The Priestley Medal was awarded to Carl Djerassi
In 1992, the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to Carl Djerassi ‘for his numerous contributions to…
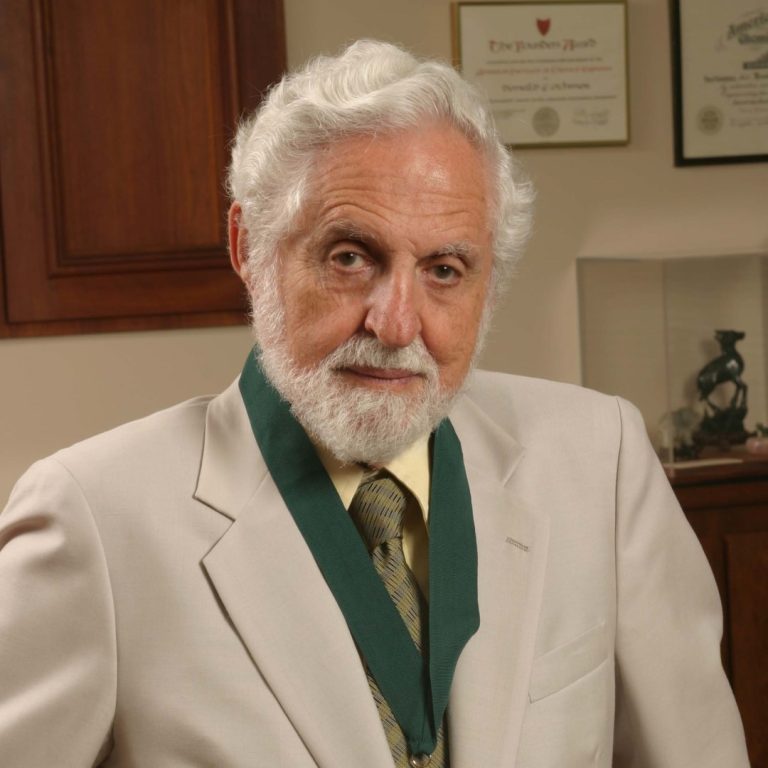

In 1992, the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to Carl Djerassi ‘for his numerous contributions to…
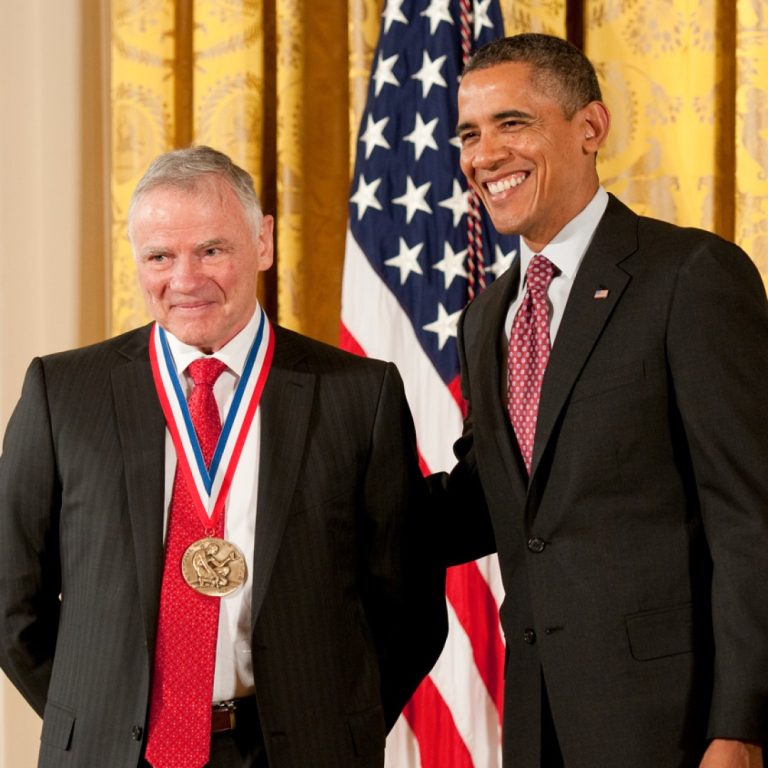

