50th anniversary of the Salk Polio vaccine
On Apr. 12, 2005 marked the 50th anniversary of the announcement that the polio vaccine, developed by Jonas…
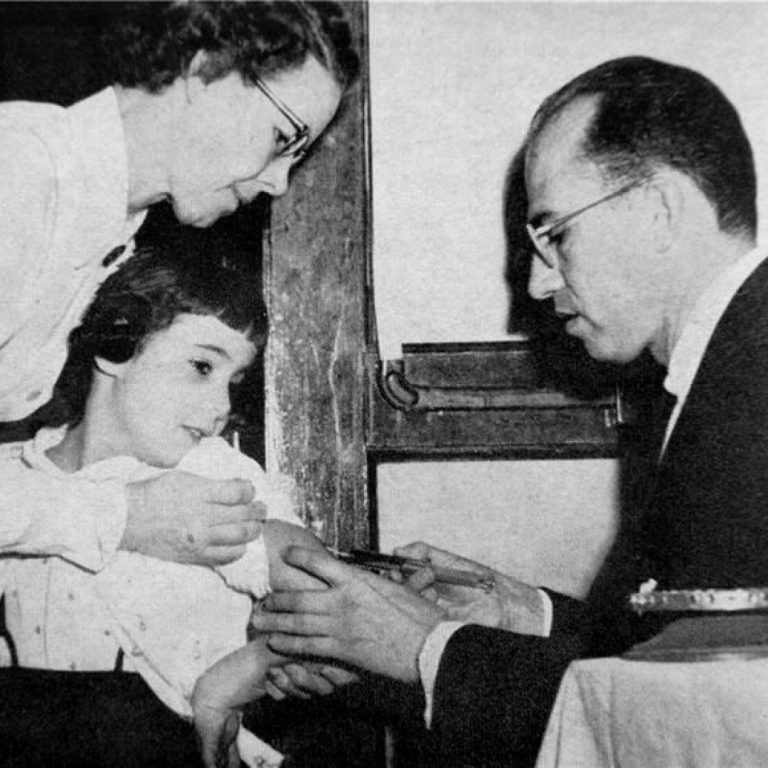
On Apr. 12, 2005 marked the 50th anniversary of the announcement that the polio vaccine, developed by Jonas…

On Dec. 13, 2002, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had licensed a combined diphtheria…
On Jun. 21, 2002, all 53 Member States in the World Health Organization (WHO) European Region were certified…

In 2002, the Rotary International launched a Polio Eradication Fundraising Campaign with a fundraising target of $80 million…
On Oct. 29, 2000, the Regional Commission for the Certification of Poliomyelitis Eradication certified that the Western Pacific…

In 2000, the use of Oral polio vaccine (OPV) was discontinued in the U.S. to eliminate the risk…
On Jun. 17, 1999, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP)…

In April 1999, a pandemic planning framework was published by the World Health Organization (WHO) that emphasized the…

In 1997, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) recommended adoption of a sequential series of two doses of…

