Groundbreaking ceremony for the McArdle Cancer Research Institute building was held
On Oct. 13, 1962, the groundbreaking ceremony for the McArdle Cancer Research Institute building was held. The construction…

On Oct. 13, 1962, the groundbreaking ceremony for the McArdle Cancer Research Institute building was held. The construction…

In 1961, the CDC expanded its reach into chronic disease by investigating a cancer cluster in Illinois.

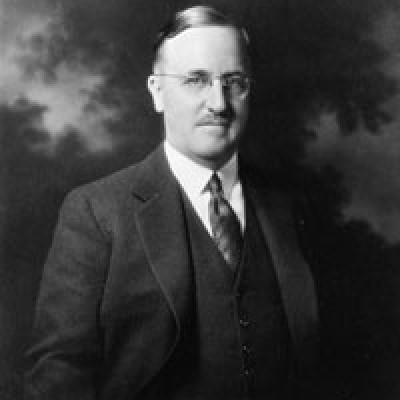
In 1956, the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to Carl S. Marvel “to recognize distinguished services…
In 1953, American chemists Harold Urey and Stanley Miller reported the production of biomolecules from simple gaseous starting…

On Jun. 1, 1951, the Ben May Laboratory for Cancer Research at the University of Chicago opened its…

In 1947, Tyson Foods, based in Arkansas, was founded by John Tyson in 1935 who began the company…

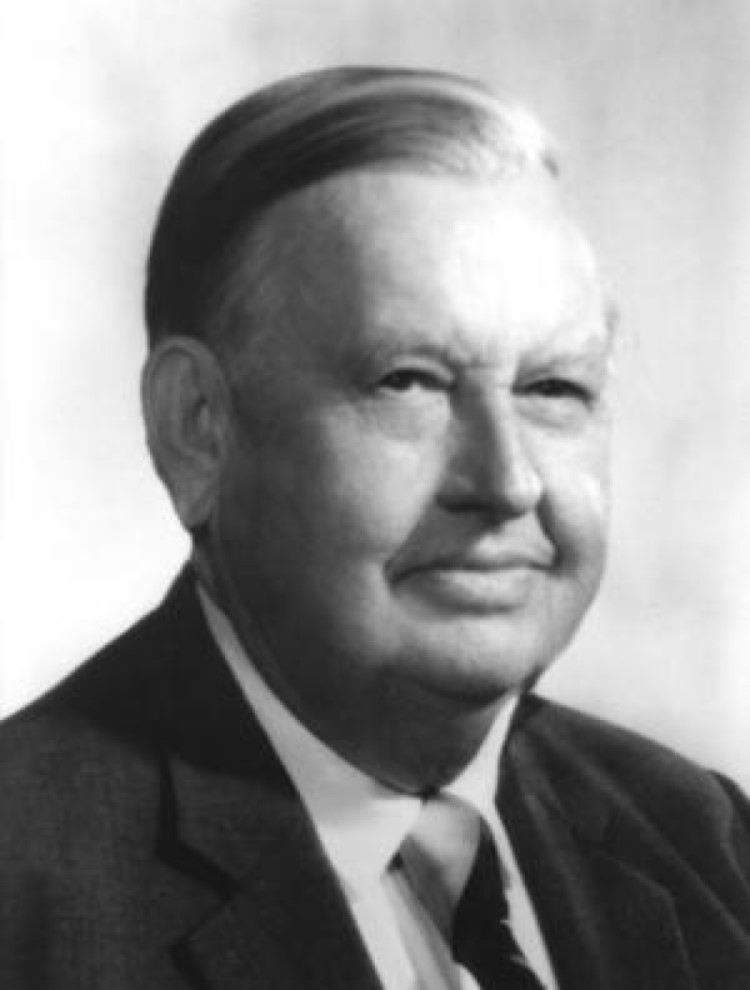
In 1946, the Priestley Medal was awarded to Roger Adams by the American Chemical Society “to recognize distinguished…
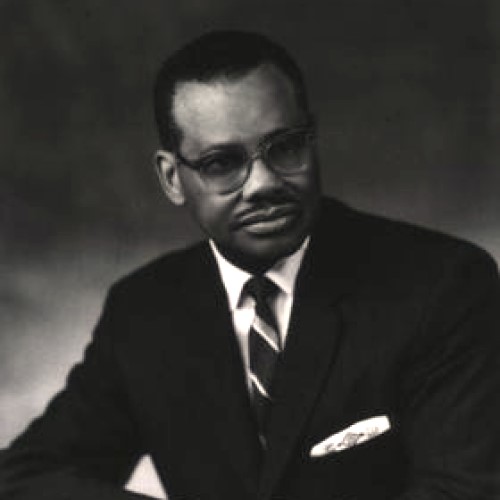

