swine flu vaccination program in the U.S. Suspended following reports of paralysis
On Oct. 13, 1976, the swine flu vaccination program in the U.S. was suspended following reports of paralysis. …

On Oct. 13, 1976, the swine flu vaccination program in the U.S. was suspended following reports of paralysis. …

In 1976, Influenza A/Victoria-like strains had been identified in New Jersey as early as January 21. The novel…

In 1970, influenza H3N2 viruses were first identified in swine during an influenza surveillance study in Taiwan. This…
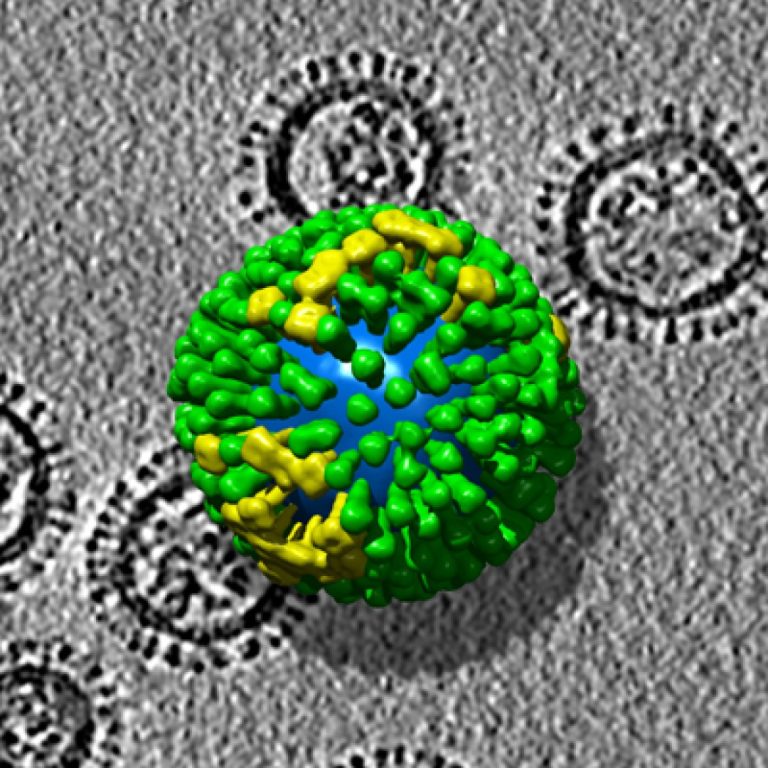
The 1968 pandemic, also known as the Hong Kong flu, was caused by an influenza A (H3N2) virus…
In 1968, a pandemic was caused by an influenza A (H3N2) virus comprised of two genes from an…
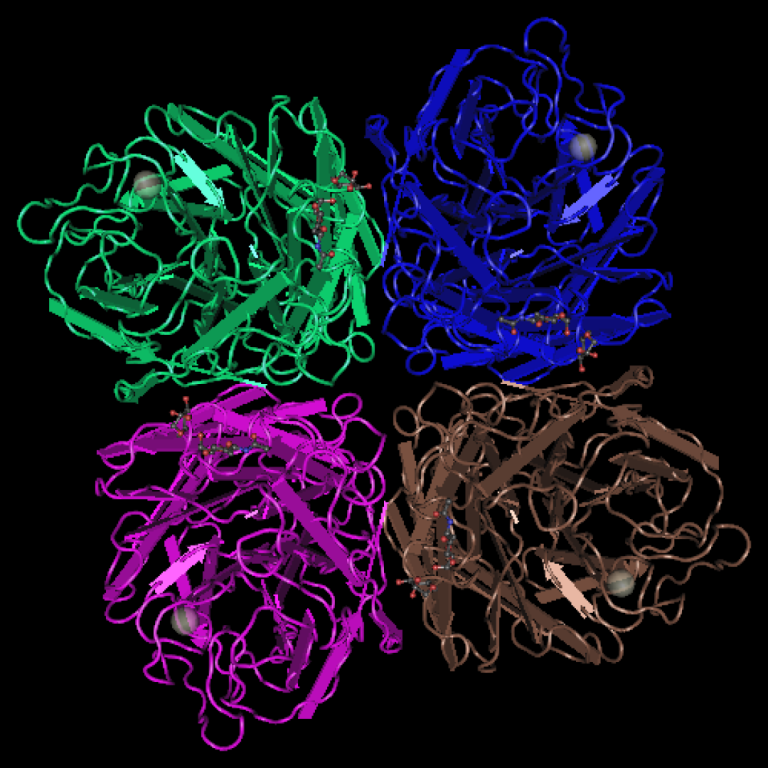
In Feb. 1957, a new influenza A (H2N2) virus emerged in East Asia, triggering a pandemic (‘Asian Flu’)….

