The National Center for Health Statisticsᅠ became an organizational component of the CDC
On Jun. 26, 1987, it was announced that the National Center for Health Statistics ᅠ(NCHS) had become an…

On Jun. 26, 1987, it was announced that the National Center for Health Statistics ᅠ(NCHS) had become an…

In 1987, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released the results of a study on…

In 1987, the University of Minnesota Cancer Center, now known as the Masonic Cancer Center, received National Cancer…

In 1987, The Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Cancer Center received National Cancer Institute (NCI) designation. CSHL researchers…

In 1987, the Case Cancer Center (Case CCC) at Case Western Reserve University was both founded and became…

On Nov. 14, 1986, the U.S. Congress created the National Vaccine Program (NVP) to coordinate the vaccine research…
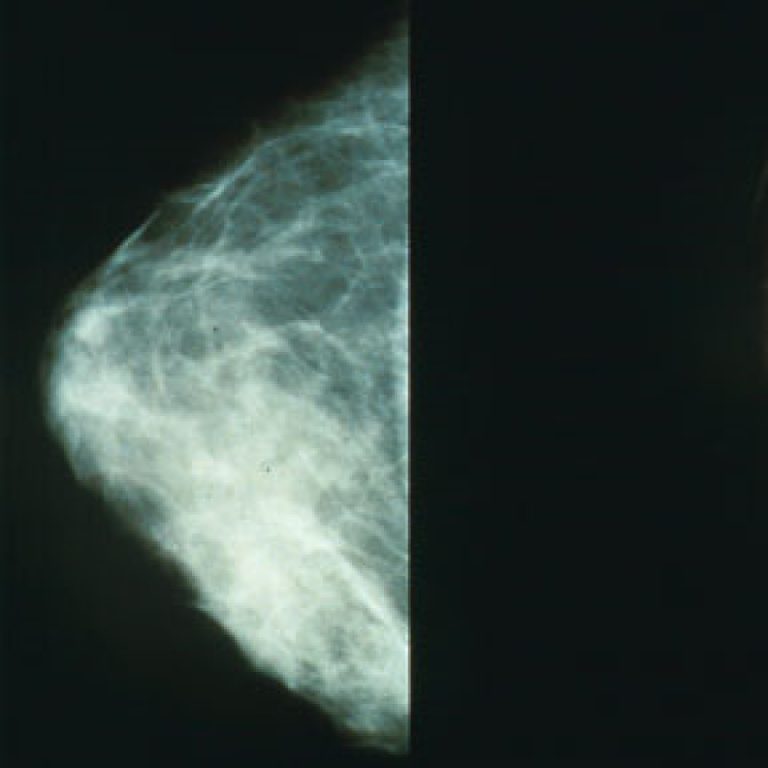
In 1986, the human HER2 proto-oncogene was cloned. HER2 is also called neu and erbB2. This finding established…

In 1986, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) established the Division of Injury Epidemiology and…
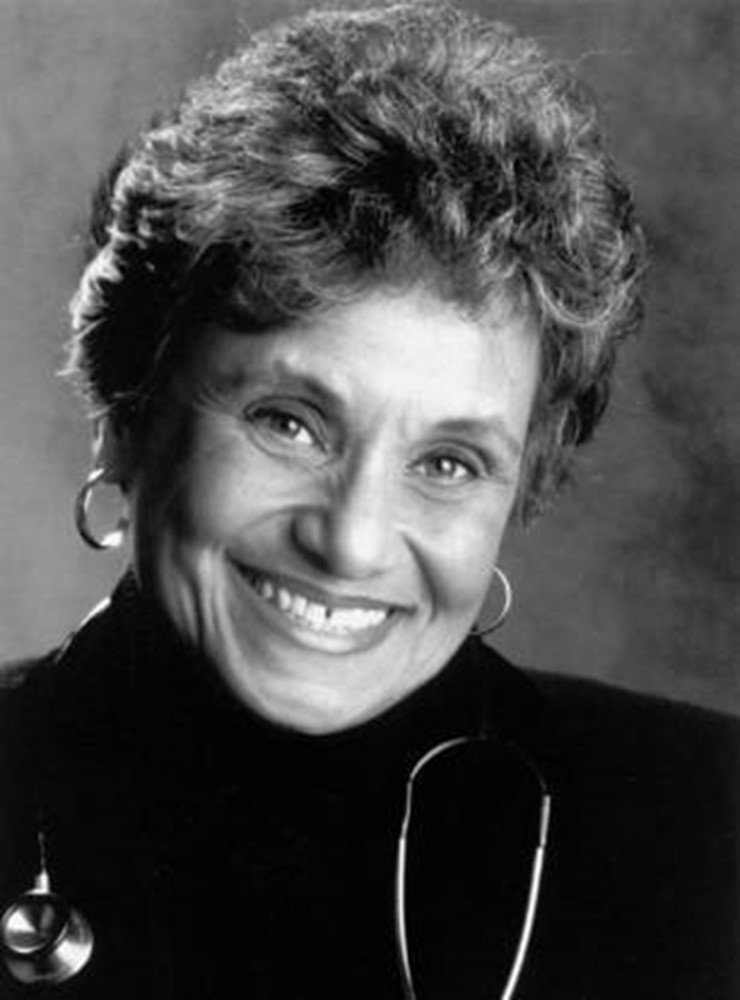

