The Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center received a $5 million gift from local philanthropist Henrietta Lee
In 1998, The Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center received a $5 million gift from local philanthropist Henrietta Lee which…

In 1998, The Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center received a $5 million gift from local philanthropist Henrietta Lee which…
On Nov. 26, 1997, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had approved the Monoclonal antibody…
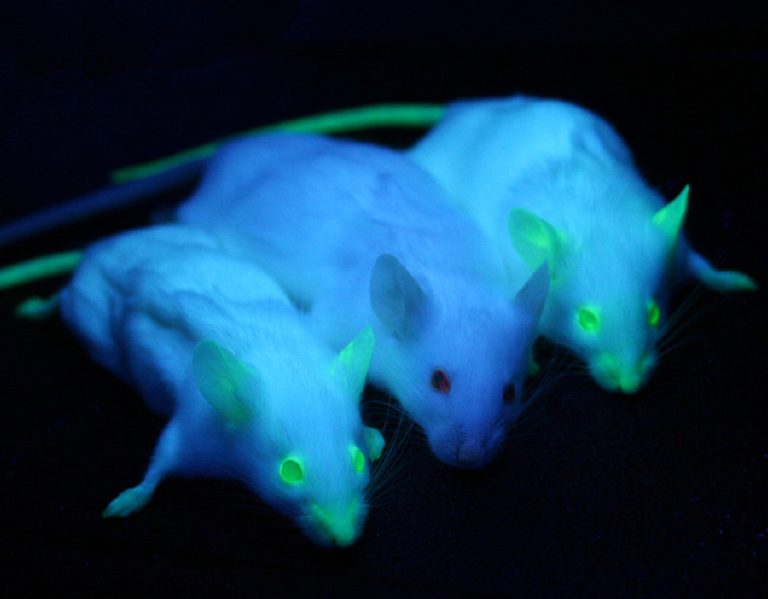

On Oct. 9, 1997, Stanford researchers announced that in a series of experiments performed in mice and rats,…

In 1997, the the University of California, Irvine (UCI) Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center (CFCCC) gained NCI designated…

In 1998, Alfred Mann gave $112.5 million to establish the University of Southern California Alfred E. Mann Institute…

In 1997, Paul D. Boyer of the University of California at Los Angeles was awarded the Nobel Prize…
In 1997, the National Fibromyalgia Association (NFA), the largest nonprofit [501(c)3] organization working to support people with fibromyalgia…
On Jan. 2, 1996, Stanford Medicine researchers announced they had discovered that the p53 protein, known to be…

In 1996, Livermore National Lab delivered to the U.S. Army for testing the first fully portable, battery-powered, real-time…
In 1996, Stanford Medicine developmental biologist Matthew Scott and a team at University of California, San Francisco discovered…

On Dec. 11, 1996, scientists from Stanford University and Affymetrix announced a new high-tech method that used a…
In 1996, the Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology was established at The Scripps Research Institute, thanks to a…

In 1996, the National Cervical Cancer Coalition (NCCC), a growing coalition of people battling cervical cancer and HPV…

On Dec. 29, 1995, the Genentech drug Nutropin AQ ((somatropin) injection for subcutaneous use) was approved by the…

On May 3, 1995, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had approved Genentech’s drug CellCept…

In 1995, Southern California Biomedical Council (SCBC), was founded with support from Rebuild LA (RLA) under its second…

In 1995, the first department of bioengineering in the U.S. was established at the University of California, San…

On Oct. 26, 1994, the University of California, Irvine (UCI) Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center (CFCCC) gained designated…