In 1957, the ‘Asian flu’ influenza pandemic emerged, resulting in the CDC setting up an influenza surveillance unit,…

In 1956, the CDC’s Influenza Branch in Atlanta was designated a World Health Organization (WHO) Collaborating Centre for…

Since 1952, global influenza surveillance has been conducted through WHO’s Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS). The…

In 1948, Dr. Isabel M. Morgan led a team that successfully inoculated monkeys with a killed-virurs vaccine. From…

In 1939, Margaret Pittman showed that sulfapyradine was effective against nontype-specific Haemophilus influenzae. Pittman discovered that there are…
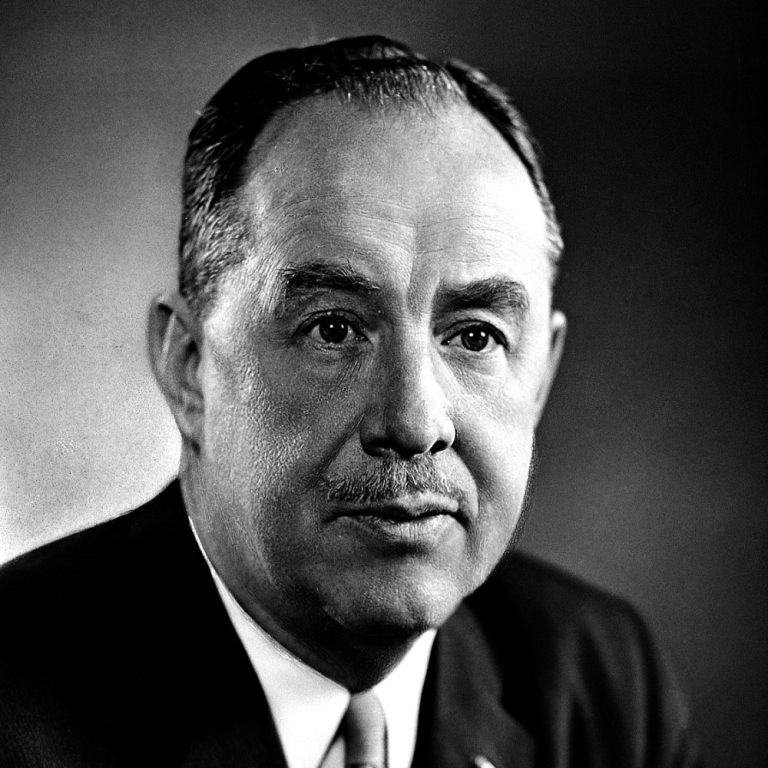

