European Vaccines Hub for Pandemic Readiness Launches
On May 23, 2025, The Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Authority (HERA) of the European Commission, through the…

On May 23, 2025, The Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Authority (HERA) of the European Commission, through the…

On May 23, 2025, the Iowa Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) reported a confirmed case of…

On May 20, 2025, the Arizona Department of Agriculture (AZDA) reported that poultry at a commercial farm located…

On May 20, 2025, member States of the World Health Organization (WHO) formally adopted by consensus the world’s…

On May 20, 2025, The Trump administration said it will limit approval for seasonal COVID-19 shots to seniors…
On May 17, 2025, The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Novavax’s COVID-19 vaccine, but placed additional conditions…
On May 16, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported 718 cases of measles have…

On May 15, 2025, the New Mexico Department of Health (NMDOH) confirmed the first measles cases in Sandoval…
On May 9, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported 709 cases of measles have…
On May 7, 2025, the New Mexico Department of Health (NMDOH) confirmed the first measles cases the first…

On May 2, 2025, the Louisiana Department of Health (LDH) reported an increase in whooping cough (pertussis) cases…

On May 2, 2025, the Centers for Disease Control reported twelve pediatric deaths associated with seasonal influenza virus…

On May 2, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported 683 cases of measles have…
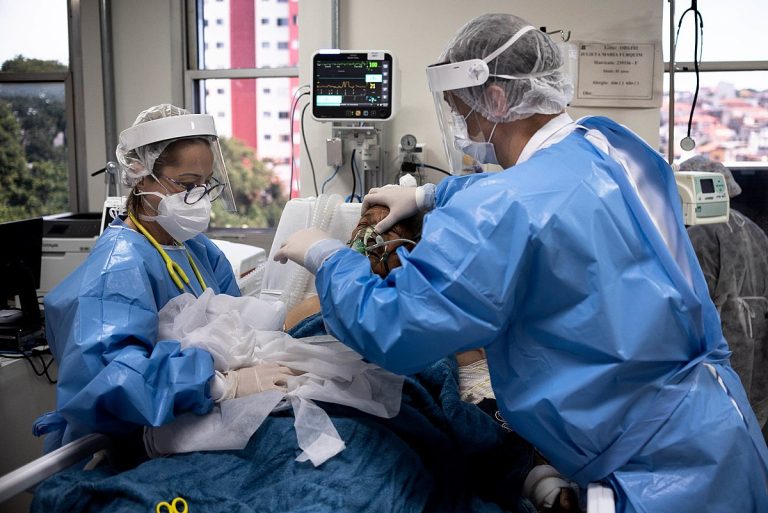
On May 1, 2025, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that hospitals are no…
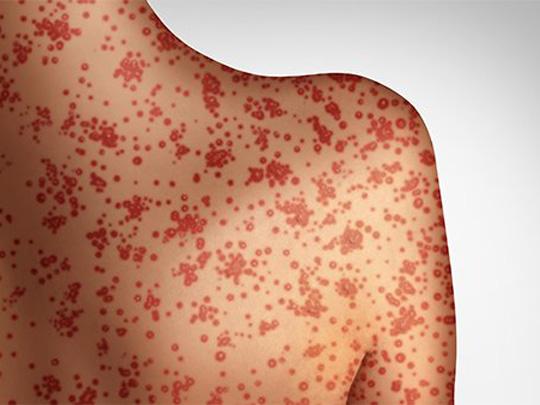
On Apr. 25, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported that 646 cases of measles…
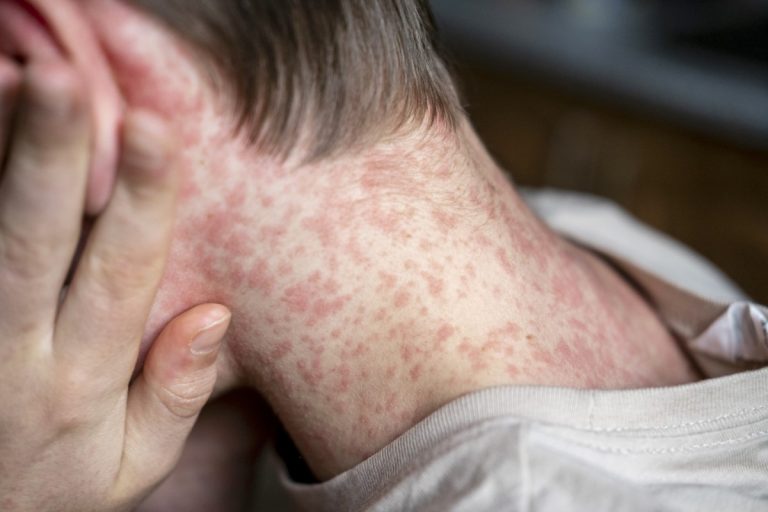
On Apr. 18, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported that 597 cases of measles…
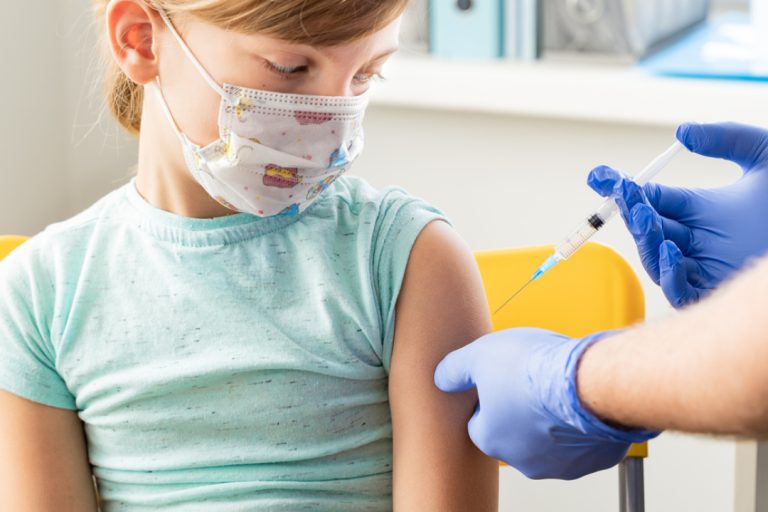
On Apr. 17, 2025, the Department of Public Health and Human Services (DPHHS) and the Gallatin City-County Health…
On Apr. 17, 2025, The Tennessee Department of Health confirmed two additional confirmed cases of measles in middle…
On Apr. 11, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (Texas DSHS) reported that 541 cases of…
On Apr. 9, 2025, Tulane University researchers announced they have developed a first-of-its-kind handheld diagnostic device that can…

On Apr. 8, 2025, the Hawaiʻi Department of Health (DOH) State Laboratories Division confirmed a case of measles…

On Apr. 7, 2025, The Indiana Department of Health (IDOH) reported the first laboratory confirmed case of measles…

On Apr. 6, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services has reported the second measles death of…

On Apr. 4, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported updated information about an outbreak…

On Apr. 4, 2025, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced that over the past two days, it convened…

On Apr. 2, 2025, the Oklahoma Children’s Hospital (OU Health) announced it had taken swift action to address…

On Apr. 1, 2025, the Tennessee Department of Health confirmed three additional cases of measles in Middle Tennessee…

On Mar. 28, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported updated information about an outbreak…
On Mar. 26, 2025, the Kansas Department of Health and Environment (KDHE) reported 23 positive cases of measles…

On Mar. 25, 2025, Ohio Department of Health (ODH) announced a measles outbreak in Ashtabula County and one…