On May 17, 1994, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved of the first genetically modified food:…
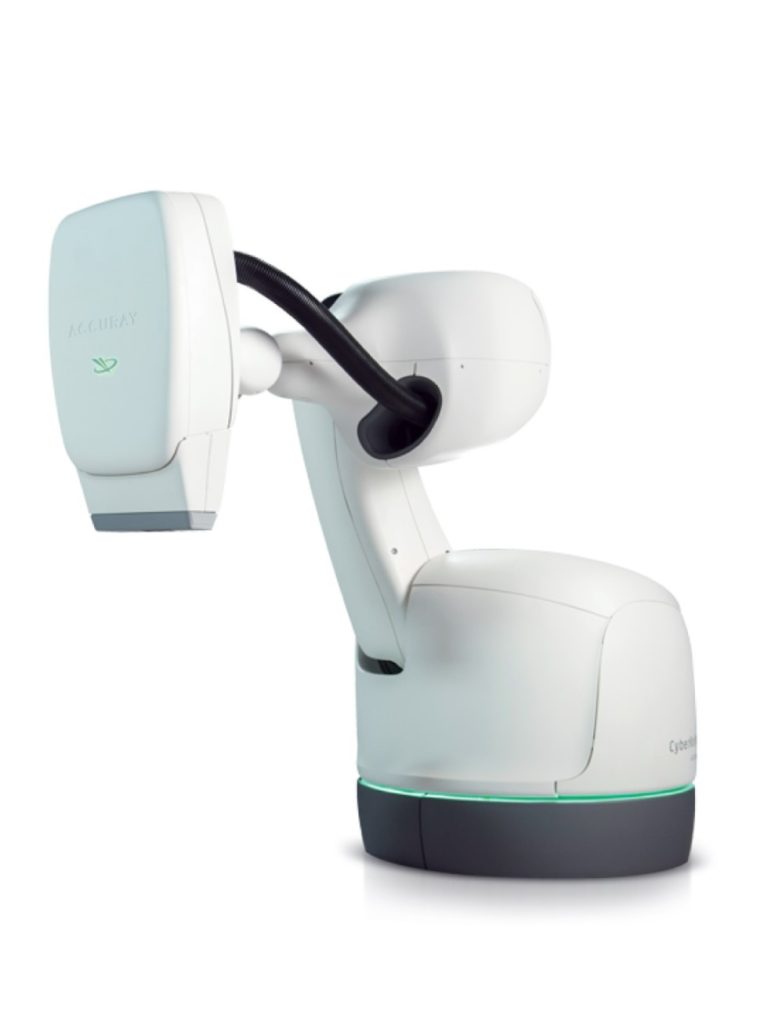
In 1994, CyberKnife developed by John Adler, MD and colleagues at Stanford University. CyberKnife’s special quality is that…

In 1994, Amgen announced it had acquired Boulder-based Synergen for a $239.6-million or $9.25 per share. Synergen was…

On Dec. 30, 1993, the Genentech drug Pulmozyme (dornase alfa) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug…

On Nov. 12 ,1993, FDA granted approval for the sale of the Ahmed Glaucoma Valve designed and manufactured…

In May 1993, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) responded to a Hantavirus outbreak in…
On Apr. 1, 1993, the FDA approved Amgen’s Epogen/Procrit for the treatment of anemia due to the effects…

In 1993, Kary B. Mullis of La Jolla, CA and a graduate of the University of California at…
In 1993, University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) researchers Cynthia Kenyon and colleagues’ announced they had discovered that…
In 1993, Stanford Medicine researchers led by William Haskell demonstrated that lifestyle changes and drug therapy decrease heart…

On Oct. 12, 1992, Edmond Fisher and Edwin Krebs of University of Washington’s (UW) School of Medicine received…
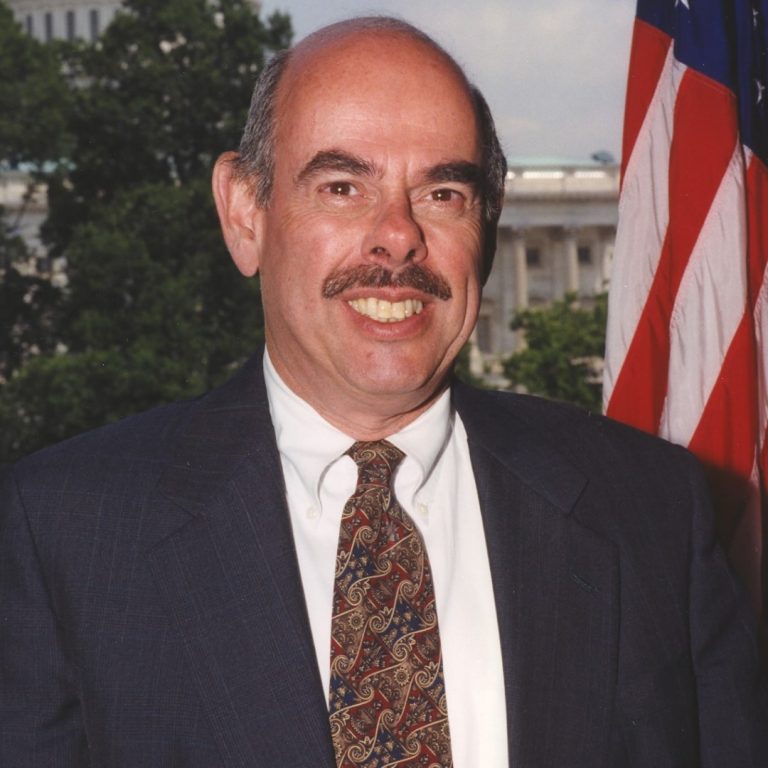

In Apr. 13, 1982, Representative Henry Waxman, U.S. Congressman from Los Angeles, held the first congressional hearing on…