Novartis and Molecular Partners announced start of EMPATHY clinical trial for ensovibep for treatment of COVID-19
On May 27, 2021, Novartis and Molecular Partners announced the start of the clinical trial EMPATHY, a Phase…

On May 27, 2021, Novartis and Molecular Partners announced the start of the clinical trial EMPATHY, a Phase…
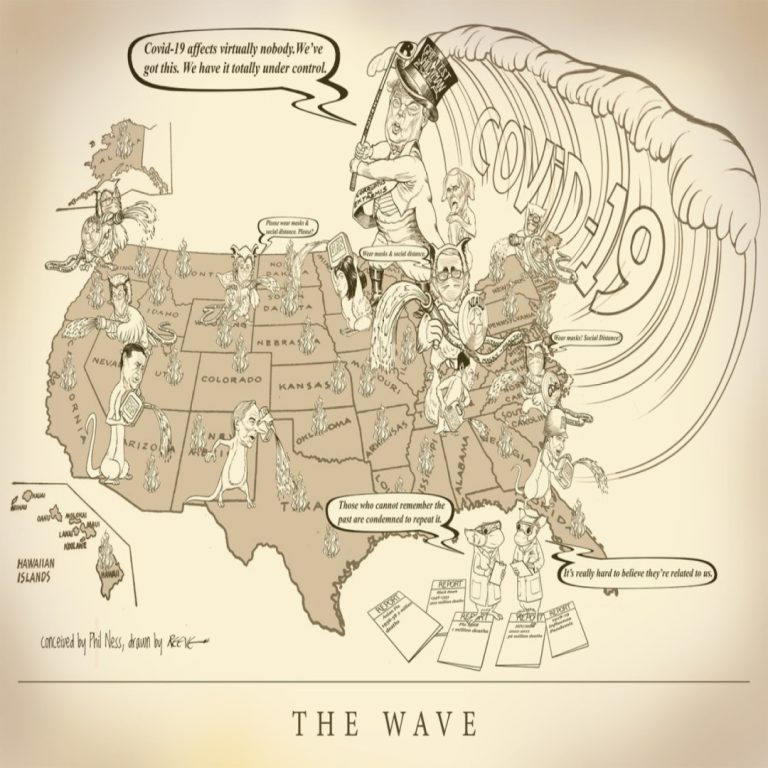
Cast of Characters: Donald Trump, President | Mike Pence, Vice President | Anthony S. Fauci, MD, Director, National…

COVID-19 and it’s naysayers are attacking Science and Reason. The defenders must suffer the slings and arrows from…

On Apr. 19, 2021, scientists at the Texas A&M University Global Health Research Complex (GHRC) announced they had…

On Apr. 6, 2021, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that nearly 80 percent of…

On Mar. 17, 2021, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced the investment of $10…
On Mar. 16, 2021, research from the WHO and partners showed that the COVID-19 pandemic was severely affecting…

On Mar. 11, 2021, Abbott announced the formation of the Abbott Pandemic Defense Coalition, a first-of-its-kind global scientific…

On Mar. 11, 2021, Rigel Pharma announced the completion of patient enrollment in a multi-center Phase 2 clinical trial to…

On Mar. 11, 2021, ImmunityBio announced it was developing a novel hAd5 ACE2 Decoy therapeutic vaccine to neutralize…

On Mar. 11, 2021, Altimmune announced that it had expanded its previously-announced AdCOVID manufacturing collaboration with Lonza. Under the…

On Mar. 11, 2021, Johnson & Johnson announced that the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP)…

On Mar. 10, 2021, the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) announced that it had identified additional personnel authorized…
On Mar. 5, 2020, Adaptive Biotechnologies announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had issued an…
On Mar. 1, 2021, a study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis provided evidence that…

On Feb. 18, 2021, scientists at the University of Oxford announced that the Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy…

On Feb. 17, 2021, Altimmune announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had cleared the Companyls…

On Feb. 17, 2021, Immunic announced that its lead asset, IMU-838, the company’s selective oral DHODH inhibitor, had…

On Feb. 11, 2021, the Oregon Department of Agriculture (ODA) lifted the quarantine on the Oregon mink farm…
On Feb. 8, 2021, Repligen and Navigo Proteins announced that they have completed the development and initiated the commercial…

On Feb. 4, 2021, Merck affirmed its position regarding use of ivermectin during the COVID-19 pandemic, and do…
On Jan. 28, 2021, OraSure Technologies announced its OMNIgene®·ORAL (OME-505) saliva collection device, a product of Ottawa-based subsidiary…

On Dec. 24, 2020, AIM ImmunoTech announced that the post-COVID-19 ‘Long Hauler’ portion of the active AMP-511 Expanded…
On Dec. 10, 2020, Moderna announced that the first adolescent participants had been dosed in the Phase 2/3…

On Nov. 19, 2020, Cue Health announced that, as of November 9, the U.S. Department of Health and…

On Nov. 19, 2020, Dallas-based company, Worlds Inc., the U.S. Air Force and Texas A&M University announced a…

On Nov. 17, 2020, the Mayo Clinic reported that more than 900 employees had contracted COVID-19 in the…
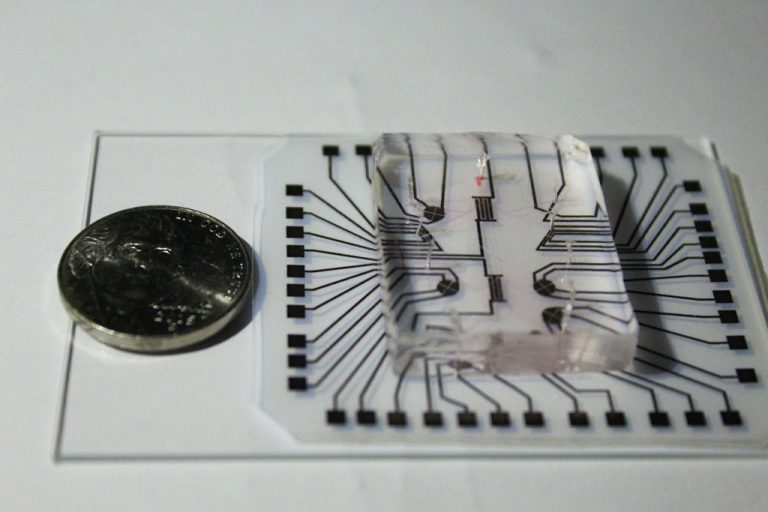
On Nov. 4, 2020, using the cutting-edge genetic editing technique known as CRISP ‘lab on a chip’ technology,…

On Nov. 3, 2020, OraSure Technologies announced its DNA Genotek subsidiary has received Emergency Use Authorization from the…

On Nov. 1, 2020, the U.S. Department of Defense announced the start of rapid, on-site COVID-19 testing for…