Tu Youyou won a share of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for her discoveries concerning a novel therapy against Malaria
On Oct. 5, 2015, Tu Youyou was awarded a half share of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or…
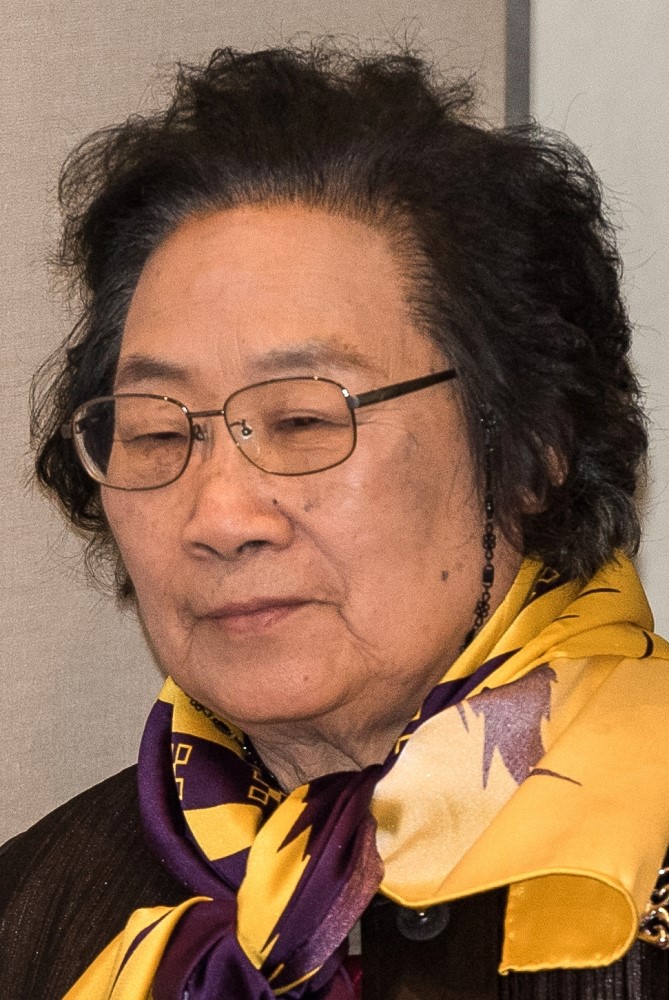

On Oct. 5, 2015, Tu Youyou was awarded a half share of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or…

On Nov. 27, 2014, two papers were published in Science that announced the completion and preliminary analyses of…

On Apr. 25, 2008, marked the first-ever World Malaria Day established by the United Nations to ensure that…

On Feb. 12, 2007, a study published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry by researchers led by Dr….
On Apr. 12, 2006, chemical engineer Jay Keasling helped create an affordable anti-malaria drug, artemensins, by producing arteminsic…
In 2006, the Malaria Atlas Project (MAP) was founded as an international research collaboration that tracks the global…
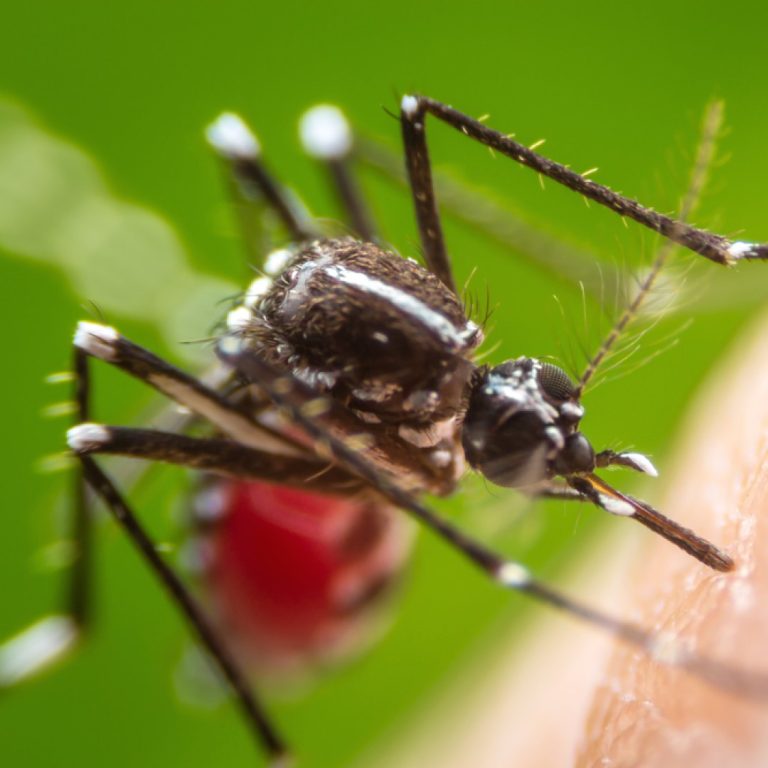

