Novavax’s Nuvaxovid™ 2025-2026 Formula COVID-19 Vaccine Approved in the U.S.
On Aug. 27, 2025, Novavax announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the Nuvaxovid™ 2025-2026…
On Aug. 27, 2025, Novavax announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the Nuvaxovid™ 2025-2026…

On Aug. 18, 2025, Lewis and Clark Public Health (LCPH) officlials in Montana have confirmed a single case…

On Aug. 18, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services is reporting the end of this year’s…

On Aug. 18, 2025, the World Health Organization announced Nepal has eliminated rubella as a public health problem,…

On Aug. 7, 2025, The first paper from a multi-year clinical research study has been published in The…

On Jul. 24, 2025, a University of Minnesota study shows that widespread immunity through vaccination or natural infection…

On Jul. 17, 2025, a new world-leading biosecurity centre in Essex has been announced that will protect the…
On Jul. 9, 2025, Alberta has the most measles cases in North America on a per-capita basis, worrying…
On Jul. 8, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported a total of 753 cases…

On Jul. 5, 2025, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported that between January 1 and July 1, 2025,…

On Jun. 29, 2025, Cambodian health authorities confirmed two new human cases of H5N1 avian influenza involving a…
On Jun. 27, 2025, the World Health Organization (WHO) Scientific Advisory Group for the Origins of Novel Pathogens…
On Jun. 26, 2025, the New Mexico Department of Health (NMDOH) announced that five people who are incarcerated…

On Jun. 24, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported a total of 750 cases…

On Jun. 24, 2025, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) announced results from the Global Burden…

On Jun. 23, 2025, Texas A&M research shows wearable health tech can detect infections like COVID-19 and flu…

On Jun. 17, 2025, the New Mexico Department of Health (NMDOH) announced that wastewater in Deming has tested…
On Jun. 17, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported a total of 750 cases…

On Jun. 12, 2025, U.S. Health Secretary Robert Kennedy Jr. named eight members to serve on a key…

On Jun. 11, 2025, the Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services (DPHHS) reported a total of…

On Jun. 11, 2025, The Iowa Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is reporting the state’s third…

On Jun. 11, 2025, Novavax announced results of the initial cohort of its COVID-19-Influenza Combination (CIC) and stand-alone trivalent…
On Jun. 10, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported 744 cases of measles have…
On Jun. 9, 2025, Oakland County Health Division in Michigan is notifying the public about a measles exposure…
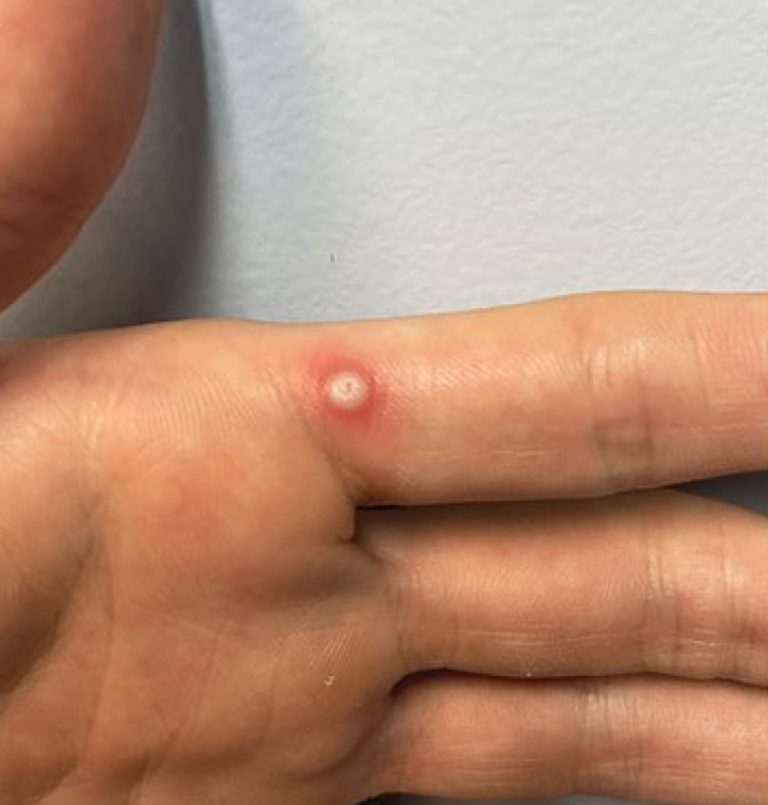
On Jun. 9, 2025, the World Health Organization (WHO) said the mpox outbreak is still a public health…

On Jun. 9, 2025, the Navajo County Public Health Services District (NCPHSD), in coordination with the Arizona Department…

On Jun. 6, 2025, the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) reported 742 cases of measles have…

On Jun. 6, 2025, the Arizona Department of Agriculture (AZDA) reports poultry at a fourth commercial farm located…
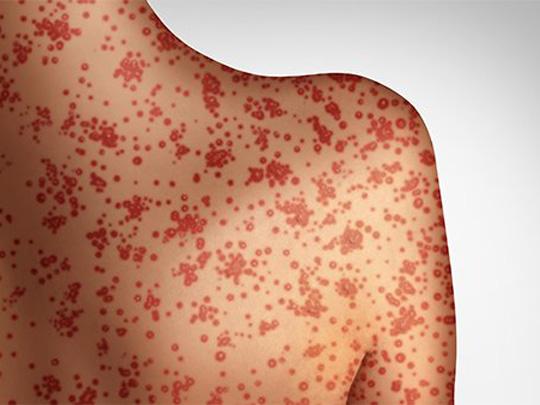
On Jun. 6, 2025, the South Dakota Department of Health has notified the public of potential measles exposure…

On Jun. 4, 2025, an international team of researchers published a study in the preprint server medRxiv that…