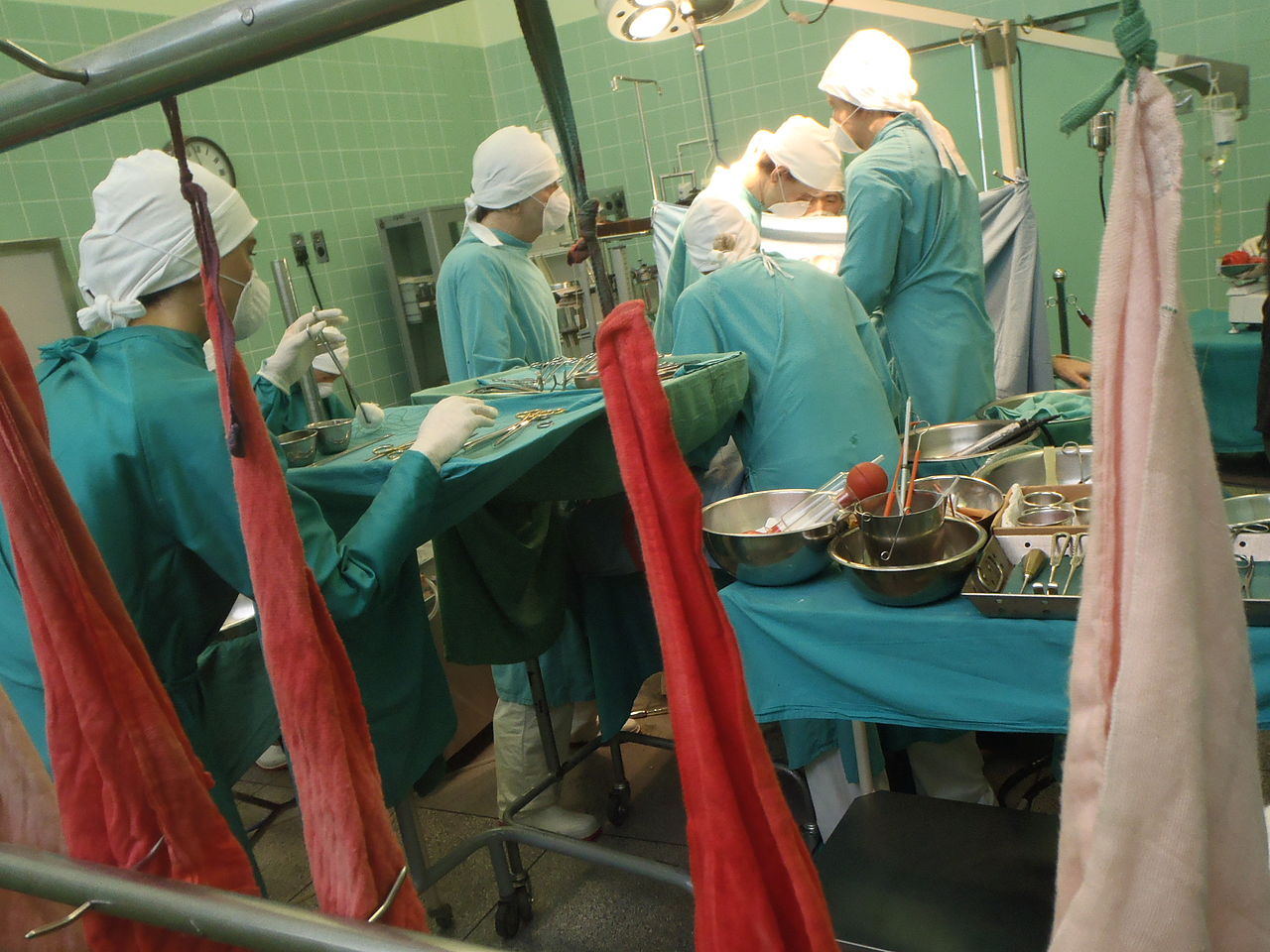
Surgeon Christiaan Barnard performed first human to human heart transplant
On Dec. 3, 1967, surgeon Christiaan Barnard performed the first human to human heart transplant in Cape Town, South Africa. The transplant patient 55-year-old Louis Washkansky, who had diabetes and incurable heart disease, survived eighteen days.
Although the first heart transplant patient survived only 18 days, four of Groote Schuur Hospital’s first 10 patients survived for more than one year, two living for 13 and 23 years, respectively. This relative success amid many failures worldwide did much to generate guarded optimism that heart transplantation would eventually become a viable therapeutic option.
This first heart transplant and subsequent ongoing research in cardiac transplantation at the University of Cape Town and in a few other dedicated centres over the subsequent 15 years laid the foundation for heart transplantation to become a well-established form of therapy for end-stage cardiac disease. During this period from 1968 to 1983, Chris Barnard and his team continued to make major contributions to organ transplantation, notably the development of the heterotopic (‘piggy-back’) heart transplants; advancing the concept of brain death, organ donation and other related ethical issues; better preservation and protection of the donor heart (including hypothermic perfusion storage of the heart; studies on the haemodynamic and metabolic effects of brain death; and even early attempts at xenotransplantation.
Tags:
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
Credit:
