WHO recommended follow-up care, low-dose anticoagulants for COVID-19 patients
On Jan. 26, 2021, WHO recommends that patients who have COVID-19 – both confirmed and suspected – should…
On Jan. 26, 2021, WHO recommends that patients who have COVID-19 – both confirmed and suspected – should…

On Jan. 22, 2021, COVAX, the global initiative to ensure rapid and equitable access to COVID-19 vaccines for…

On Jan. 22, 2021, Pfizer and BioNTech announced an advance purchase agreement with COVAX for up to 40…

On Jan. 12, 2021, the four leading international health and humanitarian organizations announced the establishment of a global…

On Jan. 12, 2021, the WHO announced that global scientists were intensifying research into COVID-19 to expand its…
On Dec. 31, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) listed the Comirnaty COVID-19 mRNA vaccine for emergency use,…
On Dec. 21, 2020, the WHO reported that authorities of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern…

On Dec. 18, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced that it had arrangements in place to access…

On Nov. 30, 2020, Mateon Therapeutics announced that the India arm of ARTI-19 global study was on track…
On Nov. 18, 2020, marked the end of the 11th Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the…
On Oct. 22, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Wikimedia Foundation announced a collaboration to expand…
On Oct. 21, 2020, results from an international, randomized, controlled clinical trial indicated that a four-month daily treatment…

On Oct. 15, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced Interim that results from the Solidarity Therapeutics Trial,…
On Oct. 14, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced that prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries…
On Oct. 14, 2020, recognizing the urgent need for new tools to combat vector-borne diseases (VBDs), and in…
On Oct. 8, 2020, UNICEF, WHO, the World Bank Group and the Population Division of the United Nations…

On Oct. 2, 2020, the WHO and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia signed a contribution agreement in the…
On Sept. 28, 2020, the World Health Organization announced agreements to make available, for low and middle-income countries,…

On Sept. 23, 2020, the WHO with the UN, specialised agencies and partners called on countries to develop…

On Aug. 25, 2020, the independent Africa Regional Certification Commission (ARCC) for Polio Eradication officially declared that the…

On Aug. 23, 2020, the World Heath Organization (WHO) reported that 172 economies were engaged in discussions to…

On Aug. 13, 2020, data from the WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) revealed that 43 per cent of…
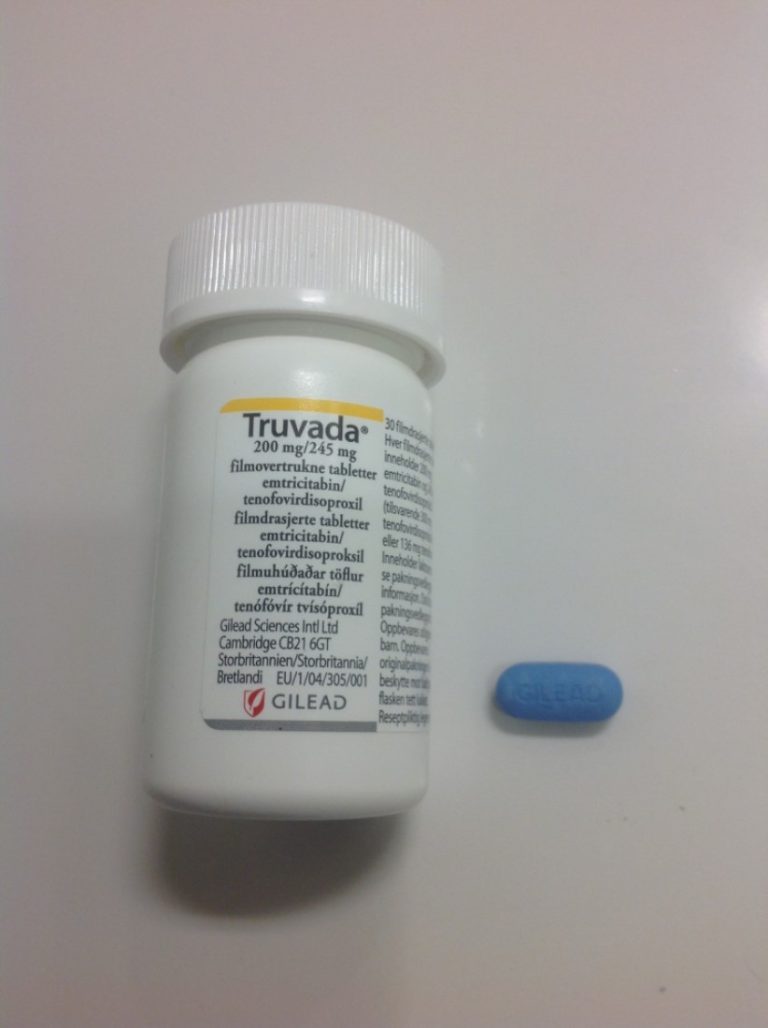
On Aug. 11, 2020, Gilead Sciences announced that the China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) had approved a…

On Jul. 22, 2020, the WHO and UNICEF announced the COVID-19 Law Lab initiative which will gather and…
On Jul. 15, 2020, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis reported they had joined…
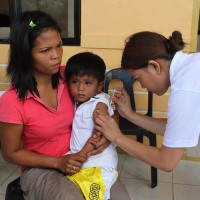
On Jul. 14, 2020, the WHO and UNICEF warned of an alarming decline in the number of children…

On Jul. 9, 2020, WHO announced the initiation of the Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response (IPPR)…
On Jul. 8, 2020, seventy-three countries warned that they were at risk of stock-outs of antiretroviral (ARV) medicines…
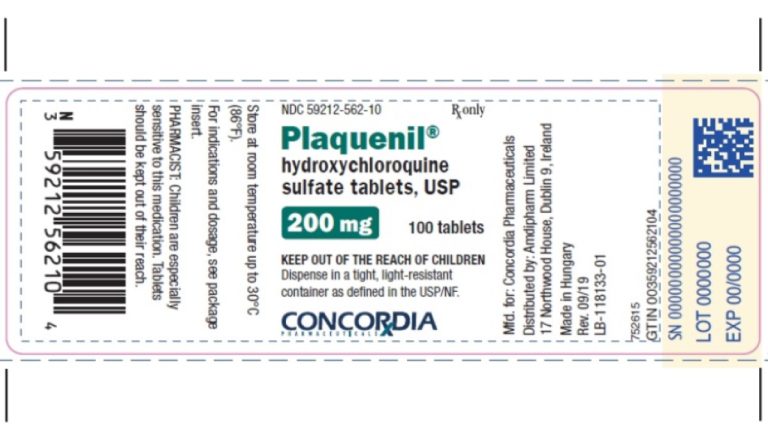
On Jul. 4, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) accepted the recommendation from the Solidarity Trial’s International Steering…

On Jun. 25, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced the end of the 10th outbreak of Ebola…