The British Columbia Cancer Institute officially opened in Vancouver
On Nov. 5, 1938, the British Columbia Cancer Institute, BC Cancerメs first cancer treatment centre officially opened in…

On Nov. 5, 1938, the British Columbia Cancer Institute, BC Cancerメs first cancer treatment centre officially opened in…

On Jul. 28, 1928, House Joint Resolution 468, 75th Congress, was passed, “To dedicate the month of April…

In 1938, the National Advisory Cancer Council, created by the National Cancer Institute Act of Aug. 5, 1937,…

In 1938, the U.S. Public Health Service, under the National Cancer Institute Act of 1937, approved the establishment…

On Aug. 5, 1937, The National Cancer Institute Act, P.L. 244, 75th Congress, was signed by President Franklin…

On Aug. 5, 1937, Senate Bill 2067 (Public Law 244) established the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and made…

On Apr. 29, 1937, Congressman Maury Maverick of Texas introduced House Resolution 6767 to promote research in the…

On Jul. 8, 1937, Congressman Maury Maverick of Texas introduced H.R. 6767, “To promote research in the cause,…

On Apr. 2, 1937, Senator Homer T. Bone of Washington introduced S. 2067, “Authorizing the Surgeon General of…

In May 1935, Kenneth Lynch and William Atmar Smith from the Medical College of South Carolina published an…

On May 29, 1929, Senator W. J. Harris, Georgia, introduced S. 4531, authorizing a survey in connection with…

On Apr. 23, 1929, Senator W. J. Harris, Georgia, introduced S. 466, “To authorize the Public Health Service…

On May 4, 1929, Clarence Cook Little founded The Roscoe B. Jackson Memorial Laboratory in Bar Harbor, Maine,…

On Mar. 7, 1928, Senator Matthew Neely (D) of West Virginia introduced S. 3554, “To authorize the National…

In 1928, George Papanicolaou discovered that vaginal cell smears (the Pap smear) revealed the presence of cervical cancer….
In 1928, the sword symbol of the Americal Cancer Society (ASCC) came from a 1928 nationwide poster contest…

On Feb. 4, 1927, a decade before the National Cancer Institute (NCI) was established, Senator Matthew Neely (D)…

In 1925, Joseph W. Schereschewsky, head of a PHS Special Cancer Investigations Laboratory established in 1922 in Cambridge,…

In 1925, Harper Hospital established an animal laboratory to research cancer, pellagra, tuberculosis, and bone tumors.

In 1922, the Public Health Service opened a Special Cancer Investigations Laboratory at Harvard Medical School.

In 1920, Dr. Albert C. Broders, a surgical pathologist at the Mayo Clinic, published a description of a…

In 1916, the first AACR publication, The Journal of Cancer Research, was launched in 1916. The journal was…

In 1915, Yamagiwa Katsusaburo, a Japanese pathologist, was the first to prove chemical carcinogenesis when he gave coal…

On May 22, 1913, The American Society for the Control of Cancer was created at a meeting of…

In 1913, the first known article on cancer’s warning signs was published in the popular women’s magazine (Ladies’…

In 1912, cancer cells were grown in the laboratory, the first long-term “tissue culture.”

On Apr. 13, 1911, U.S. v. Johnson, the Supreme Court ruled against the government, finding that the product’s…
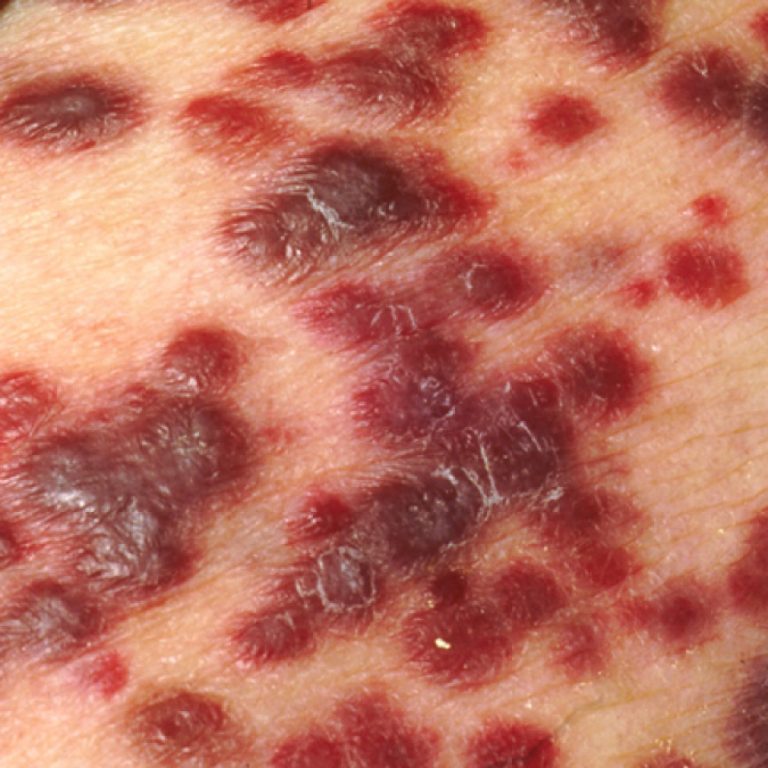
In 1911, Pathologist Peyton Rous reported a virus that causes cancer in chickens (Rous sarcoma virus) that opened…

On Aug. 31, 1909, George W. McCoy published a preliminary report in “The Journal of Medical Research” that…

On Nov. 15, 1907, the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) held its first annual meeting at the…