In 1946, Dr. Leonidas Harris Berry became the first black physician on staff at Michael Reese Hospital in…
In 1942, the Hektoen Institute opend in the former John McCormick Institute for Infectious Diseases, on South Wood…
In 1940, Howard Florey, Ernst Chain and others in England discover how to purify and preserve penicillin. The…
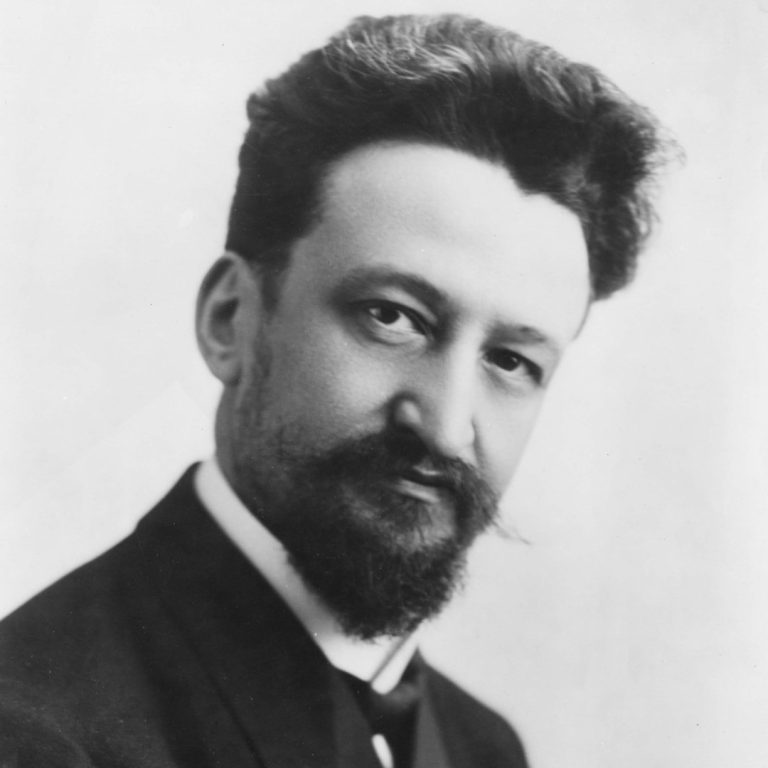

On Mar. 15, 1937, the world’s first blood bank was opened at Cook County Hospital in Chicago by…

In 1931, Drs. Ralph Falk and Don Baxter launched the Don Baxter Intravenous Products Corporation, the first commercial…

In 1931, The Cook County School of Nursing opened in the former Illinois Training School for Nurses, now…
In 1930, Ralph Lillie demonstrated that the cause of psittacosis was a rickettsia-like organism (later placed in the…

In 1925, the Cook County Hospital treated nearly 42,000 patients, and a new building program began at a…
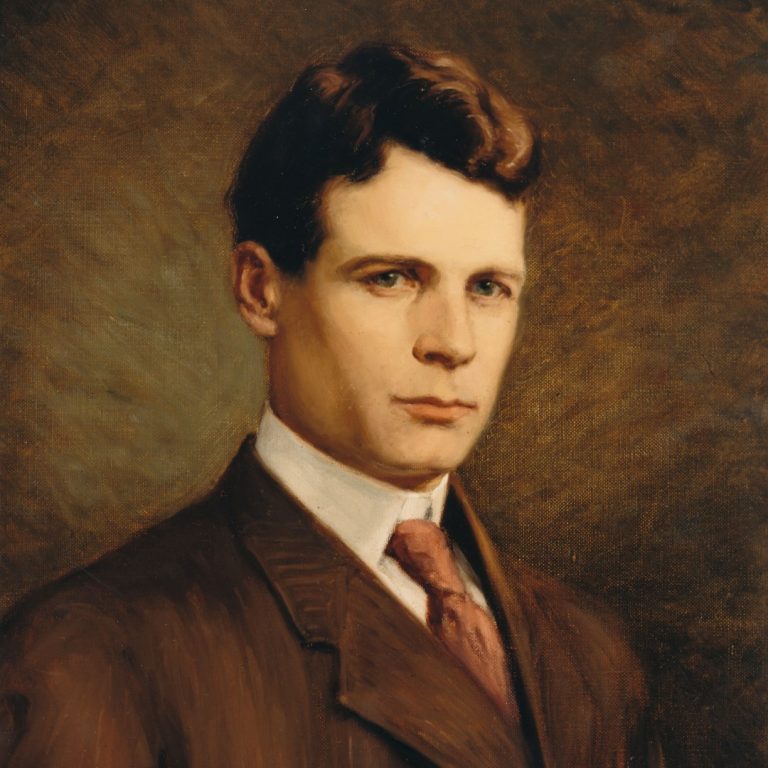