In 1938, Thomas Francis, Jr., MD and Jonas Salk, MD served as lead researchers at the University of…
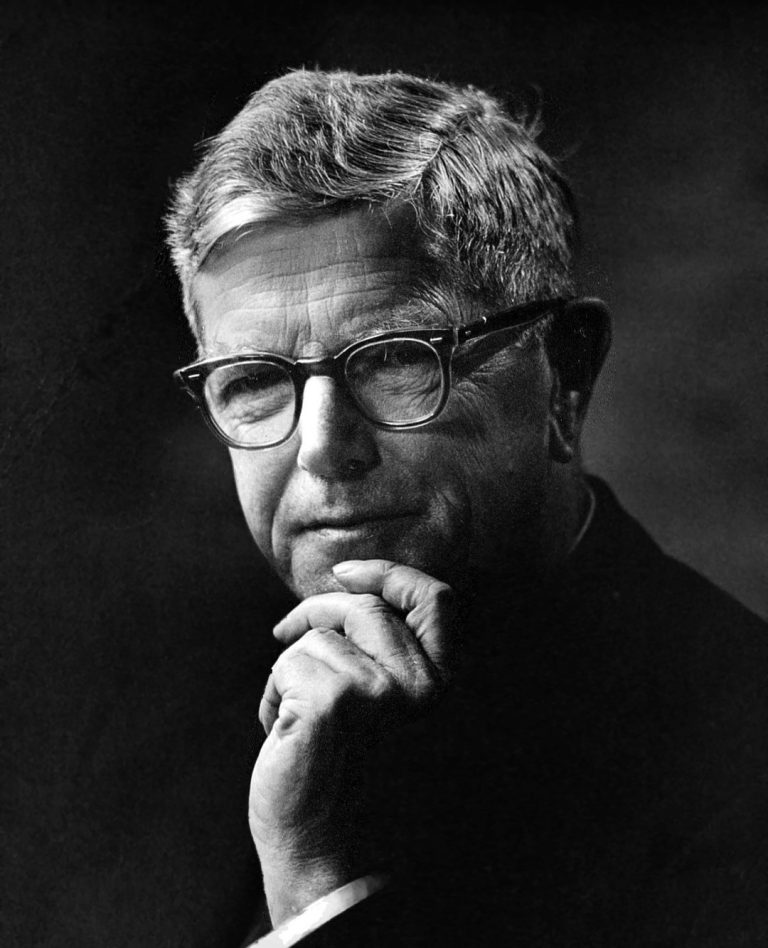

In 1936, Sir Macfarlane Burnet discovered that influenza virus could be grown in embryonated hens’ eggs. This led…
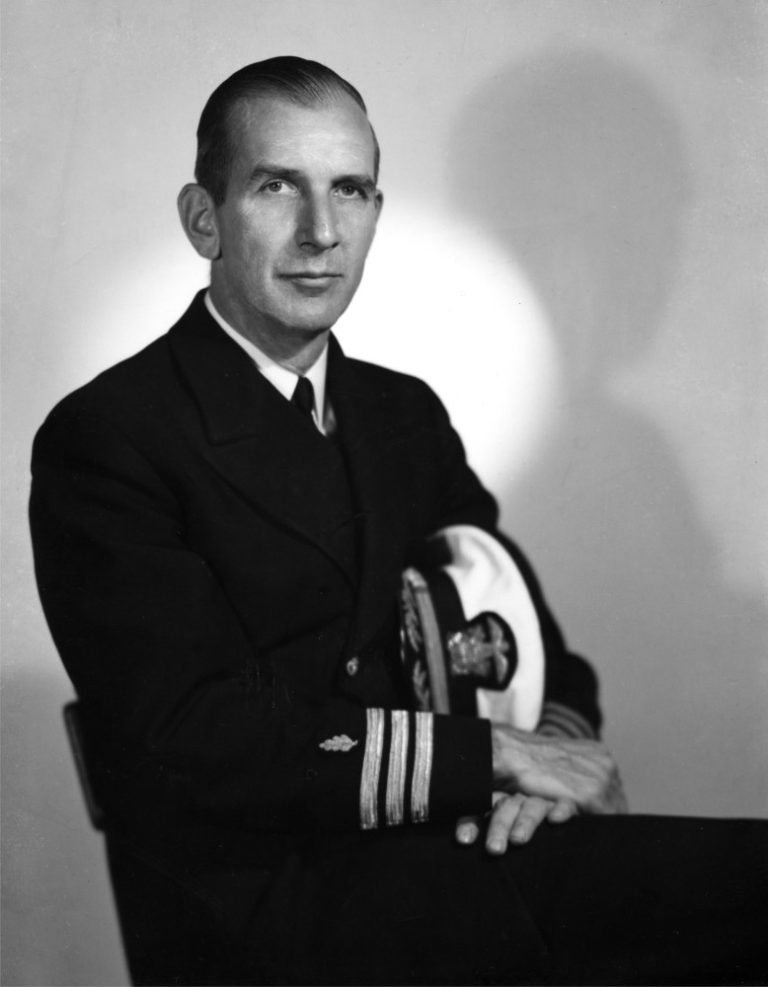

