After a plague epidemic kills 100,000 people in Naples, Rome begins inspecting all incoming ships
In 1656, after a plague epidemic kills 100,000 people in Naples, Rome began inspecting all incoming ships and…

In 1656, after a plague epidemic kills 100,000 people in Naples, Rome began inspecting all incoming ships and…

In 1647, Boston officials enacted an ordinance requiring all arriving ships to stop at the harbor entrance or…

In 1636, Harvard University, the oldest institution of higher learning in the U.S., was founded by a vote…

In 1634, the Florentine scholar, Francesco Rondinelli, wrote a report about a disease contagion, now known as the…

In 1629, sanitary legislation was drawn up in Venice that required health officers to visit homes during plague…

In 1621, potatoes from Peru were planted in Germany, another example of foreign microbes finding new homes. Botanist…

In 1603, the Academy of the Lynx-Eyed was founded by Federico Cesi, the first academy of sciences to…

In 1580, the first pandemic or worldwide epidemic, that clearly fit the description of influenza occurred in Italy….

In 1521, the first maritime quarantine opened in Marseilles, France. The quarantine system in Marseille lasted from 1620…
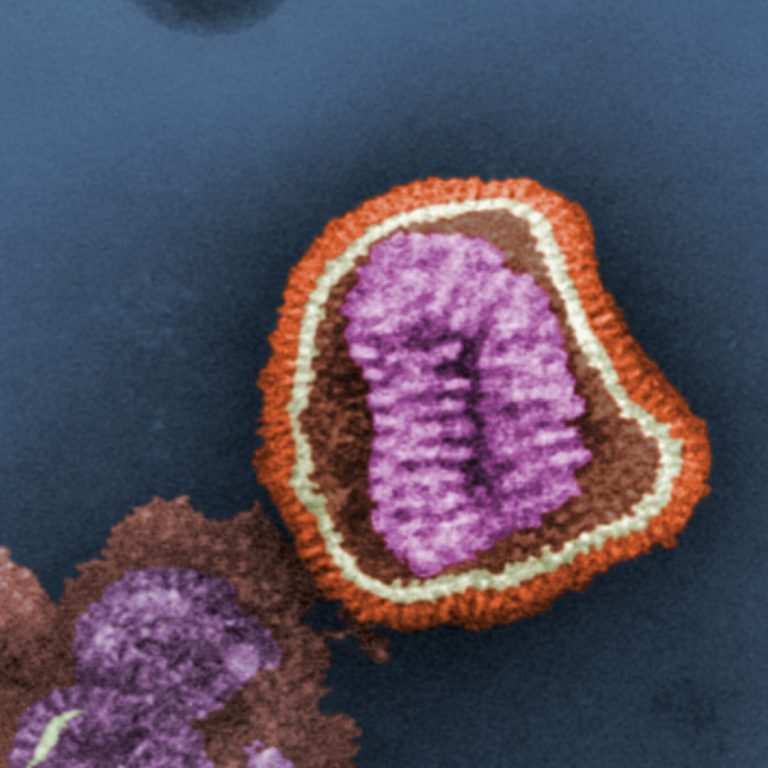
In 1510, history’s first recognized influenza pandemic originated in Asia and rapidly spread to other continents through eyewitness…

In 1403, Venice established the world’s first known maritime quarantine station, or lazaretto, on Santa Maria di Nazareth,…

In 1377, ships entering Italian ports during plague outbreaks were required to lie at anchor for forty days…

In 1370, the town of Ragusa in Italy established a quarantine station where all people arriving from plague-infected…

In 1363, Guy de Chauliac published Chirurgia Magna what will become the definitive guide for surgeons for the…

In 1348, Venice established the world’s first institutionalized system of quarantine that gave a council of three the…