On Oct. 7, 1991, the University of Washington (UW) announced a $12 million gift from Microsoft co-founder Bill…
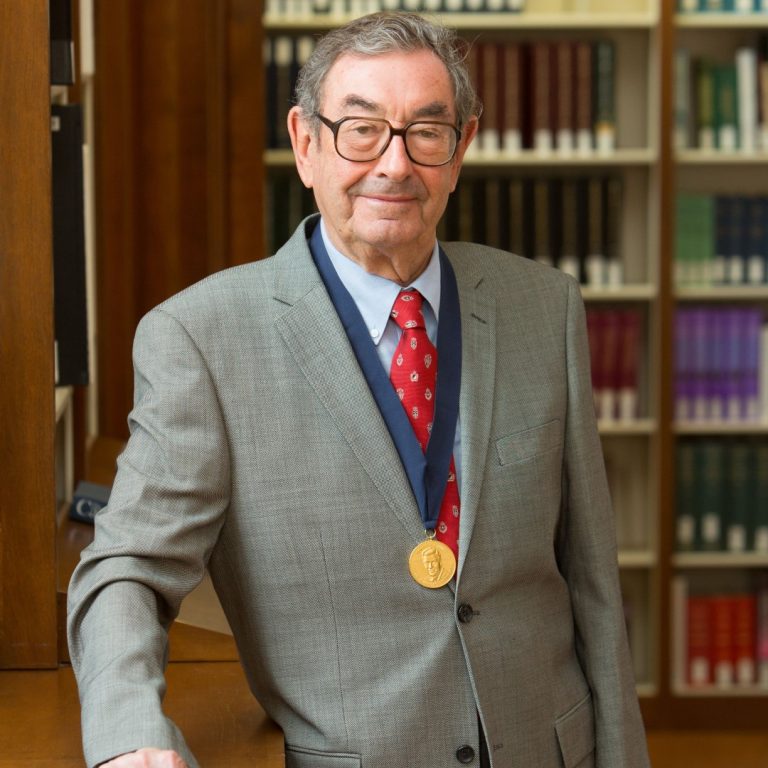

In 1991, the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to Harry B. Gray ‘for his numerous contributions…
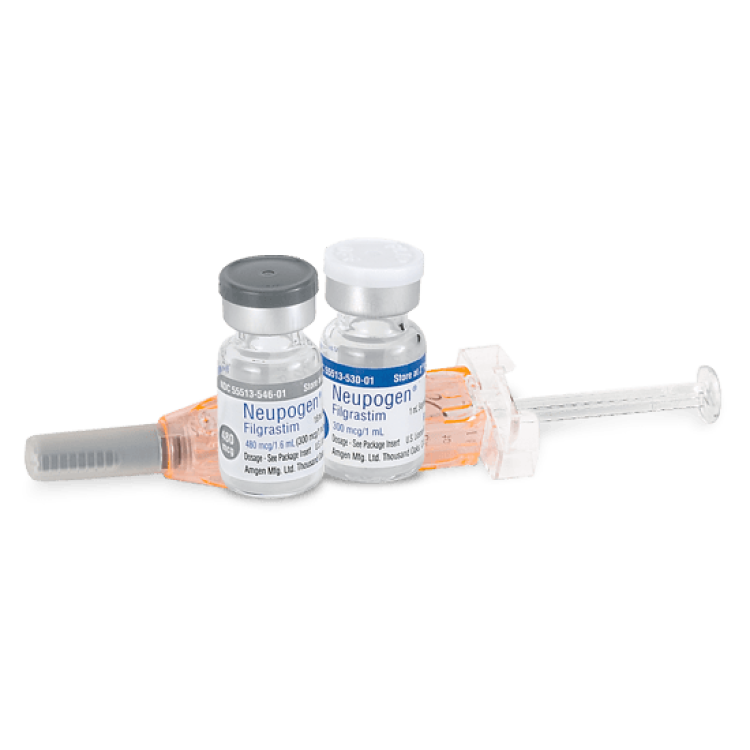
On Feb. 22, 1991, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that it had approved Amgen’s two white…
On Jan. 4, 1991, Scripps Clinic and Research Foundation and Scripps Memorial Hospital reaffiliate, announced they had merged…
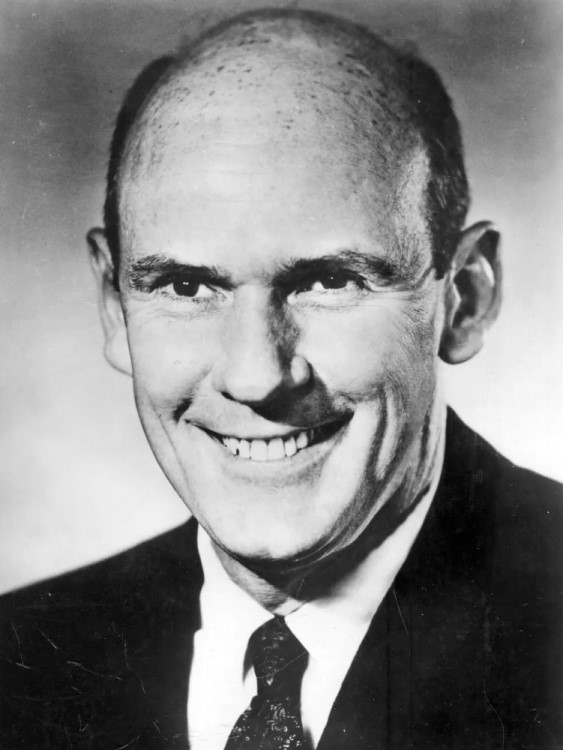

