Delaney Committee started congressional investigation of the safety of chemicals in foods and cosmetics
In 1950, the Delaney Committee started congressional investigation of the safety of chemicals in foods and cosmetics, laying…

In 1950, the Delaney Committee started congressional investigation of the safety of chemicals in foods and cosmetics, laying…

In 1950, Sidney Farber and colleagues achieved the first remissions in Wilms tumor of the kidney, a common…
In 1950, the Michigan Cancer Foundation and the American Cancer Society began sponsoring new cancer research and outreach…

In 1949, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved nitrogen mustard to kill cancer cells. The major use…

In 1949, Canadaメs first full-time cancer physicist, Dr. Harold Johns, led the world in development the cobalt bomb…

In 1947, The first attempt at coordinating cancer at University of California at San Francisco (UCSF) was a…

In 1948, the Detroit Cancer Center was established from the union of the Detroit Institute for Cancer Research…

In 1948, the National Cancer Institute’s grants program to medical, dental, and osteopathic schools was initiated for improvement…

On Jul. 1, 1947, The National Cancer Institute was reorganized to provide an expanded program of intramural cancer…

In 1947, the Southeastern Michigan Division of the American Cancer Society created the Michigan Cancer Foundation to comply…
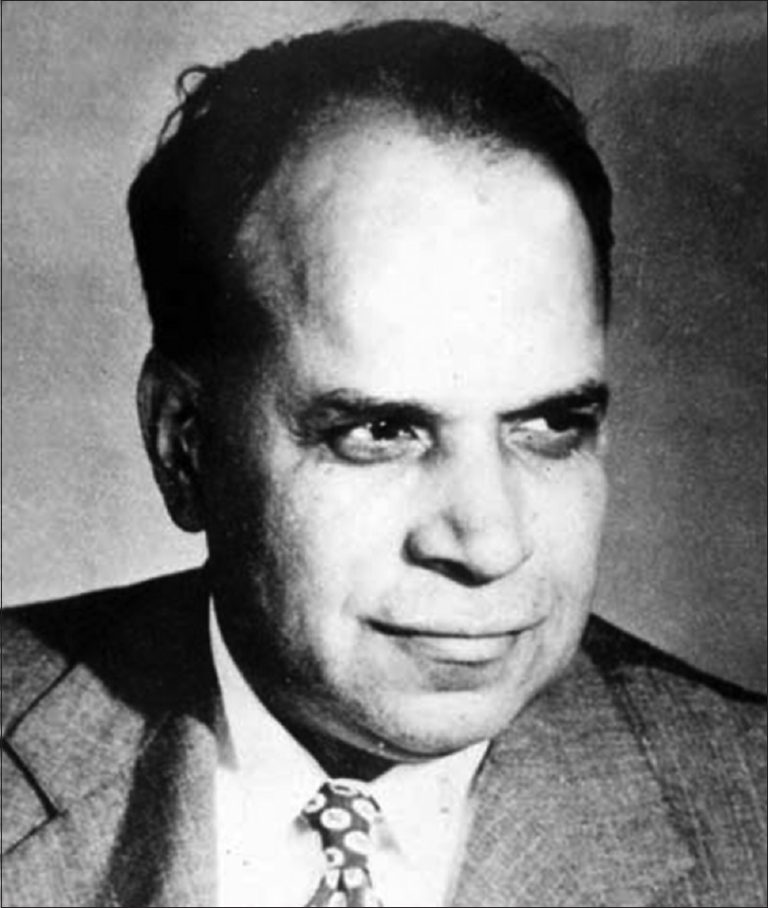

In 1947, biochemist Yellapragada SubbaRow co-discovered the first cancer chemotherapy agent for children suffering from acute leukemia. While…

In 1947, the Laboratory of Experimental Oncology (LEO) was founded as a collaborative effort between the city of…

In 1947, Sidney Farber, MD, founded a Children’s Cancer Research Foundation dedicated to providing children with cancer with…

On Jul. 1, 1946, the National Cancer Institute cancer control program was established with appropriations to the states…

In 1946, Lloyd Law of NCI introduced the L1210 murine leukemia cell line tumor used in the cancer…

