FDA approved Hybritech antibody test for prostate cancer – a first
In February 1986, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Hybritech’s Tandem-R PSA assay (P850048) with calibration…

In February 1986, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Hybritech’s Tandem-R PSA assay (P850048) with calibration…

In 1986, the Moffitt Cancer Center was established by the Florida Legislature to meet a clear and compelling…

In 1986, philanthropist Harcourt Sylvester Jr. pledged $27.5 million to benefit cancer programs at the medical school, and…

In 1986, the Office on Smoking and Health became part of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and…

In 1986, the University of Michigan Cancer Center received National Cancer Institute (NCI) designation. The Rogel Cancer Center…

In 1986, The University of Utah Cancer program earned National Cancer Institute (NCI) designation as a Cancer Center,…

In 1986, Procyte Corp. was founded as a Kirkland, Washington-based medical skin care company that developed and marketed…

In 1985, the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute (UPCI) was founded in Pittsburgh. UPCI has 320 faculty members…

In 1985, the Comprehensive Cancer Center of Metropolitan Detroit was named in honor of Meyer L. Prentis, a…

In 1985, Dr. Anthony Pawson discovered the SH2 protein domain involved in controlling cell behavior, leading to targeted…
On May 23, 1984, U.S. Surgeon General reported that there was “very solid” evidence linking cigarette smoke to…

On May 2, 1984, the new UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Centerメs original three-story cancer research building opened. In…

On Mar. 6, 1984, Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Margaret M. Heckler launched a new cancer prevention…

In 1984, The Comprehensive Minority Biomedical Program, DEA, was established to widen the focus of the minority effort…

In 1984, a policy statement regarding the relationship of National Cancer Institute (NCI), the pharmaceutical industry, and NCI-supported…
In 1984, genetic scientists led by Philip Leder created the first genetically engineered mouse model of cancer, nicknamed…
In 1984, fluoroestradiol (FES) was first developed by researchers Michael J. Welch, PhD from Washington University at St….

In 1984, St. ᅠJude Children’s Hospital launched the After Completion of Therapy Clinic, the world’s largest long-term follow-up…

In 1984, the University of Virginia Cancer Center, now Virginia Health, was founded in Charlottesville. The UVA Cancer…

In 1984, American Cancer Society (ACS) introduced dietary guidelines to reduce cancer. The ACS published Nutrition and Physical…

On Jul. 16, 1983, the National Cancer Institute launched the Community Clinical Oncology Program (CCOP) to provide a…

On Feb. 3, 1983, the University of Southern California Kenneth Norris Jr. Cancer Hospital and Research Institute (USC…

In 1983, the National Cancer Institute formed the Division of Cancer Prevention and Control to accelerate the science…
In 1983, the Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) was uncovered by the use of restriction endonucleases which cleave…

In 1983, the National Cancer Institute’s Division of Resources, Centers and Community Activities was renamed the Division of…

In 1983, the Community Clinical Oncology Program, an National Cancer Institute (NCI) resource that links community-based physicians with…

In 1983, Bristol-Myers marketed VEPESID (etoposide) for cancer.
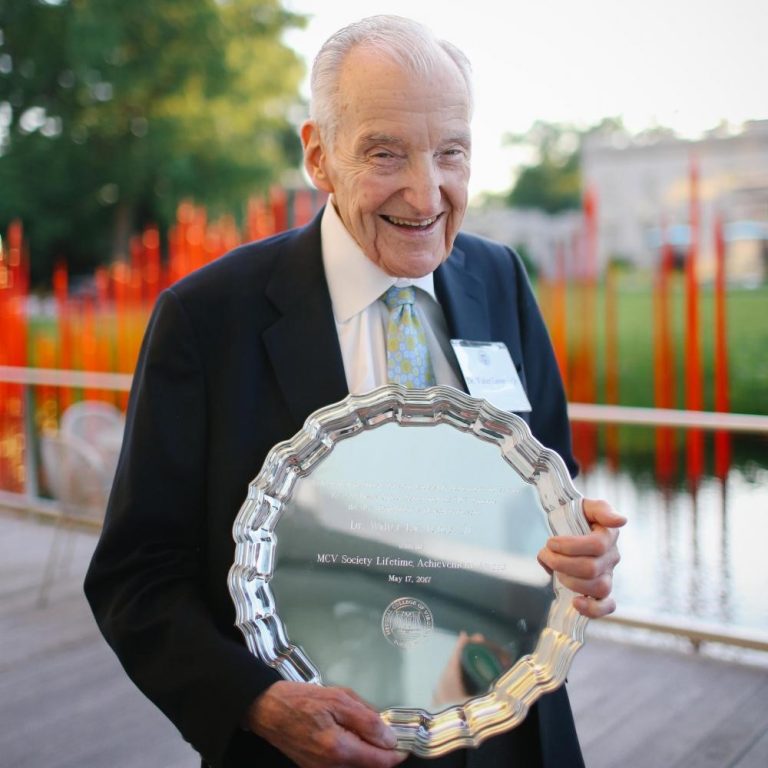

In 1983, the Massey Cancer Center opened under the direction of Dr. Walter Lawrence Jr., a surgeon and…
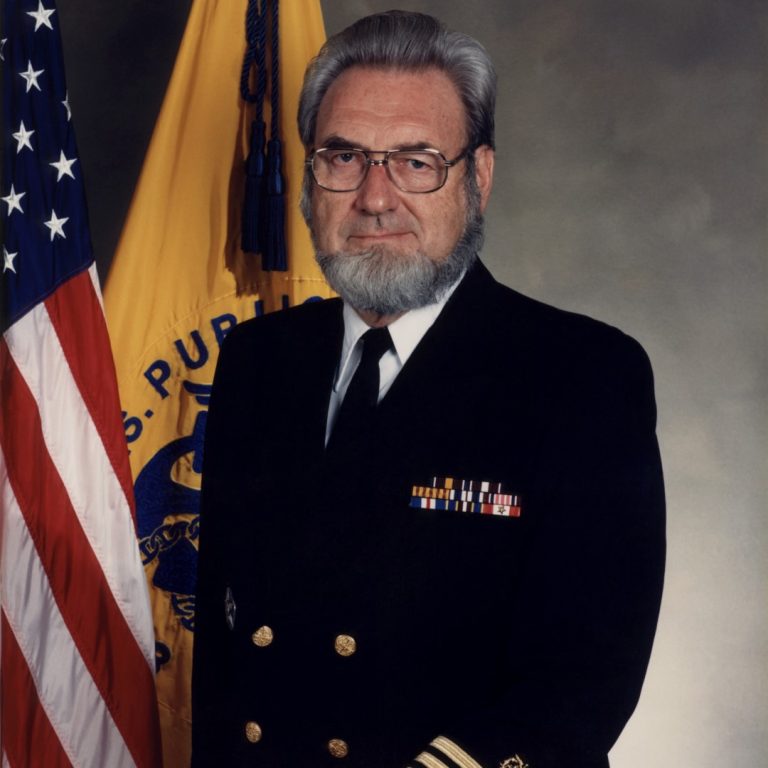

On Jan. 21, 1982, C. Everett Koop was appointed U.S. Surgeon General by President Ronald Reagan. In 1984,…

In 1982, the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Physician Data Query (PDQ) cancer information database went online. PDQ is…