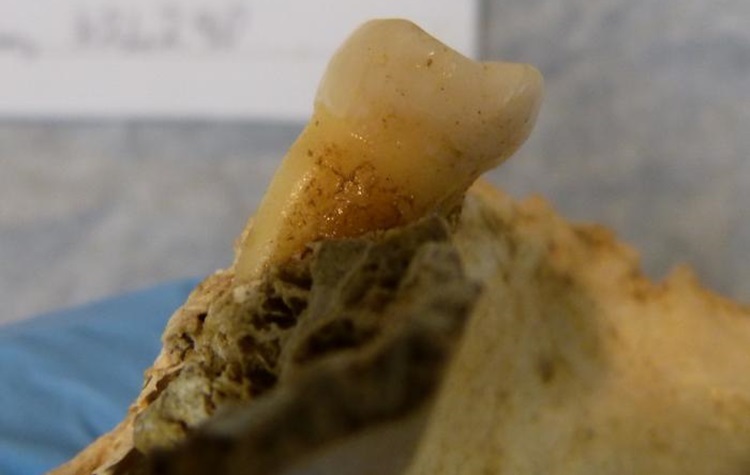
Genetic secrets from 4,000-year-old teeth illuminate the impact of changing human diets over the centuries
On Mar. 27, 2024, researchers from Trinity College Dublin announced they had recovered remarkably preserved microbiomes from two teeth dating back 4,000 years, found in an Irish limestone cave. Genetic analyses of these microbiomes reveal major changes in the oral microenvironment from the Bronze Age to today. The teeth both belonged to the same male individual and also provided a snapshot of his oral health.
The study, carried out in collaboration with archaeologists from the Atlantic Technological University and University of Edinburgh, was published in leading journal Molecular Biology and Evolution. The authors identified several bacteria linked to gum disease and provided the first high-quality ancient genome of Streptococcus mutans, the major culprit behind tooth decay. While S. mutans is very common in modern mouths, it is exceptionally rare in the ancient genomic record.
Tags:
Source: Trinity College Dublin
Credit: Photo: Example tooth prior to DNA extraction. Courtesy: Dr. Lara Cassidy, Trinity College.