In 1995, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP), American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Association of Family…
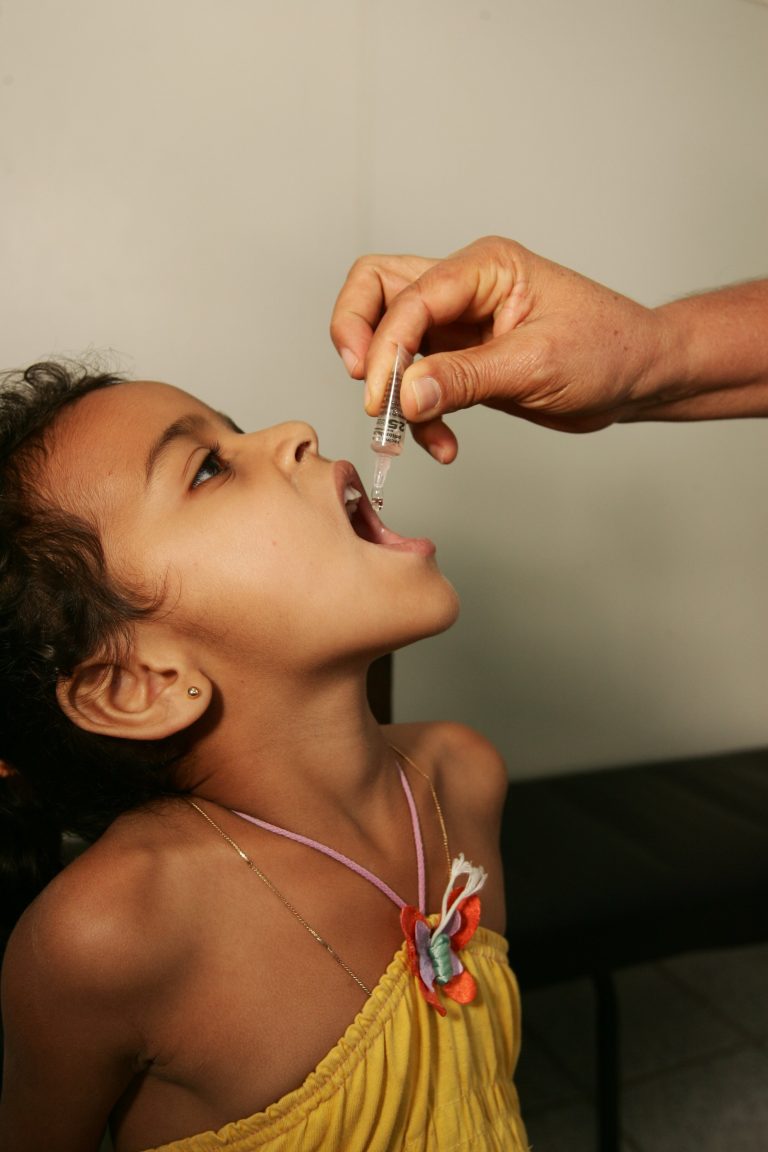
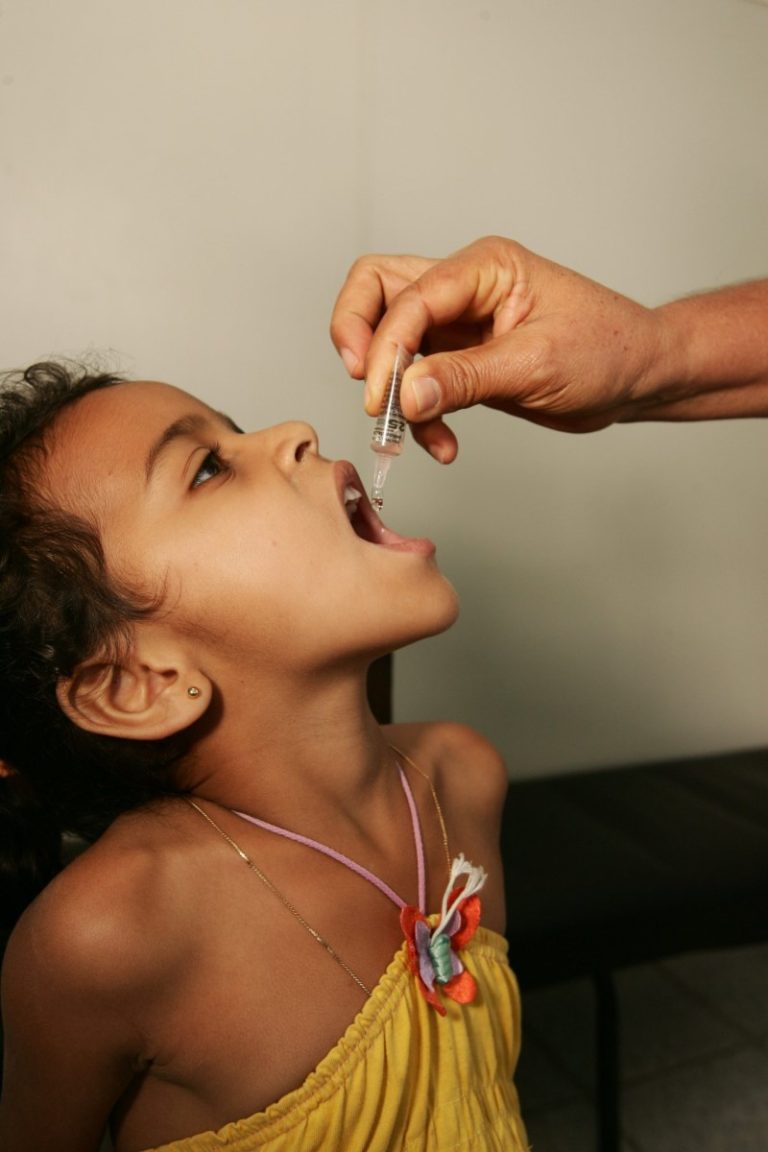
On Sept. 29, 1994, based on recommendations of the national certification committees and after review of surveillance and…