In 1991, U.S. Senator Alan Cranston (D-Calif.) underwent a state-of-the-art procedure at Stanford University Hospital to attack his…
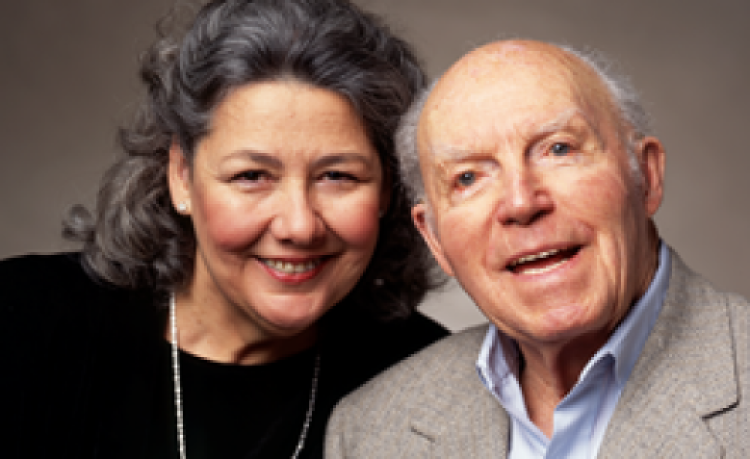

In 1991, the UC San Diego Shiley Eye Center opened with support by Donald and Darlene Shiley and…

In 1991, The UC Davis Cancer Center was founded. The center is a matrix organization and part of…
In 1991, Livermore Forensic Science Center was established to provide a comprehensive approach to forensic analyses of samples….
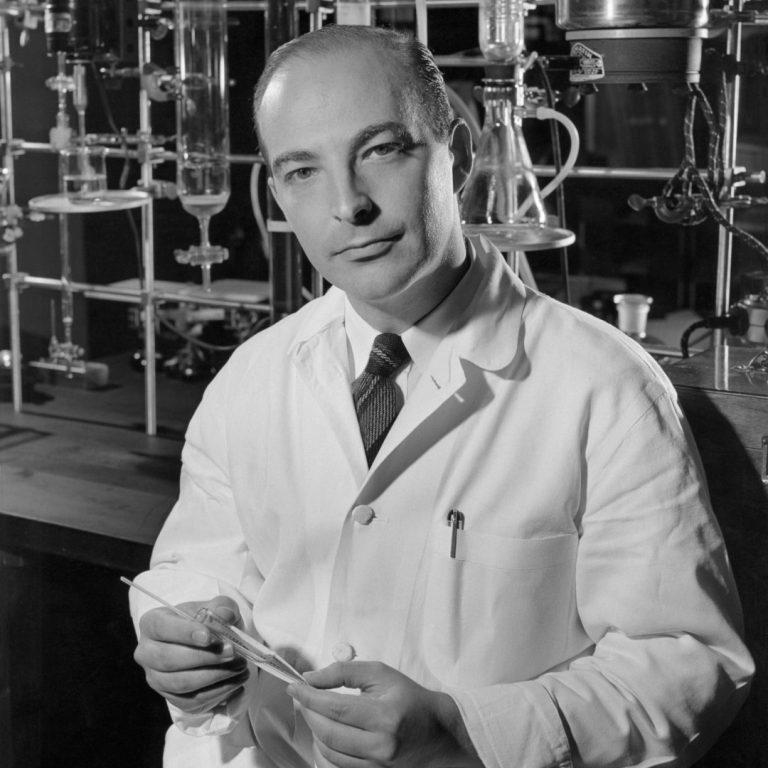

On Oct. 22, 1990, scientists from Stanford University led by Arthur Kornberg announced they had discovered a chemical…

On Apr. 22, 1990, the second Earth Day was celebrated by more than 225 million people. The first…

In 1990, BayBio, a non-profit 501(c)(3) organization headquartered in San Francisco, was founded by a consortium of universities,…