In 1348, the Duke of Milan drew up an edict mandating that all those suffering from plague should…
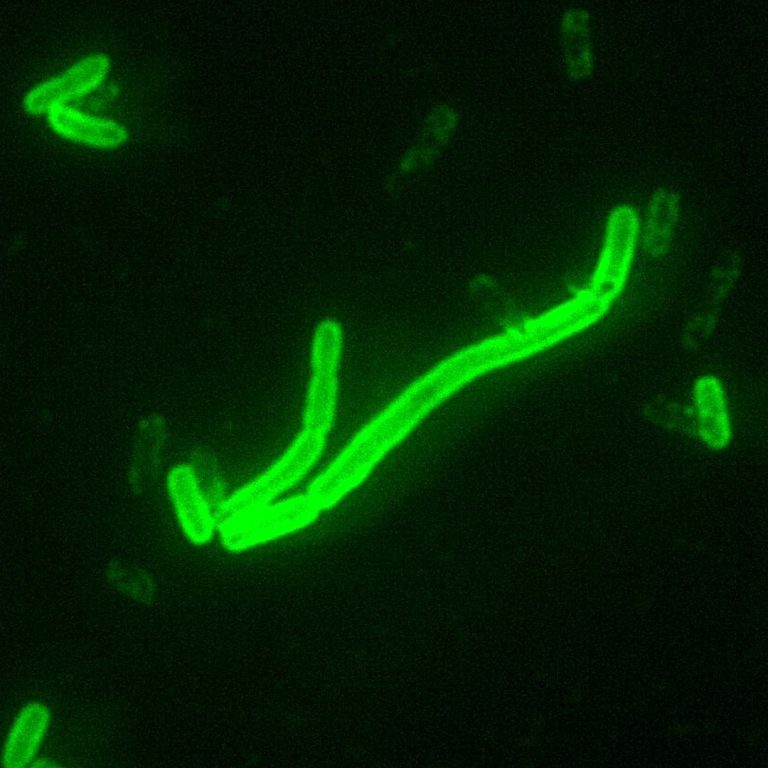
In 1346, during a siege of Kaffa (now Feodosia, Ukraine), the Tartar army catapulted bodies of plague victims…
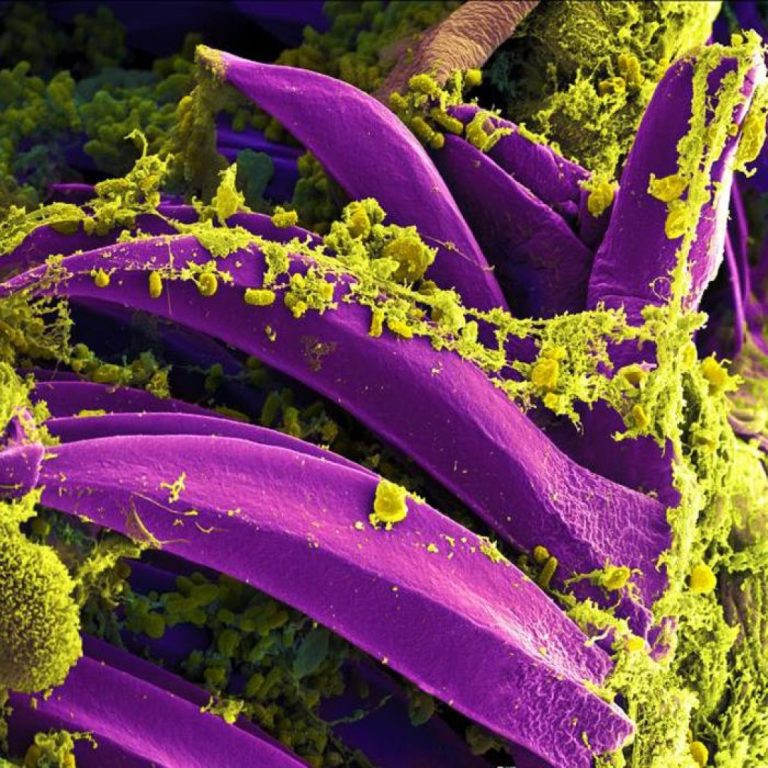
In 1346, spread by infected galleys coming from Kaffa (Crimea), the Black Death reached Genoa, as it now…