In 1986, Dr. Marilyn Hughes Gaston while deputy branch chief of the Sickle Cell Disease Branch at the…
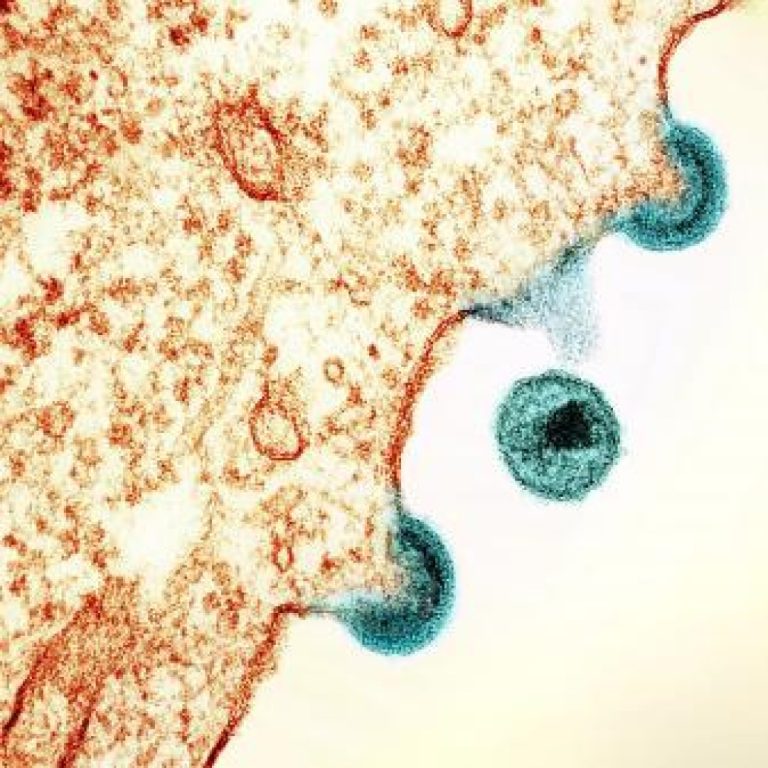
In 1985, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) revised the case definition of AIDS to…

In 1985, Federal courts ruled that private companies don’t need National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) permission for field…
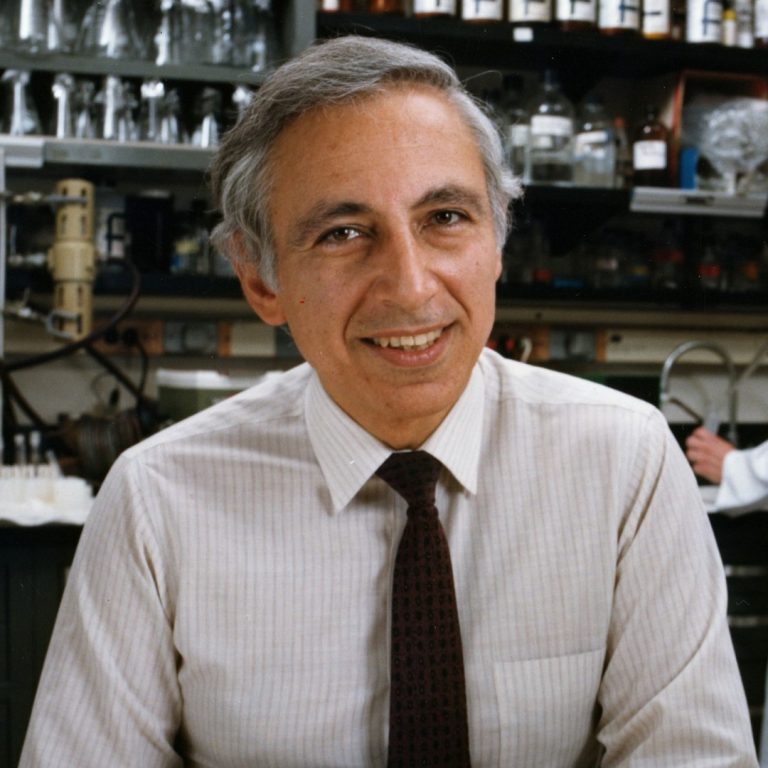