In 1921, the founding of the Rocky Mountain Laboratory (RML) can be traced back to westward migration when…
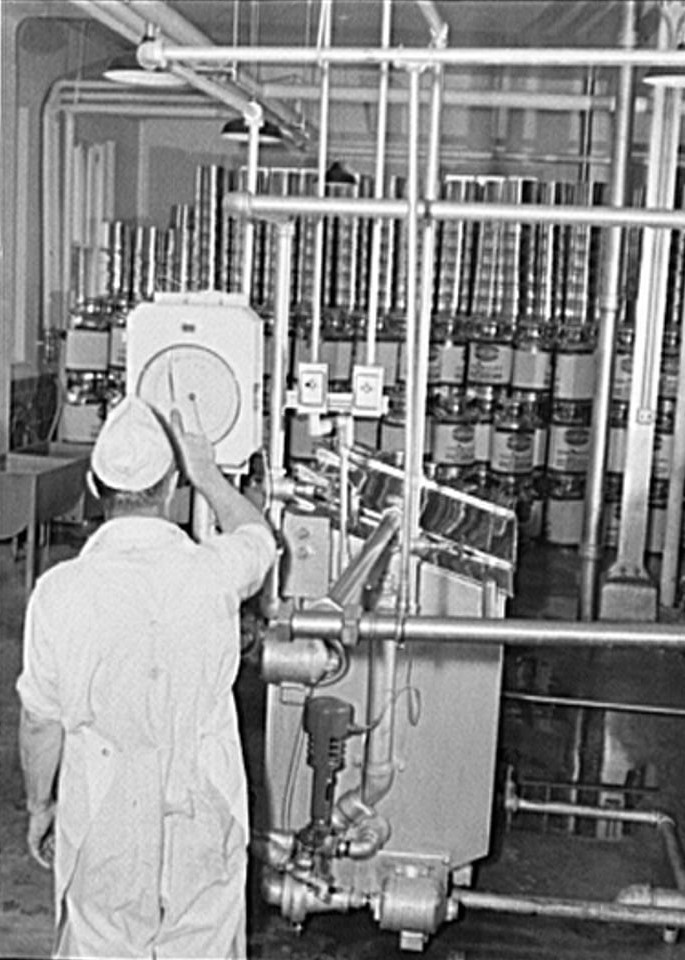