On Aug. 8, 1945, the Sloan-Kettering Institute for Cancer Research (SKI) was established. A gift of $4 million…

In 1945, the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Jonsson Cancer Center Foundation was founded by a group…

In 1944, Canadian Premier Tommy Douglas, seeing the high cancer death rate in Saskatchewan, implemented free cancer treatment…
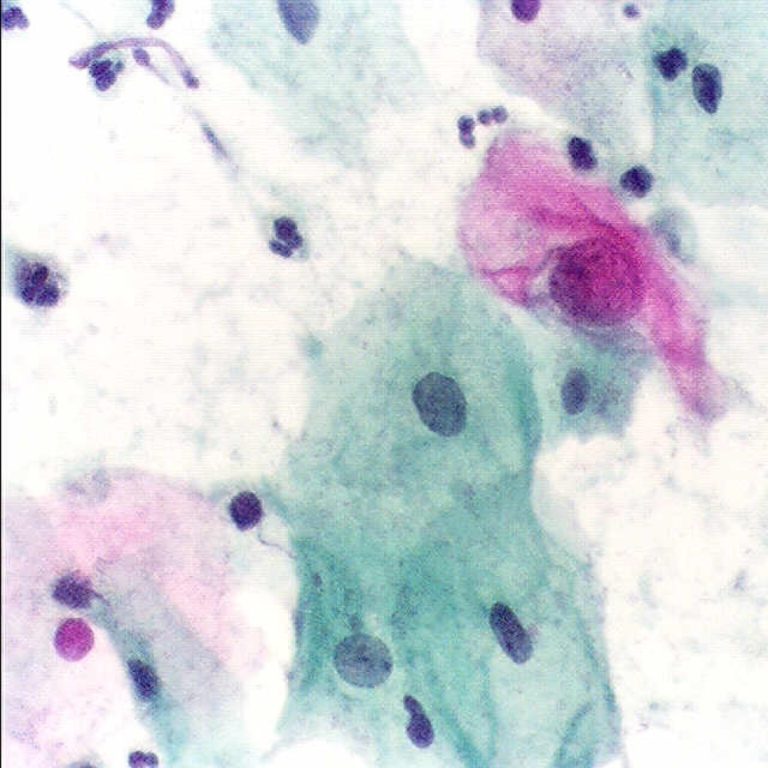
In 1943, George Nicholas Papanicolaou and Herbert Traut published their landmark book “Diagnosis of Uterine Cancer by the…

In 1943, Wilton R. Earle of NCI, who had in the 1930’s pioneered the process of growing cells…

In 1943, The Detroit Institute for Cancer Research was incorporated with just $483 and 200 shares of General…
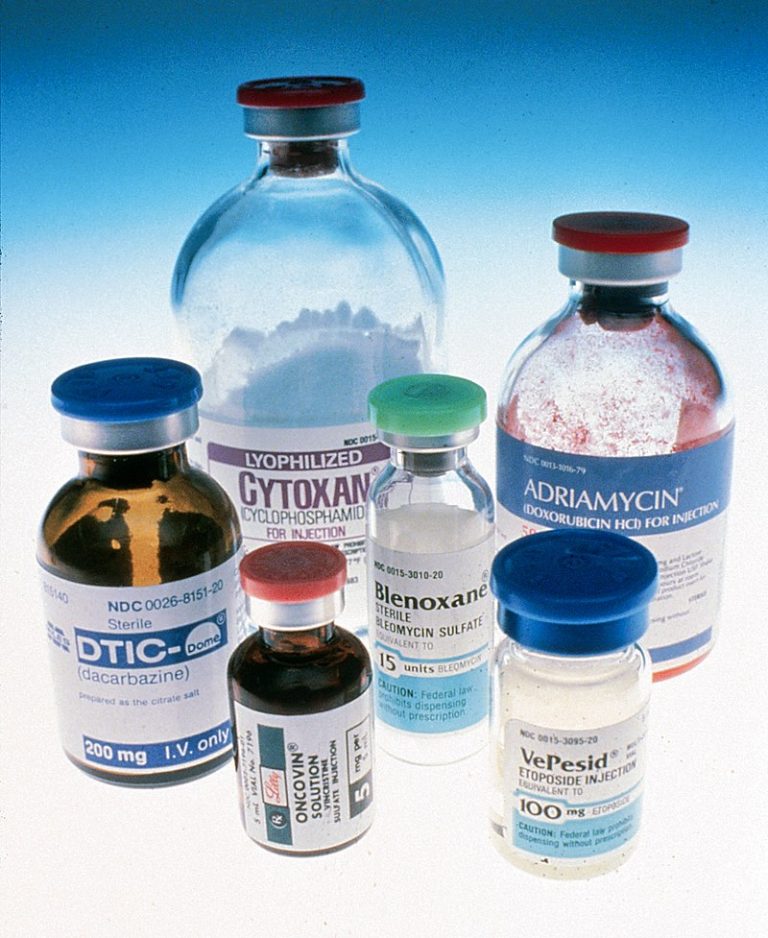
On Aug. 27, 1942, chemotherapy was first used to treat a cancer patient and the beginning of its…
In 1942, the first intravenous chemotherapy treatment of a cancer patient was performed at Yale.