In 1931, Rockefeller Institute investigator Richard Shope published the first of three landmark papers that established the etiology…
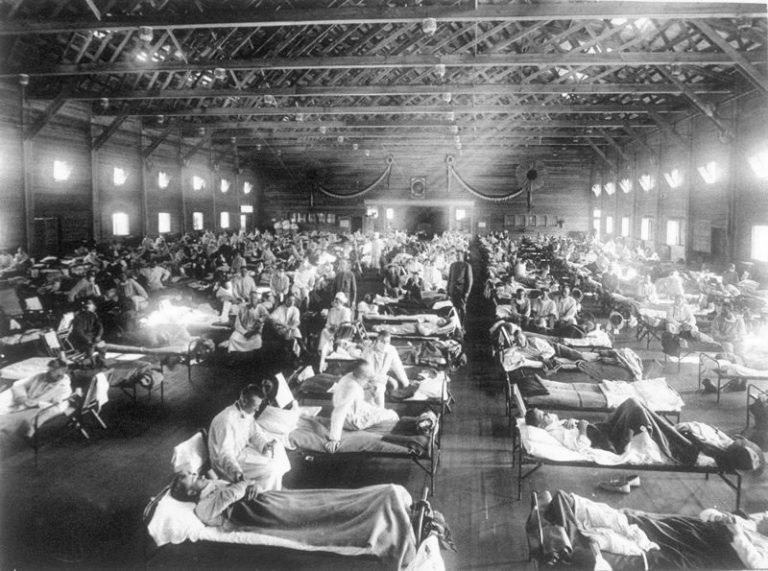
By April 1919, following upticks in influenza over winter, the final tally for New Orleans stood at 54,089…
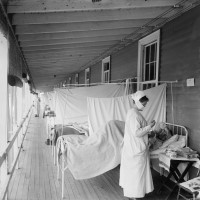
in 1919, by the end of the influenza epidemic in Omaha, almost 1,200 people had died, with a…
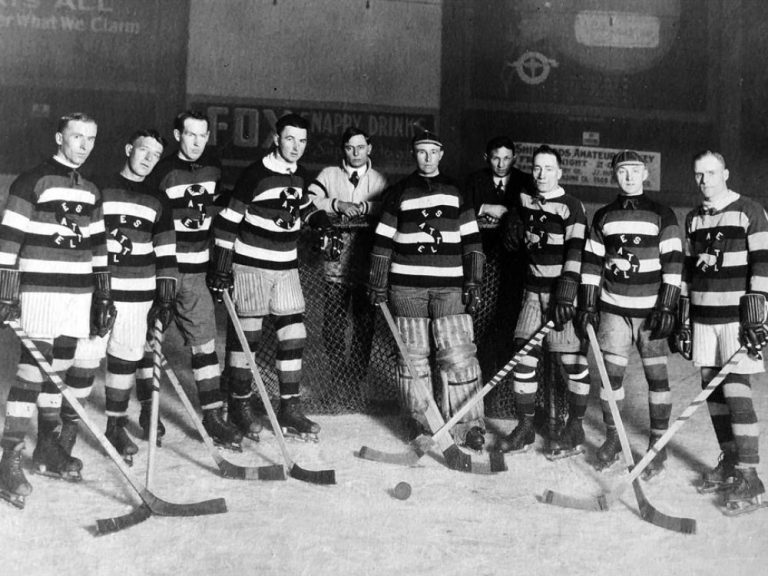