In 1919, one of the first municipal milk pasteurization programs in the U.S. was initiated by Charleston Health…
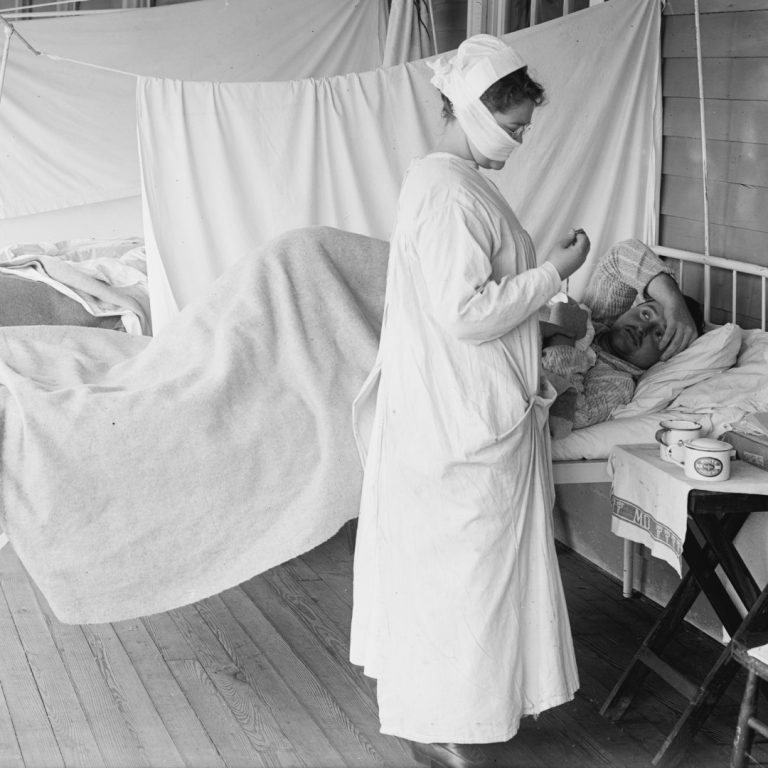
By Nov. 16, 1918, Chicago had experienced a total of 38,000 cases of influenza and 13,000 cases of…
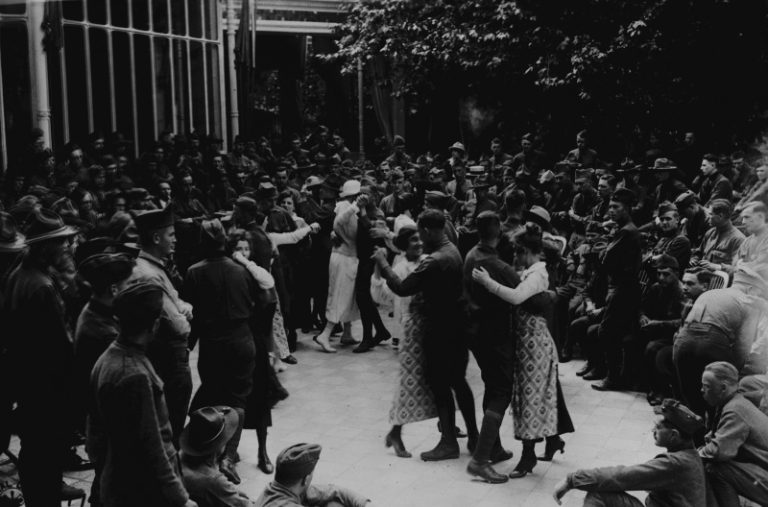

On Nov. 10, 1918, Cleveland Health Commissioner Dr. Harry L. Rockwood announced the lifting of the city’s closure…

On Nov. 1, 1918, much of Chicago reopened, with inspections and other rules in place. In most cities,…

On Oct. 16, 1918, the Illinois Influenza Advisory Commission decided to ban all non-essential public gatherings. State Health…
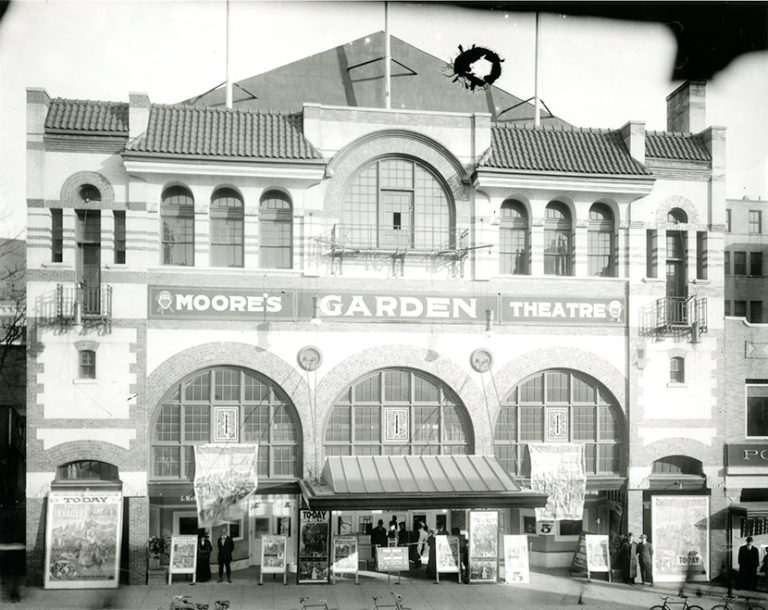

On Oct. 15, 1918, Chicago’s Advisory Commission ordered all theaters, movie houses, and night schools to close, as…

On Oct. 14, 1918, the Illinois Influenza Advisory Commission invited representatives from professional organizations, the Red Cross, clubs…