In 1990, the California Supreme Court rules in the case involving Seattle’s John Moore that a patient does…

On Dec. 29, 1989, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Oculinum’s (onabotulinumtoxinA) for treatment of strabismus…

On Jun. 1, 1989, the FDA approved Amgen’s Epogen/Procrit for the treatment of anemia associated with chronic renal…

In 1989, the Priestley Medal was awarded to George C. Pimentel by the American Chemical Society “to recognize…

In 1989, the University of California, Irvine (UCI) Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center (CFCCC) was founded as a…

In 1989, Scripps Research Institute’s graduate program was launched, building on the institute’s strengths in the integration of…

In 1989, Stanford Medicine researchers discovered the ‘homing receptor,’ which guides white blood cells into the peripheral lymph…

In 1988, Stanford Medicine researchers Irving Weissman and Mike McCune created an animal model that can be used…

On Jun. 30, 1988, The California Genetic Resources Conservation Program was closed by the Division. In 1985, California…
In 1988, pathologist Irving Weissman from Stanford Medicine isolated a rare mouse cell, known as the hematopoetic stem…

On Jun. 8, 1987, Advanced Genetic Sciences announced that its Frostban (Ice-minus) bacteria successfully protected strawberries from below-freezing…
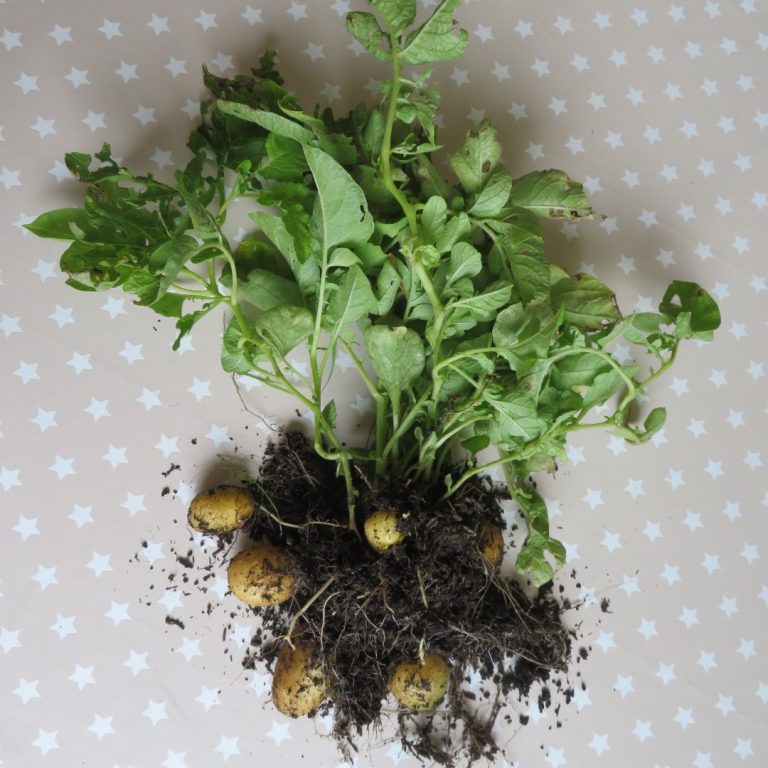

On May 26, 1987, vandals uprooted approximately 3,000 potato plants being studied with ice-minus bacterium on a half-acre…
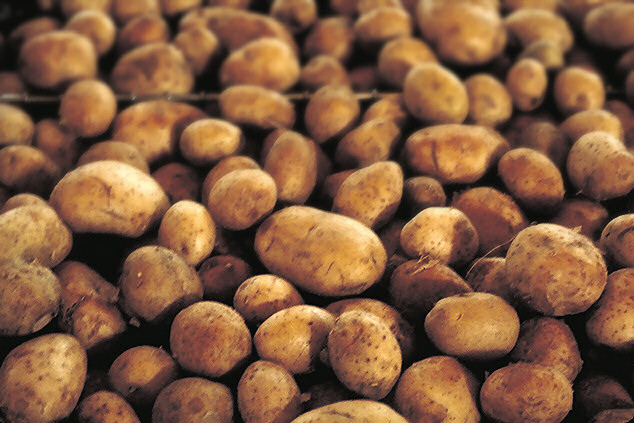

On Apr. 29, 1987, University of California, Berkeley plant pathologist Steven Lindow field-tested genetically altered Pseudomonas syringae (known…

