Washington State Secretary of Health declared a pertussis epidemic
On Apr. 3, 2012, the Washington State Secretary of Health declared a pertussis epidemic. By June 16, the…
On Apr. 3, 2012, the Washington State Secretary of Health declared a pertussis epidemic. By June 16, the…

On Feb. 21, 2012, as part of a national collaboration, Oregon Health & Science University researchers were studying…
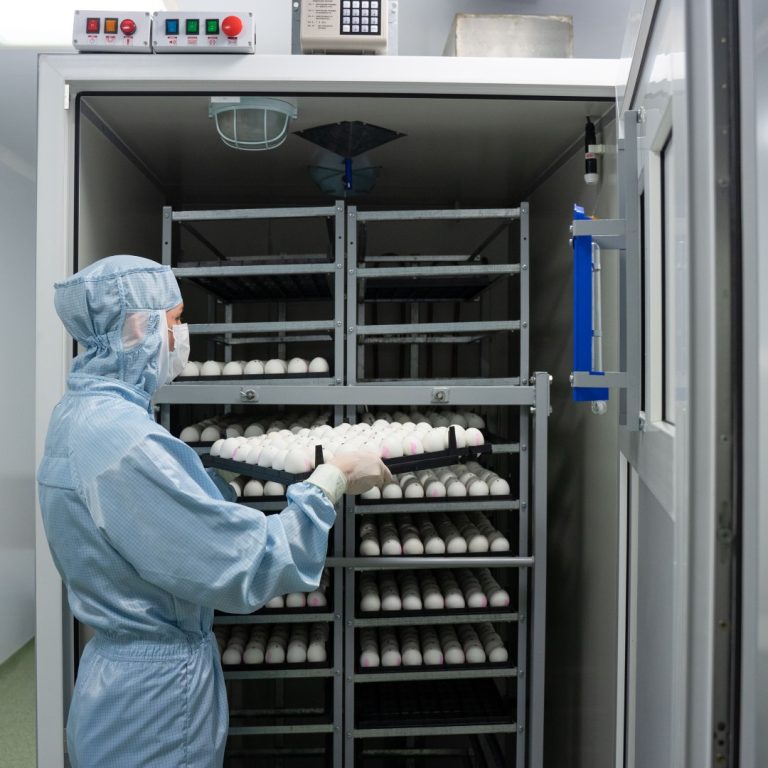

In 2012, vaccines containing cell-cultured virus became available. Even though eggs continued to be the primary means of…
On Dec. 30, 2011, Pfizer announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted approval of…
On Oct. 25, 2011, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP)…

On Aug. 25, 2011, the Institute of Medicine issued the report titled “Review of Adverse Effects of Vaccines.”…

On Jun. 22, 2011, Sanofi Pasteur opened a $101 million dollar vaccine research and development facility at Sanofi…

On Jun. 11, 2011, scientists in China reported the isolation of 2 novel reassortant highly pathogenic avian influenza…

On May 20, 2011, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) hailed vaccinations as one of…
On Apr. 22, 2011, The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of Menactra in children…
On Dec. 20, 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced approval of the first and only…
On Jul. 13, 2010, Bavarian Nordic announced that it had delivered 1 million doses of its smallpox vaccine…