In 1942, Yale cancer research began when the first use of a cancer drug was administered to a…

In 1942, The Hormel Institute was founded by Jay C. Hormel in Austin to research and find a…
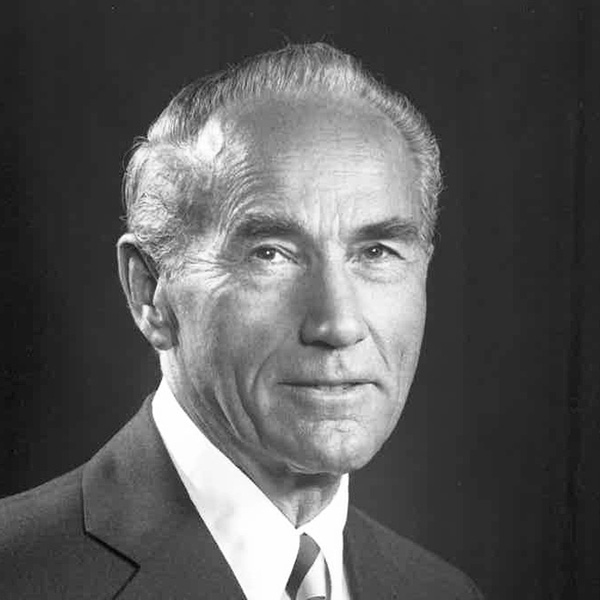

In 1942, Dr. William Hutchinson began a 47 year career in Seattle, Washington when he joined the Swedish…

On Aug. 1, 1941, Harold L. Stewart and Egon Lorenz published an article in the Journal of the…

In 1941, Charles Huggins discovers that blocking male hormones (by removal of the testicles or administration of estrogens)…

On Aug. 1, 1940, the first issue of the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (JNCI) was published….
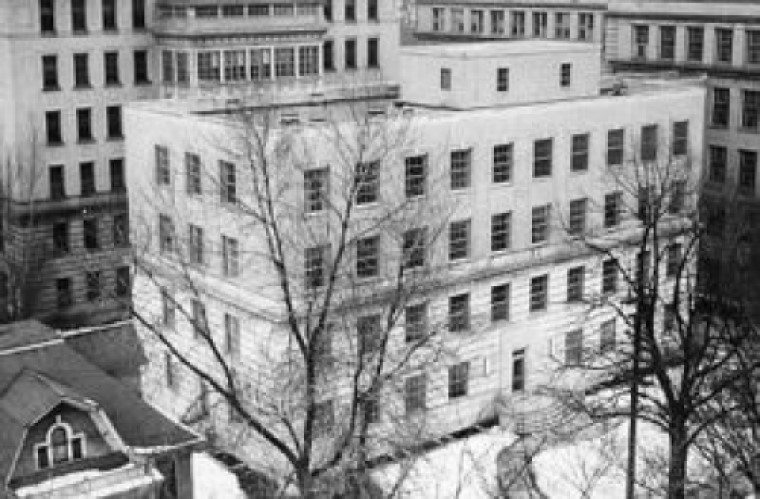

In 1940, the McArdle Memorial Laboratory was founded in Madison. McArdle Lab was one of the first basic…