On Apr. 1, 1919, the Stanley Cup playoffs between the Montreal Canadians and the Seattle Metropolitans ended tied…
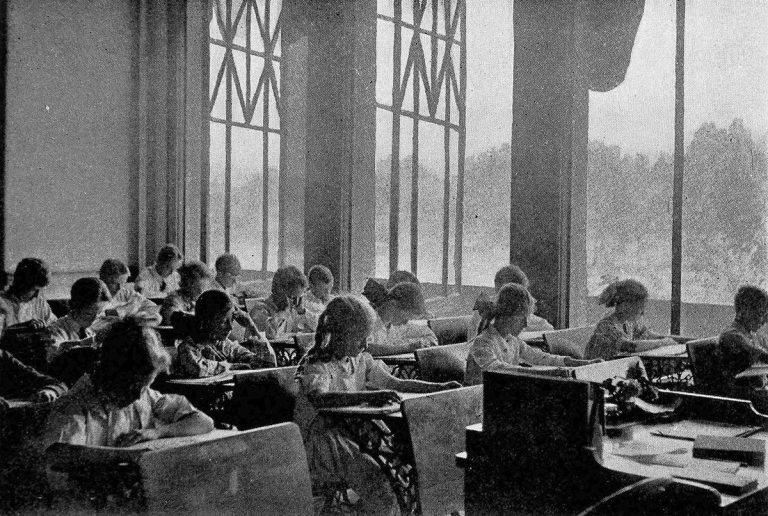

On Jan. 2, 1919, Denver slowly returned to normal after its flu epidemic, and schools reopened. School teachers…

By late February of 1919, Louisville experienced a third wave of influenza cases, but finally began to return…

In Jan. 1919, Birmingham experienced a third wave in influenza cases and deaths.

By 1919, after the end of its second winter influenza wave, Boston had experienced an excess death rate…

In 1919, Washington, D.C. suffered spikes in influenza cases throughout the remainder of 1918, and into early February…
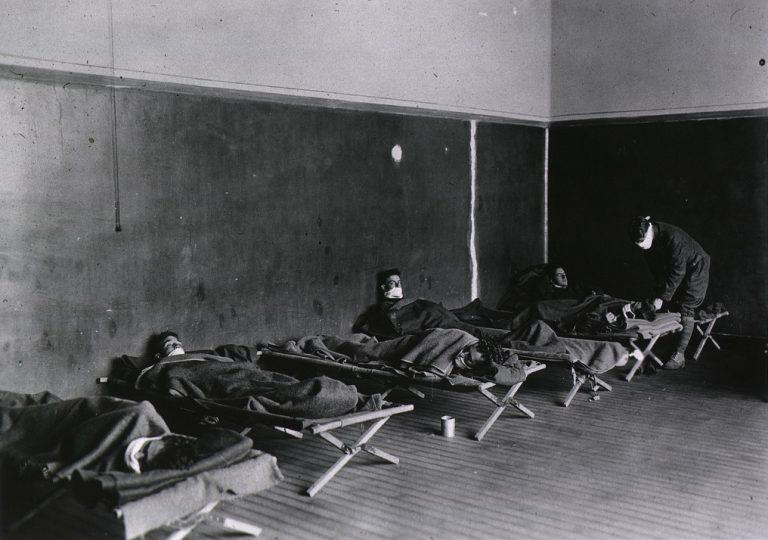
In 1919, influenza cases dwindled through the winter of 1918, yet persisted into April 1919 sporadically. About 9…

On Dec. 20, 1918, after declining influenza cases, Health Commissioner Starkloff lifted remaining St. Louis closure bans.

On Dec. 14, 1918, meeting in special session, members quickly decided that the influenza situation in Cincinnati had…
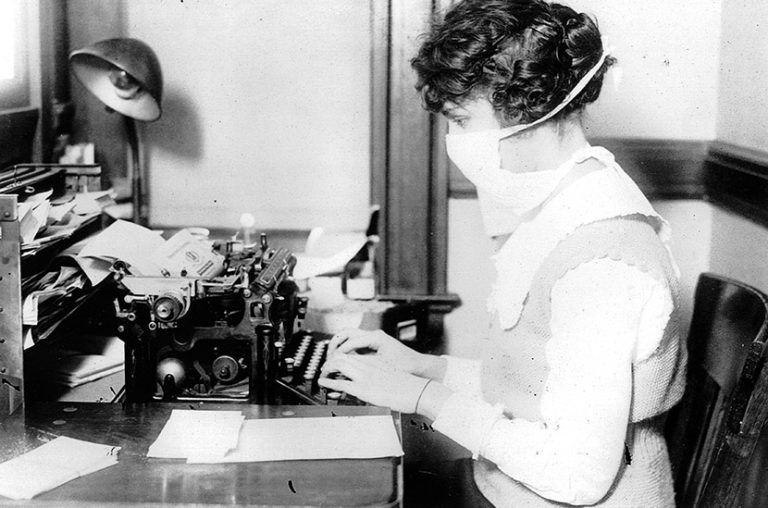

