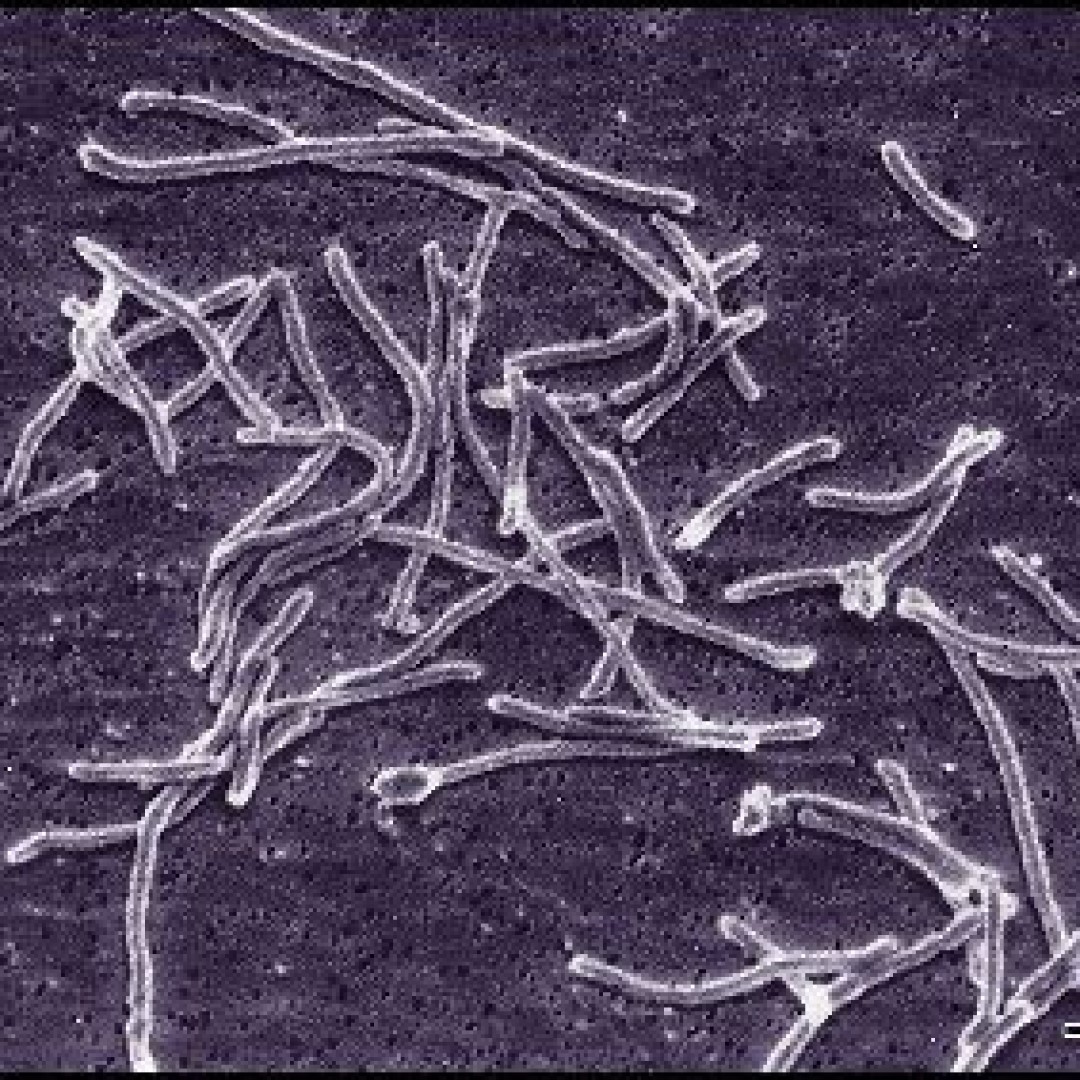
Thermus aquaticus was first discovered in Yellowstone National Park
In 1966, Thermus aquaticus was first discovered in the Mushroom Pool of Lower Geyser Basin in Yellowstone National Park by Thomas Brock from Indiana University. The heat-resistant enzyme Taq DNA polymerase is one of the most important enzymes in molecular biology because of its use in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) DNA amplification technique.
This bacterium was then studied through the 1970s and 1980s, with the basis of the patent for PCR founded on the themo-stable enzyme taq polymerase from T. aquaticus YT-1. PCR amplifies the amount of DNA in a sample. In 1985, Kary Mullis invented the PCR process by applying heat, the DNA molecule’s two strands are separated and the DNA building blocks that have been added are bonded to each strand. With the help of the enzyme DNA polymerase, new DNA chains are formed and the process can then be repeated.
PCR has been of major importance in both medical research and forensic science. In 1993, Mullis was awarded one-half of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his invention of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method.”
Tags:
Source: U.S. Geological Survey
Credit: Photo: Bacterium Thermus aquaticus. Courtesy: U.S. Geological Survey