On Aug. 20, 1994, the entire Western Hemisphere was certified as “polio-free” by the International Commission for the…

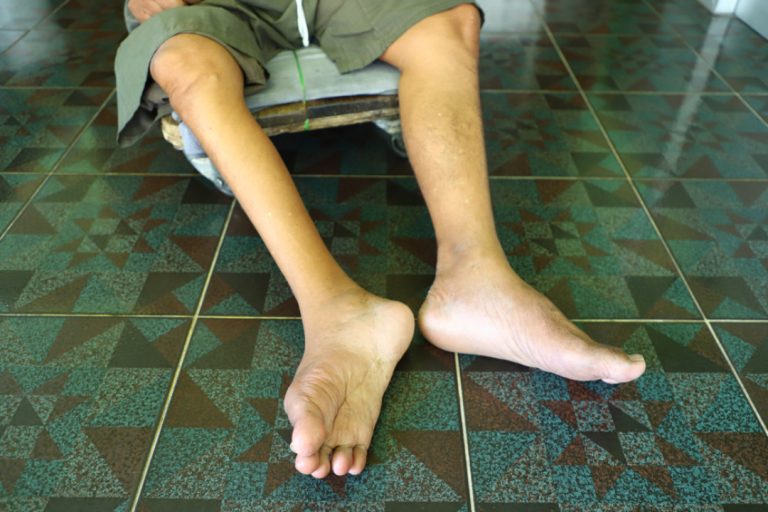
In 1991, the last case of indigenous polio in the Western Hemisphere occurred in a 5-year-old boy, Luis…

In 1990, the Global Polio Laboratory Network (GPLN) was formally established by the World Health Organization (WHO), national…
On Mar. 11, 1988, the World Health Assembly (the ministers of health of all member states of the…

In 1988, the World Health Assembly adopted a resolution for the worldwide eradication of polio, marking the launch…

In 1986, the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act was enacted by Congress. The Department of Health and Human…

In 1986, The National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act (PDF – 312 KB), as amended, created the National Vaccine Injury…
In 1985, Rotary International established its PolioPlus program, which held two fundraising events. Rotary has contributed over $500…

On Jul. 27, 1979, the last cases of wild type 1 poliovirus occurred in the U.S. among unvaccinated…

In 1979, the last wild case of polio was recorded in the U.S. However, in 1993, the virus…
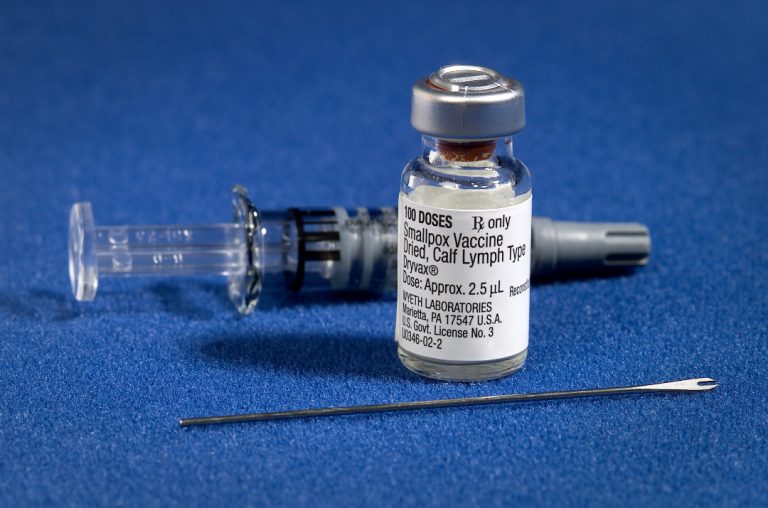
On Oct. 30, 1977, Ali Maow Maalin, a hospital cook in Merca, Somalia, was diagnosed with smallpox by…