On Oct. 12, 1918, Chicago’s Influenza Health Commissioner Dr. John Dill Robertson requested from the Chief of Police…
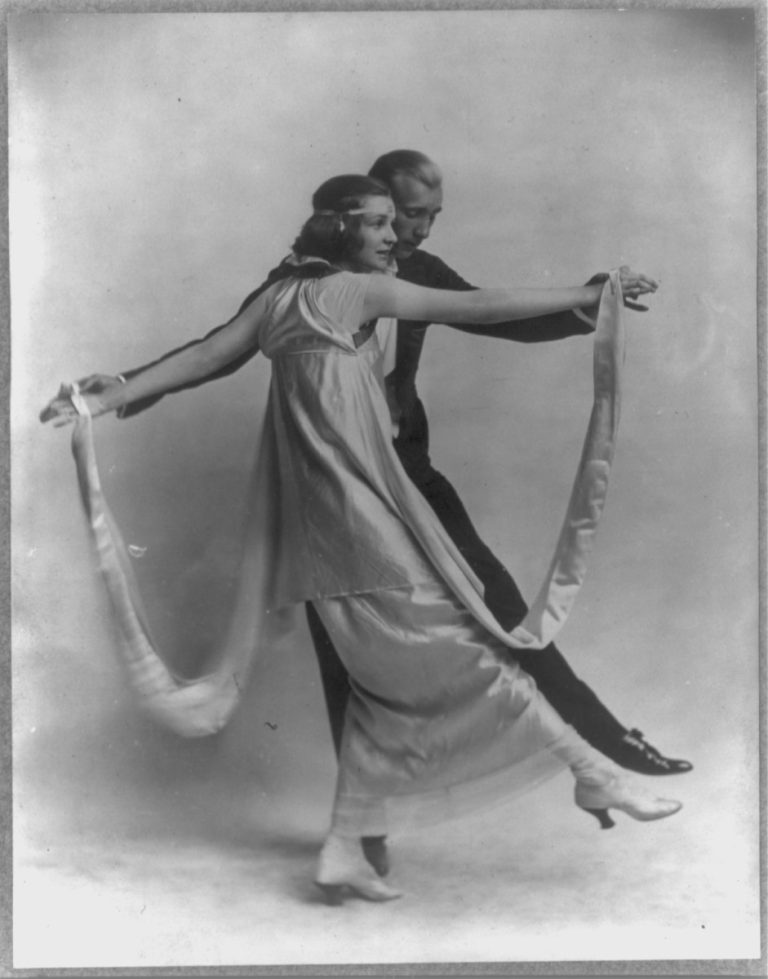

On Oct. 11, 1918, the Illinois Influenza Advisory Commission passed a binding resolution banning public dancing and public…

By Sept. 30, 1918, with 260 cases in Chicago, Health Commissioner Dr. John Dill Robertson ordered isolation of…
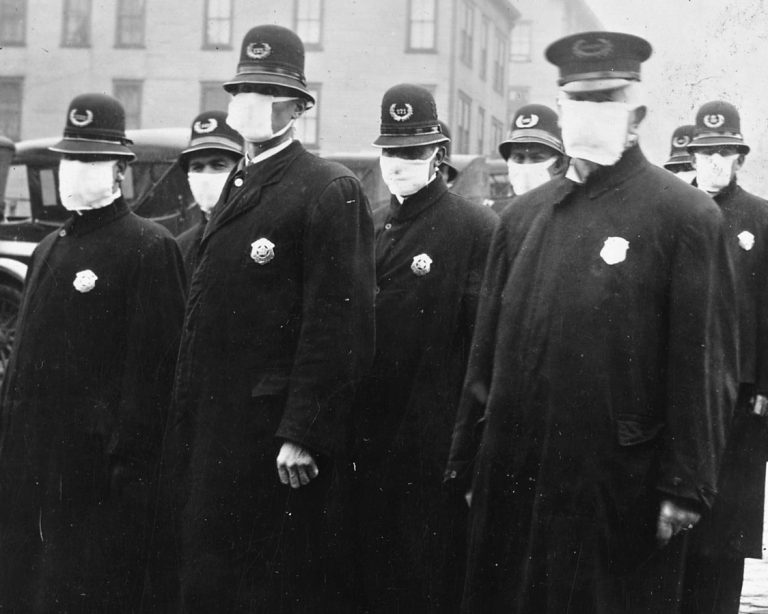