On Apr. 24, 1987, Advanced Genetic Sciences (AGS) sprayed Frostban on an acre of strawberry plants in Brentwood,…
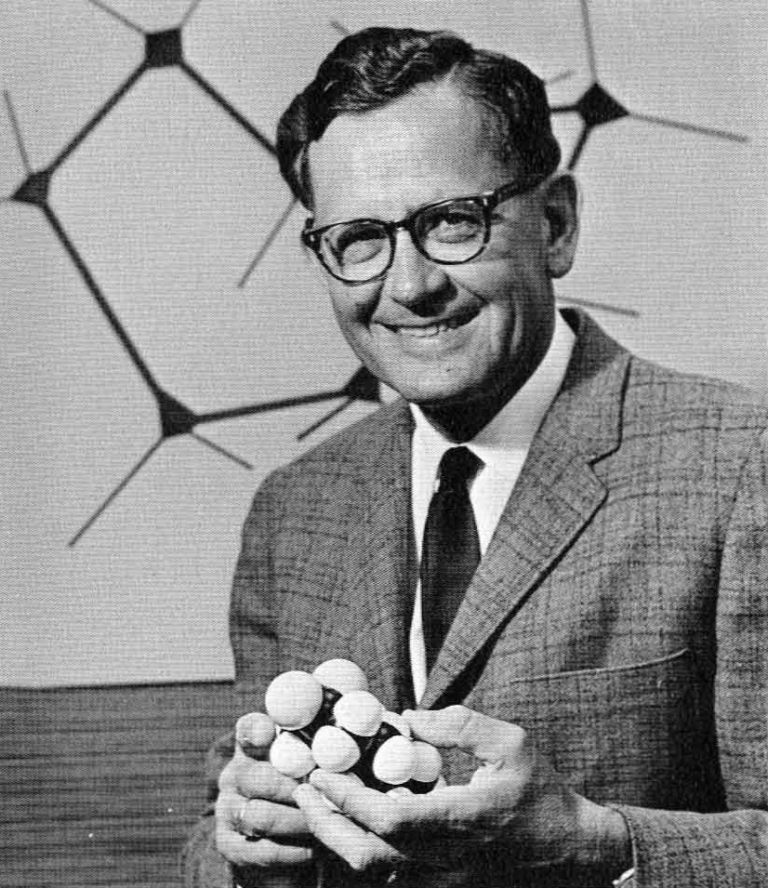

In 1987, the the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to John D. Roberts ‘for his numerous…
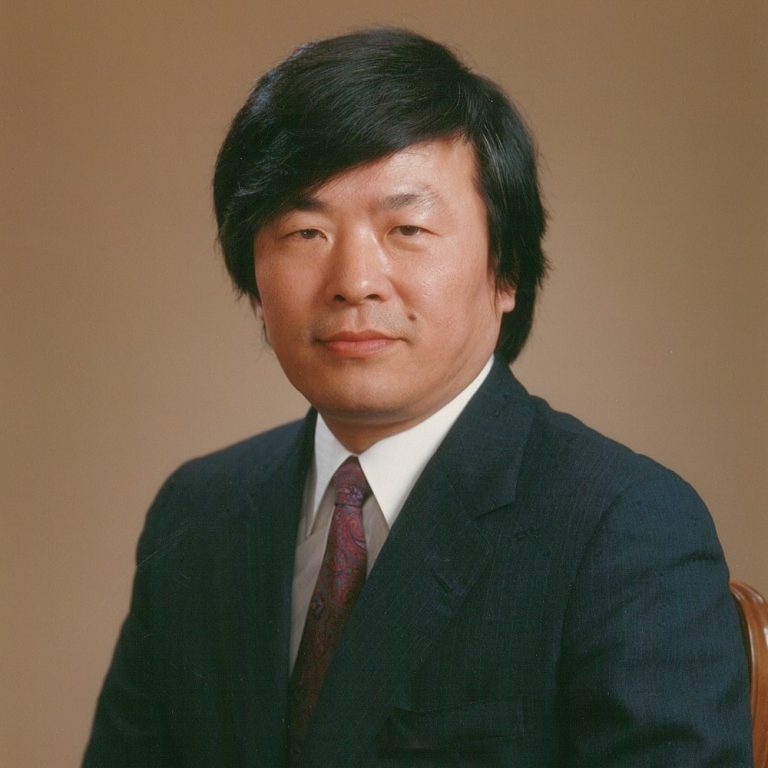

In 1987, University of California, San Diego Alumnus Susumu Tonegawa was awarded he Nobel Prize for Physiology or…

In 1987, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Genentech’s drug tPA Activase (alteplase). Activase is a…
In 1987, Richard Lerner, chair of the Scripps Department of Molecular Biology, was appointed the research institute’s new…