In 1977, Joseph A. Califano, Jr., Secretary of the Dept of Health, Education, and Welfare (later Health and…

In 1975, The World Health Assembly passed a resolution to create the Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI) to…
In 1974, the Expanded Programme on Immunization was created within World Health Organization (WHO) in response to poor…

In 1973, the publication “Biohazards in Biological Research,” was edited by S. Hellman, M. Oxman, and R. Pollack. …

On Nov. 25, 1969, President Richard Nixon issued his “Statement on Chemical and Biological Defense Policies and Programs”…

On Jun. 12, 1966, the Serum Institute of India was founded in 1966 by Dr. Cyrus Poonawalla with…
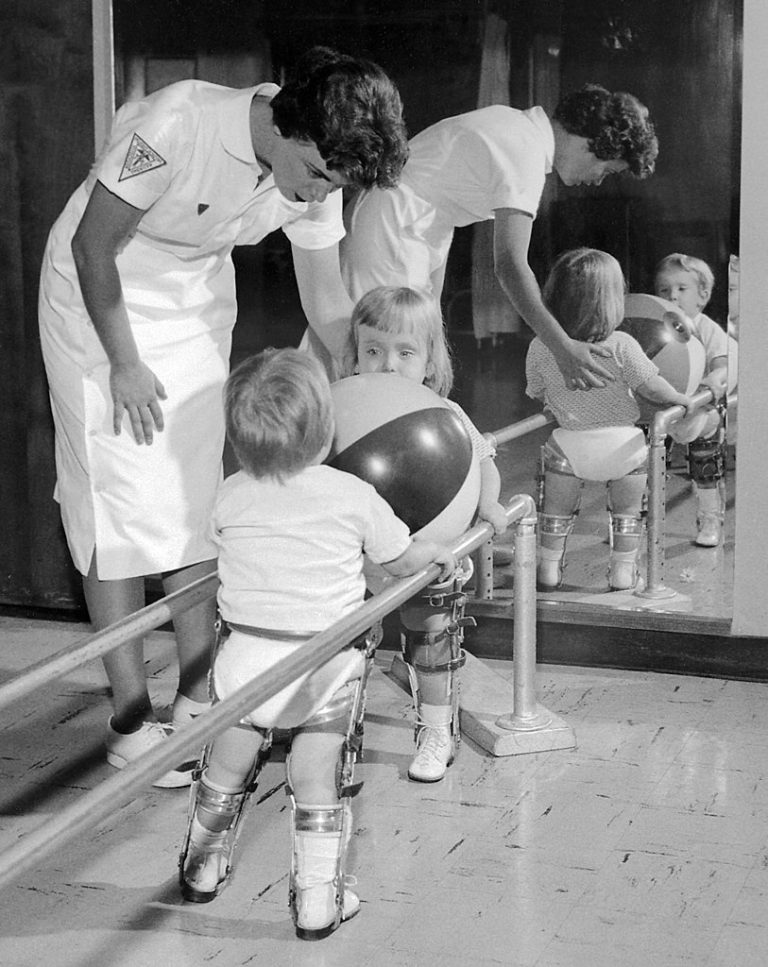

On Jun. 25, 1963, the Trivalent oral polio vaccine was licensed. The vaccine development began in 1957 by…

In 1963, the U.S. Congress established the Immunization Grant Program; polio incidence plummeted to only 396 reported cases…