On Apr. 23, 1984, a National Cancer Institute (NCI) scientist, Dr. Robert C. Gallo announced his team’s discovery of…
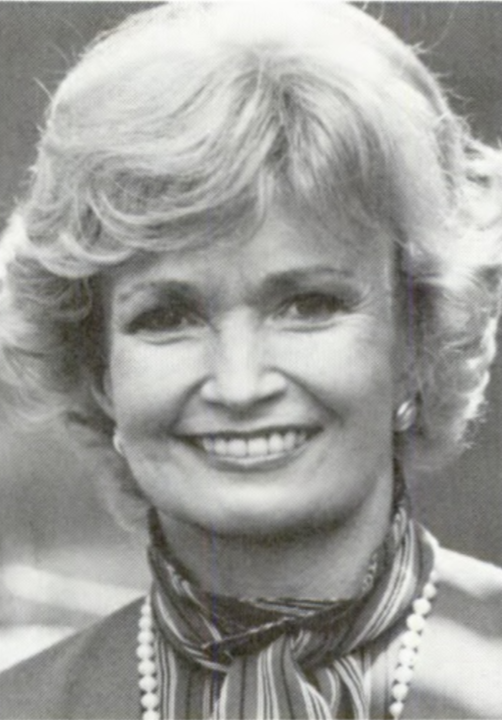

On Mar. 6, 1984, Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Margaret M. Heckler launched a new cancer prevention…

In 1984, a policy statement regarding the relationship of National Cancer Institute (NCI), the pharmaceutical industry, and NCI-supported…

In 1984, the University of California, San Diego (UC San Diego) was selected as one of the original…

In 1983, the National Cancer Institute’s Division of Resources, Centers and Community Activities was renamed the Division of…

In 1983, The Meyer L. Prentis Comprehensive Cancer Center of Metropolitan Detroit now known as the Karmanos Cancer…

In 1983, the National Institute of Health’s (NIH) Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee unanimously approved Lindow test. Stephen Lindow,…

On Jul. 27, 1982, a meeting in Washington, DC, attended by federal officials, university researchers, community activists, and…
On Jan. 15, 1982, the second AIDS patient was admitted to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious…
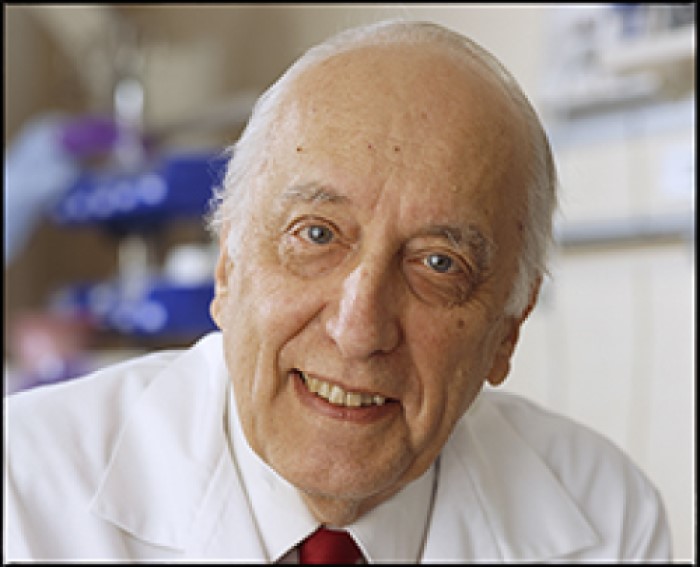

On Jun. 16, 1981, Dr. Thomas Waldmann with the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes…

In 1981, the National Cancer Institute (NC) awarded The City of Hope Cancer Center NCI-designation. City of Hope’s…