On Mar. 23, 2010, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommended that physicians temporarily suspend use of…
On Mar. 19, 2010, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) recommended use of a reduced (4-dose) vaccine schedule…
On Feb. 24, 2010, a 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13 [Prevnar 13, Wyeth Pharmaceuticals, a subsidiary of Pfizer])…
On Feb. 24, 2010, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) recommended universal Influenza vaccination for those 6 months…
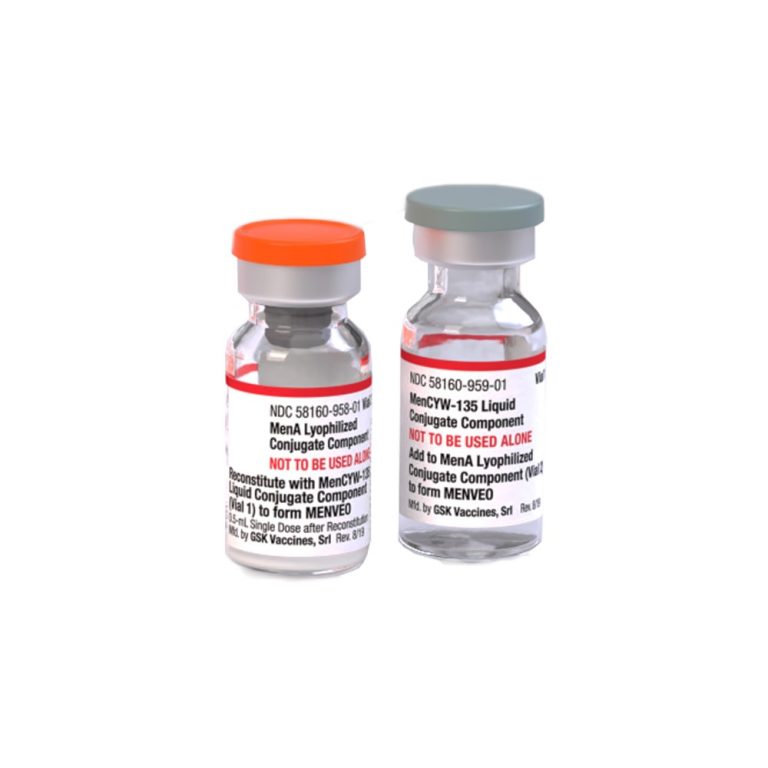
On Feb. 19, 2010, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had licensed a quadrivalent meningococcal…
On Jan. 29, 2010, the Bill and Melinda Gates announced that their foundation will commit $10 billion over…
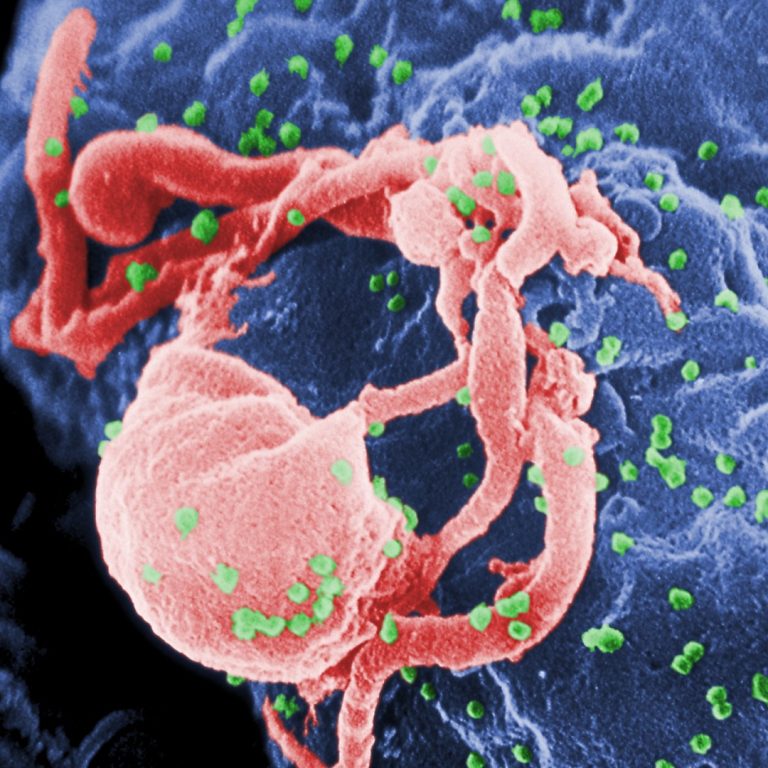
On Dec. 3, 2009, the Thai HIV vaccine clinical trial results were published in the New England Journal…

On Nov. 12, 2009, the Global Coalition against Child Pneumonia was established to raise awareness about the toll…
On Oct. 21, 2009, Merck announced that the company will not resume production of monovalent measles, mumps, and…

On Oct. 16, 2009, GlaxoSmithKline announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved Cervarix [Human papillomavirus…
On Sept. 24, 2009, the second Phase III HIV-1 vaccine trial, also known as RV144, that began in…

On Jun. 23, 2009, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced advanced development contract for…
On Jun. 11, 2009, the Dr. Margaret Chan, Director-General World Health Organization (WHO), declared the world was at…

On May 22, 2009, the U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services (HHS) directed $1 billion toward development…
On Apr. 15, 2009, Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) and the University of Washington (UW), along with…
On Feb. 25, 2009, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended routine hepatitis A vaccination for household…

On Feb. 12, 2009, the Vaccine Court ruled that MMR vaccine, when administered with thimerosal-containing vaccines, does not…

On Jan. 15, 2009, the U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services (HHS) awarded Novartis a $487 million…