Multi-country outbreak reported in Twelve member nations not endemic for Mpox Virus
On May 21, 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported that since May 13, 2022, cases of mpox were reported from 12 Member States that are not endemic for mpox virus, across three WHO regions. New countries that reported mpox included nine European nations, Australia, Canada and the U.S.
To date, all cases whose samples were confirmed by PCR have been identified as being infected with the West African clade. Genome sequence from a swab sample from a confirmed case in Portugal, indicated a close match of the monkeypox virus causing the current outbreak, to exported cases from Nigeria to the United Kingdom, Israel and Singapore in 2018 and 2019.
Mpox is a viral zoonosis (a virus transmitted to humans from animals) with symptoms very similar to those seen in the past in smallpox patients, although it is clinically less severe. It is caused by the monkeypox virus which belongs to the orthopoxvirus genus of the Poxviridae family. There are two clades of mopox virus: the West African clade and the Congo Basin (Central African) clade. The name mpox originates from the initial discovery of the virus in monkeys in a Danish laboratory in 1958. The first human case was identified in a child in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970.
Tags:
Source: World Health Organization
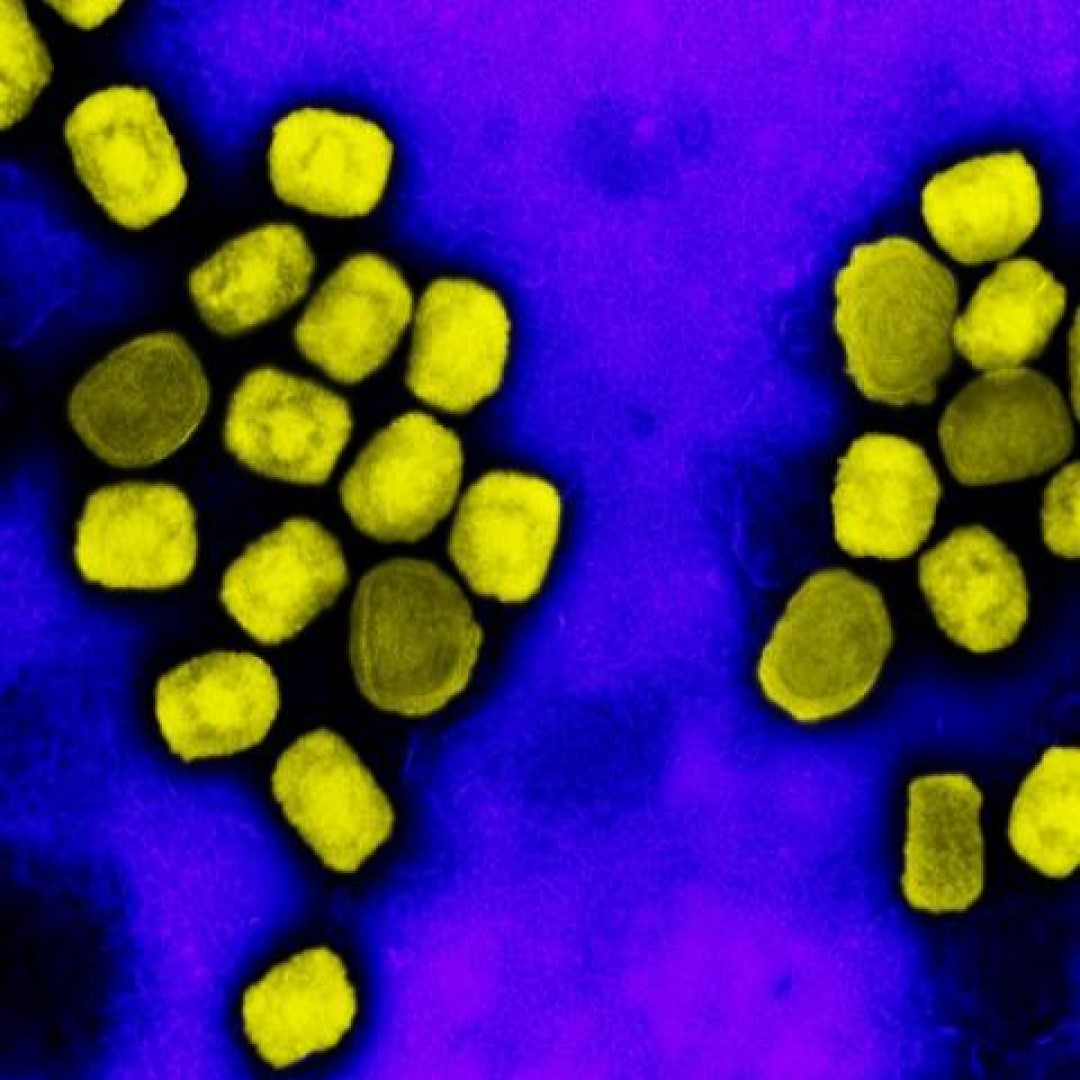
Credit: Photo: Colorized transmission electron micrograph of mpox virus particles (purple) cultivated and purified from cell culture, Fort Detrick, Maryland. Courtesy: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
