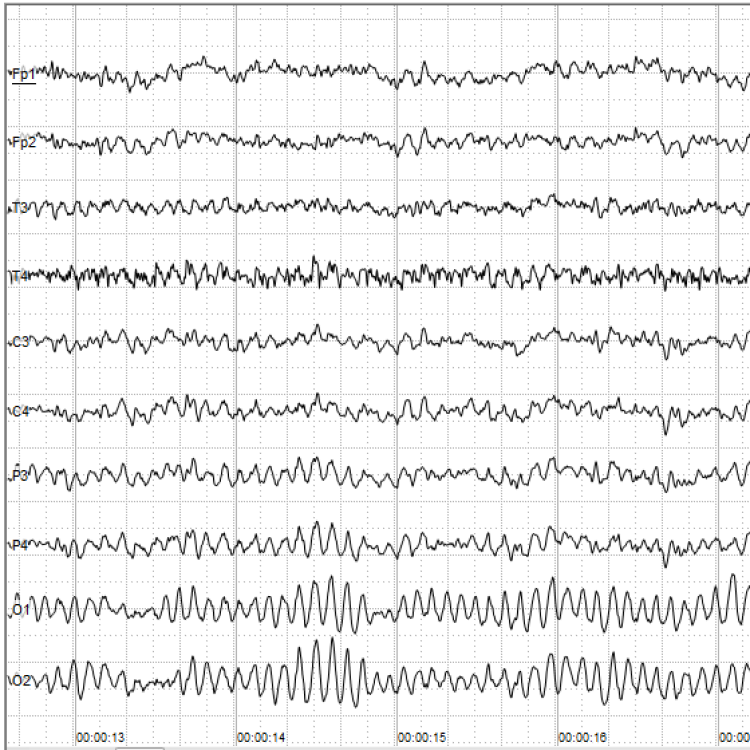
In 1935, a University of Iowa laboratory was the first to record human electroencephalograph (EEG) activity, led by…
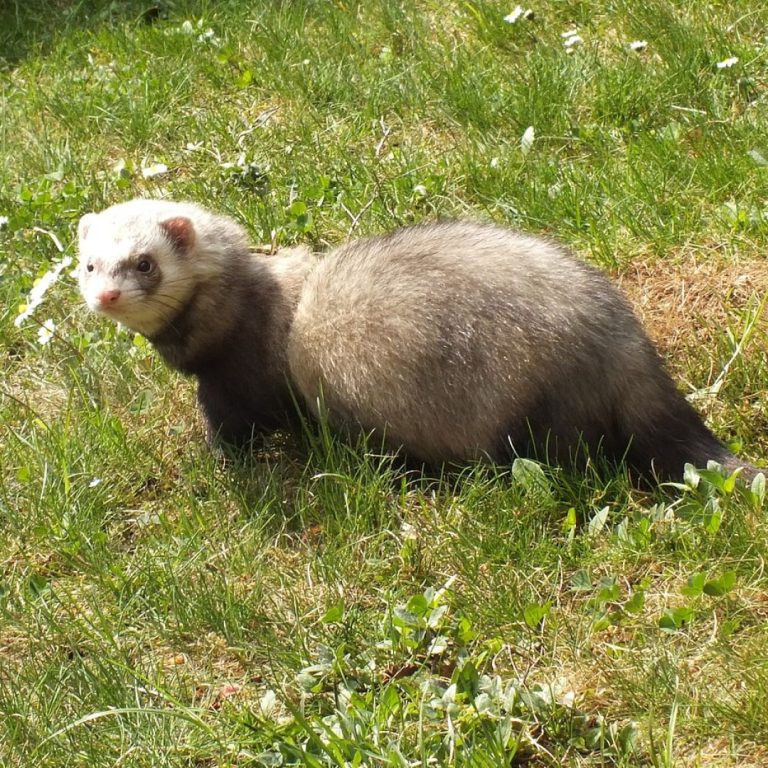

On Jul. 8, 1933, Christopher Andrewes, Laidlaw and W Smith from the Medical Research Council (MRC) reported that…
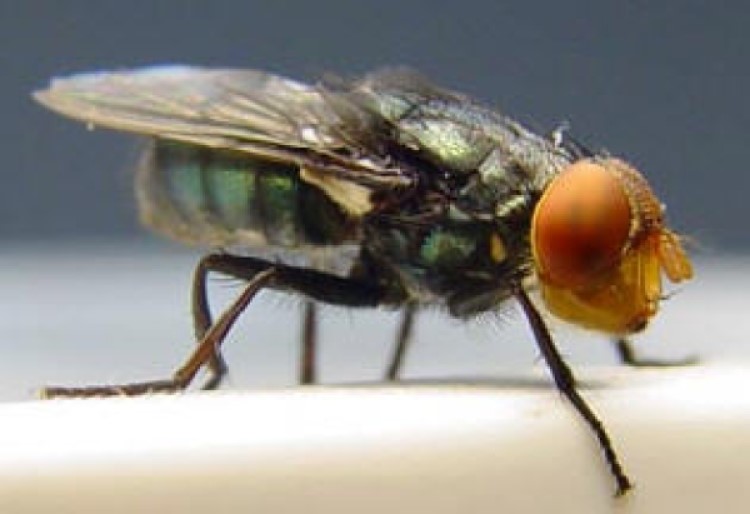

In 1933, the New World Screwworm (NWS) was first documented as a significant problem in the Southeast following…