On Dec. 12, 1918, following an increase in influenza cases, Cincinnati Health Officer Dr. William H. Peters recommended…
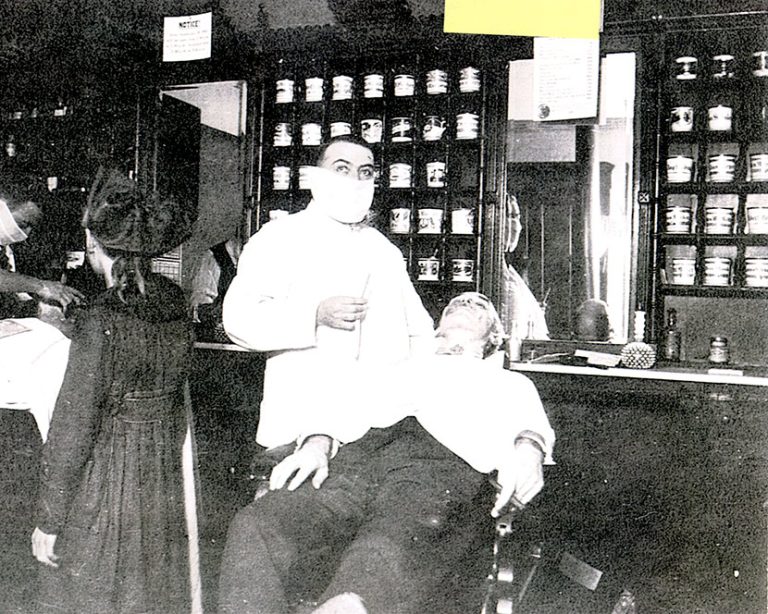

On Dec. 6, 1918, Salt Lake City and Utah health officials met to modify their closure order, to…
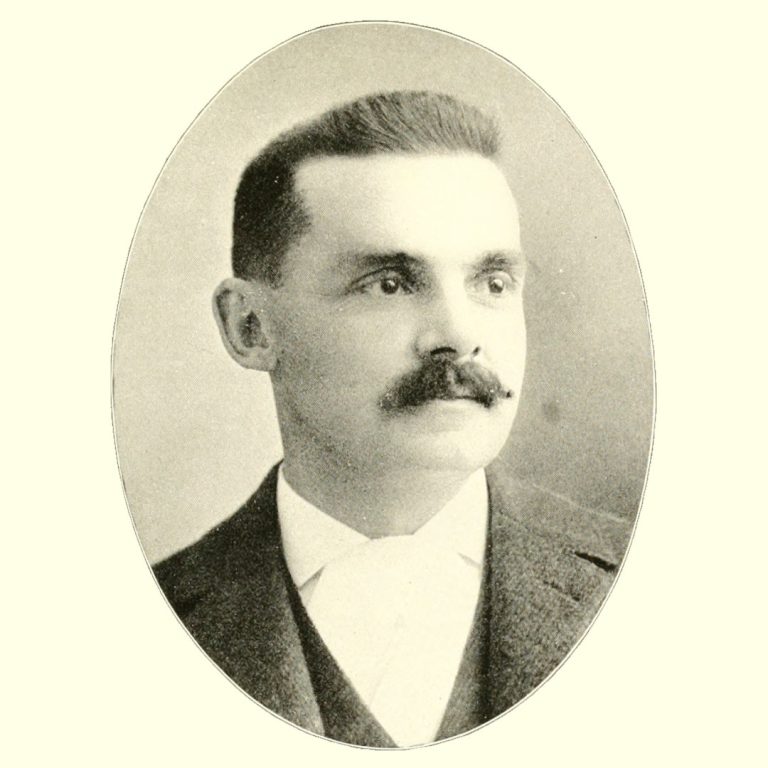