On Oct. 30, 2005, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation announced three grants totaling $258.3 million for advanced…

In 1985, the CDIPD was founded as an NIH-NIAID-supported Tropical Disease Research Unit (TDRU) at University of California,…
In 1981, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) established the International Health Program Office, now…
On Oct. 30, 1977, Ali Maow Maalin, a hospital cook in Merca, Somalia, was diagnosed with smallpox by…
In 1964, a new herpesvirus, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), was discovered in cultured tumor cells derived from a Burkitt…
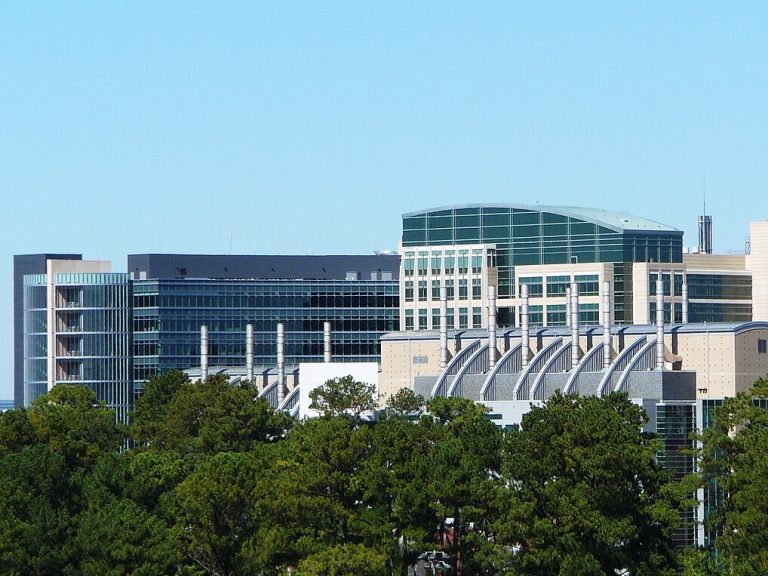

On Sept. 8, 1960, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) new permanent headquarters opened in Atlanta,…

In 1955, Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was approved for medical use in the U.S. Chloroquine was discovered in 1934 by…

In 1949, the office of Malaria Control declared the U.S. was free of malaria as a significant public…

On Apr. 7, 1948, the World Health Organization (WHO) was founded and is today the United Nations agency…

On Jul. 1, 1947, the National Malaria Eradication Program commenced. The Program was a cooperative of state and…
On Jul. 1, 1946, the Communicable Disease Center (CDC) opened its doors and occupied one floor of a…
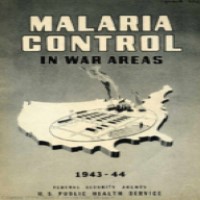
In 1942, the Malaria Control in War Areas (MCWA) agency was established in Atlanta, Georgia, now known as…
In 1942, a classic manual describing and illustrating the stages of the malaria parasites was prepared by Aimee…
In 1939, the National Malaria Society was founded. In 1951, the criteria for eradication as put forth by…