In 1981, the La Jolla Cancer Research Foundation, the Cancer Center received its National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designation. The…
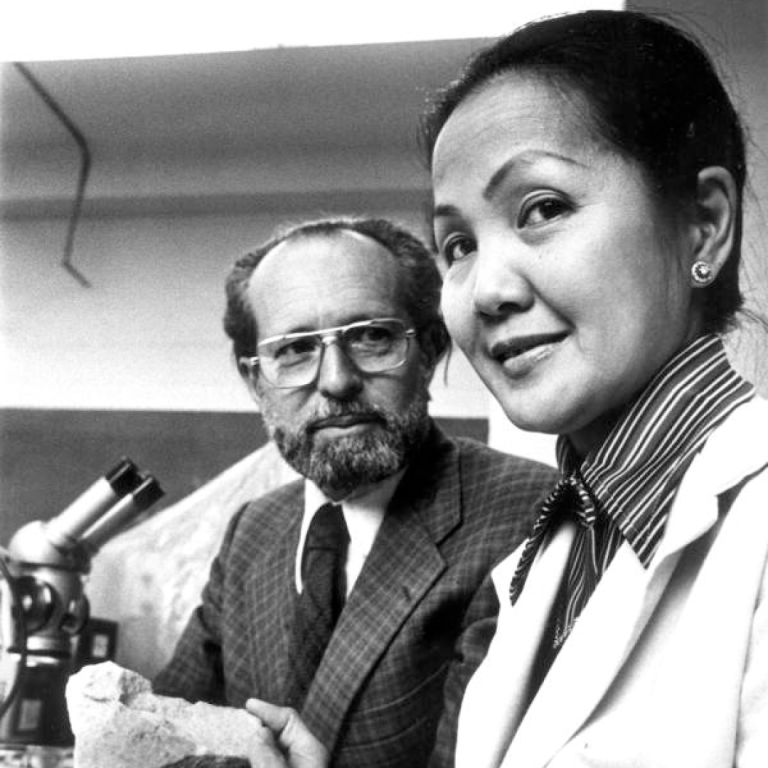

In 1981, Filipino and American scientist Dr. Roseli Ocampo-Friedmann received the U.S. Congressional Antarctic Service Medal for her…

On Dec. 17, 1980, the Health Programs Extension Act of 1980 (P.L. 96-538), introduced by Sen. Edward Kennedy,…

On Dec. 12, 1980, the U.S. Congress enacted the Bayh-Dole Act (P.L. 96-517, Patent and Trademark Act Amendments of…

On Dec. 12, 1980, the U.S. Senate passed Joint Resolution 213 which designated the National Institutes of Health’s…
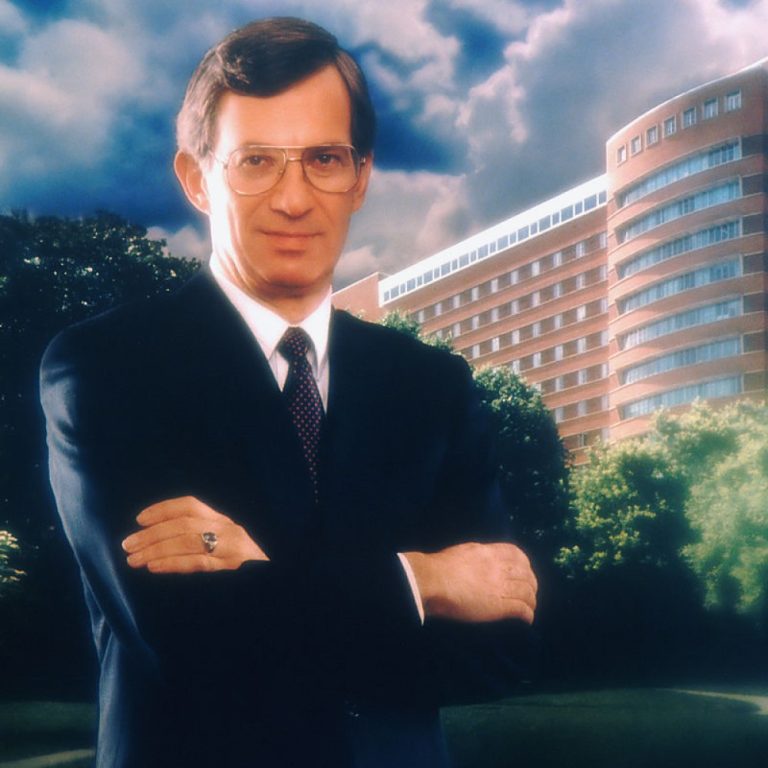

On Jul. 9, 1980, Dr. Vincent T. DeVita, Jr. became the ninth director of the National Cancer Institute…

On Apr. 10, 1980, the Alzheimer’s Association was established. In 1979, Jerome H. Stone and representatives from several…

In 1979, early concern over the dangers of recombinant DNA has waned and the National Institutes of Health…