in 1919, thanks to Health Commissioner Dr. Max C. Starkloff’s strong leadership in the influenza epidemic, St. Louis…
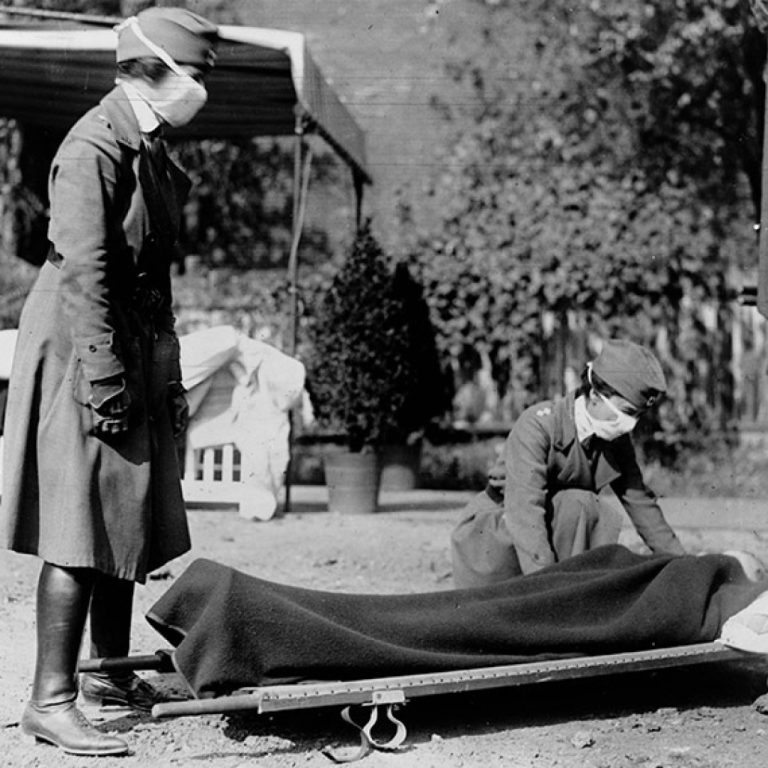

By the end of the 1918 influenza epidemic, Los Angeles experienced a lower epidemic death rate than many…
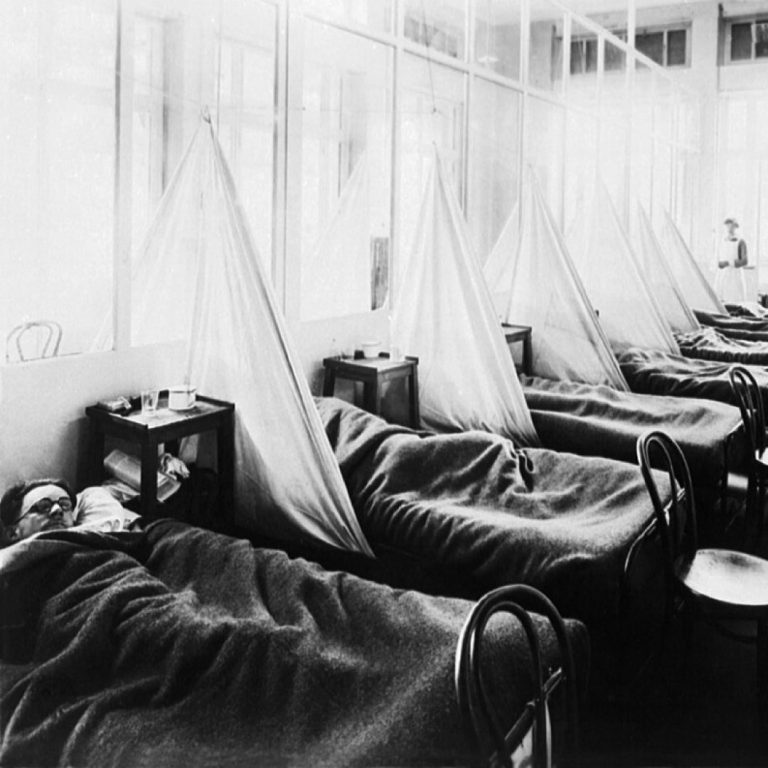
At the end of 1918, Baltimore had a total of almost 24,000 reported cases of influenza and 4,125…