On Sep. 27, 1918, a young Denver University student named Blanche Kennedy, died of pneumonia a few days…
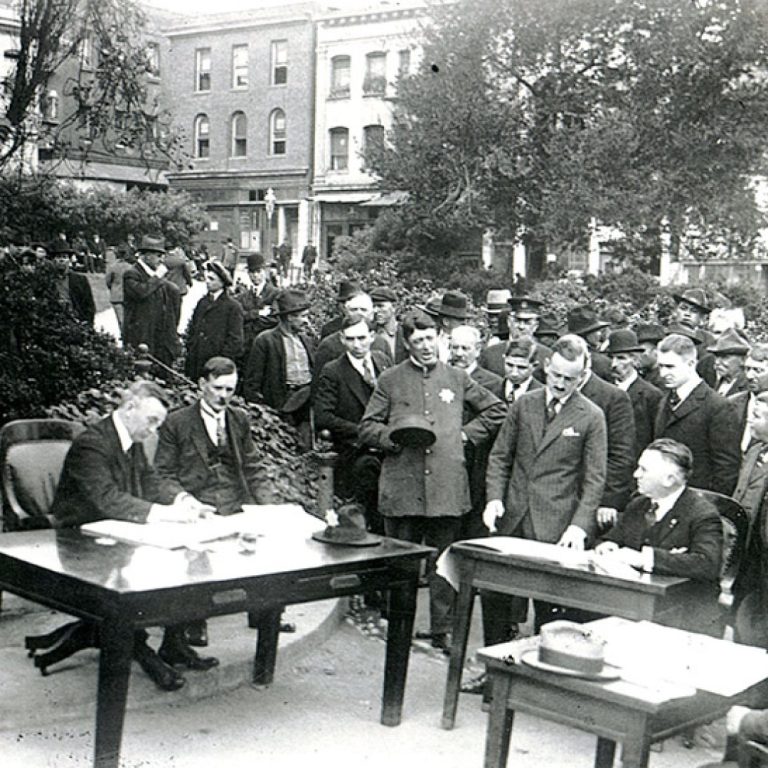

On Sept. 23, 1918, the Spanish Flu reached San Francisco when city health officer Dr. William C. Hassler…
On Sept. 21, 1918, between the start of Chicago’s epidemic and the removal of restrictions on November 16,…
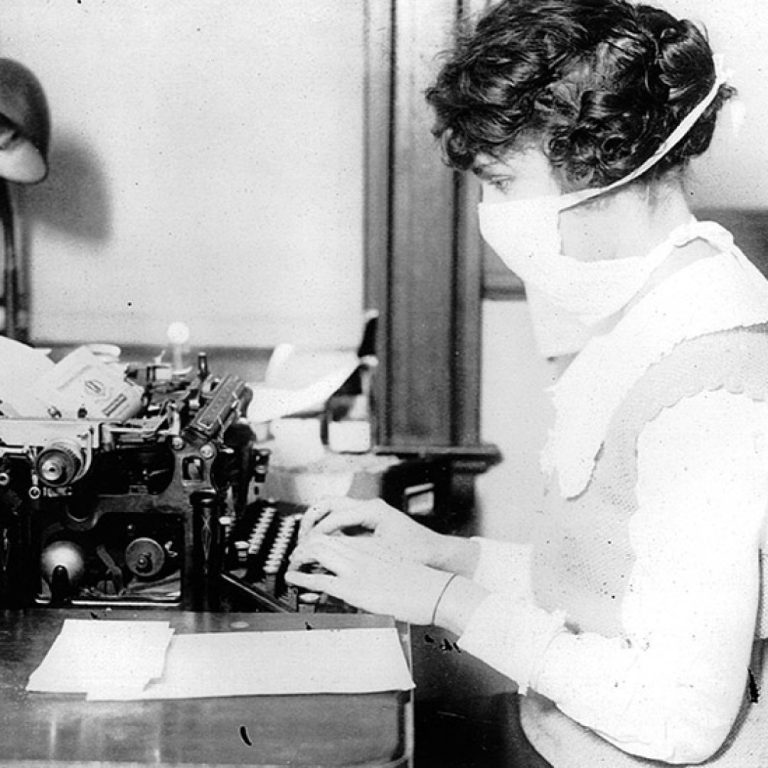

On Sept. 16, 1918, Chicago’s Health Commissioner announced that officials had “the Spanish influenza situation well in hand…