In 1911, William Krauss, Ph.G., M.D. of the University of Tennessee College of Medicine published the first paper…
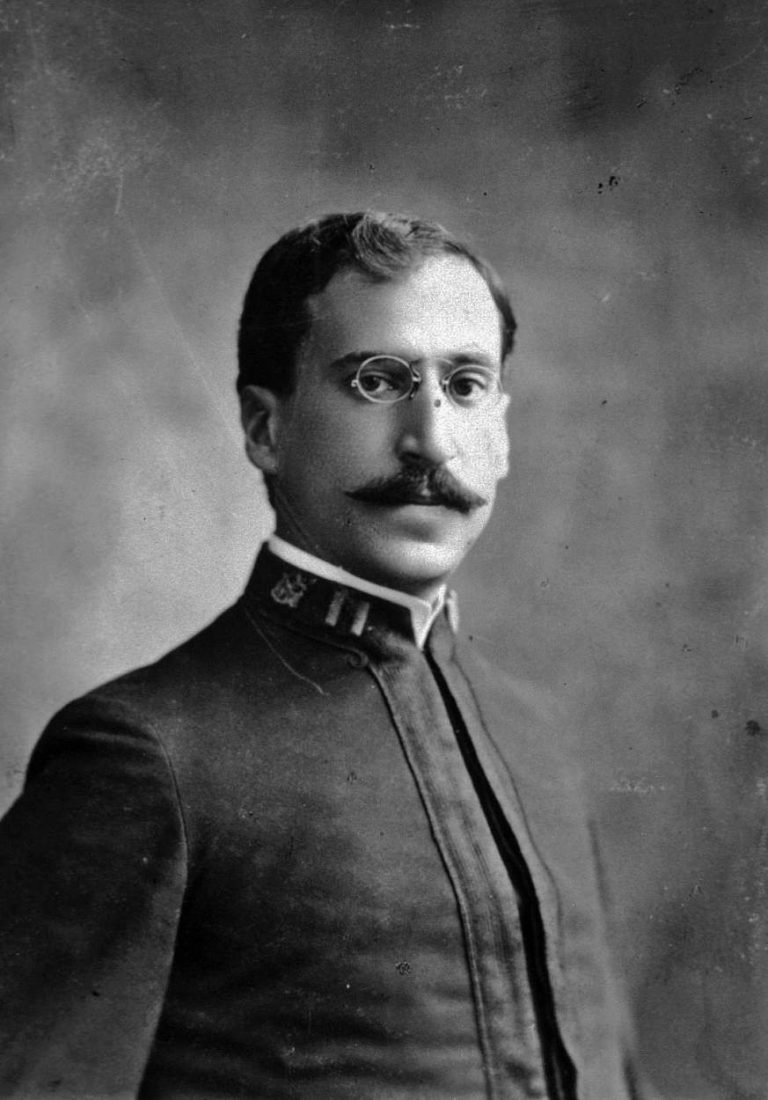

In 1908, Milton J. Rosenau and John F. Anderson established the standard unit for tetanus antitoxin. A pioneer…
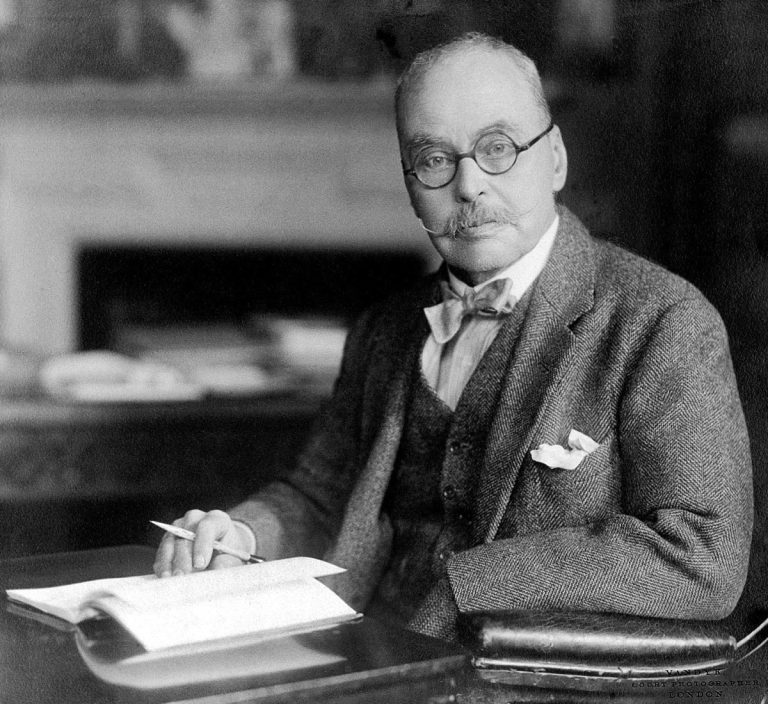

In 1902, Ronald Ross was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for his work, using pigeons,…

On Aug. 20, 1897, Sir Ronald Ross made his landmark discovery. While dissecting the stomach tissue of an…

In 1880, french Military surgeon Charles Laveran while stationed in Algiers discovered the cause of malaria (“bad air”)…

In 1878, Sir Patrick Manson demonstrated that a parasite that causes human disease could infect a mosquito. In…