In 1322, an Arab chieftain first used artificial insemination to produce superior horses.
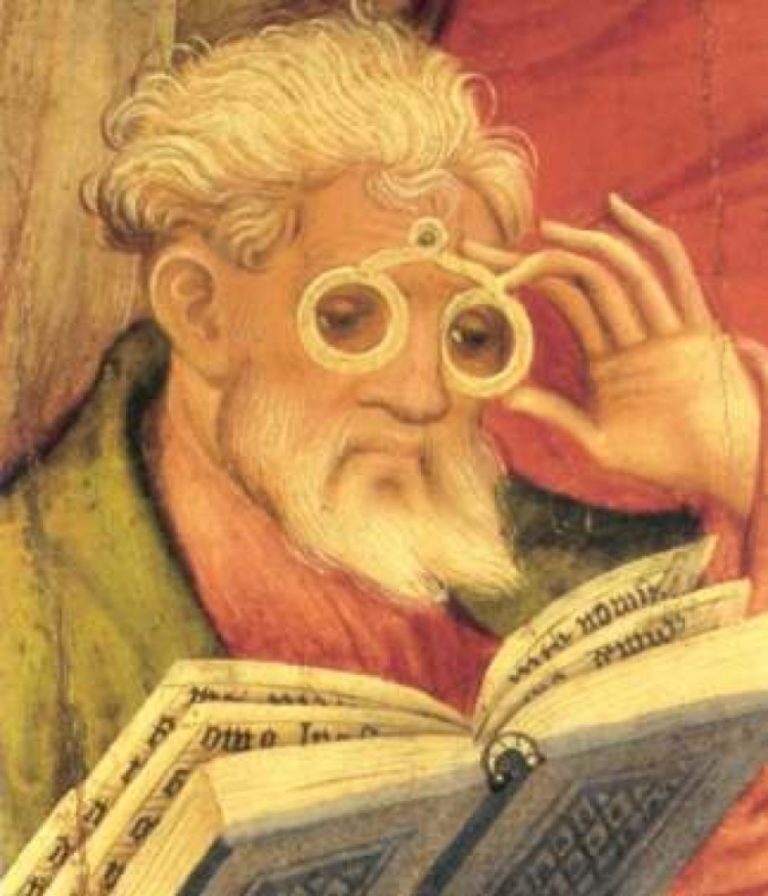

In 1285, spectacles were invented in Italy using convex lenses for the farsighted. The “Glasses Apostle” painting in…

In 1202, King John of England proclaimed the first English food law, the Assize of Bread, which prohibited…
In 1200, quarantines in Europe were common with more than 19,000 leprosaria, or houses for leper patients located…
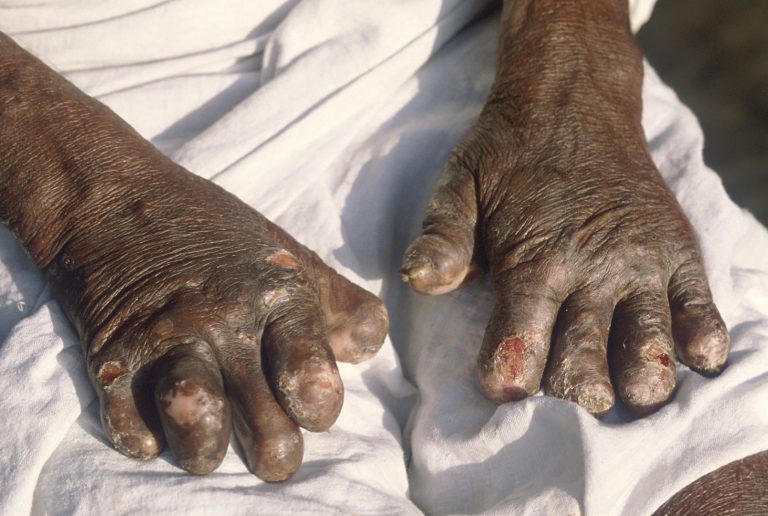
In 1179, the Third Lateran Council decreed with Canon 23 living arrangements for lepers and how their necessary…
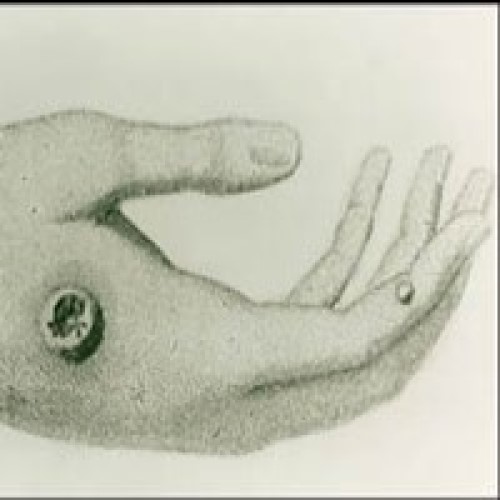
In 1100, the variolation technique was developed, involving the inoculation of children and adults with dried scab material…
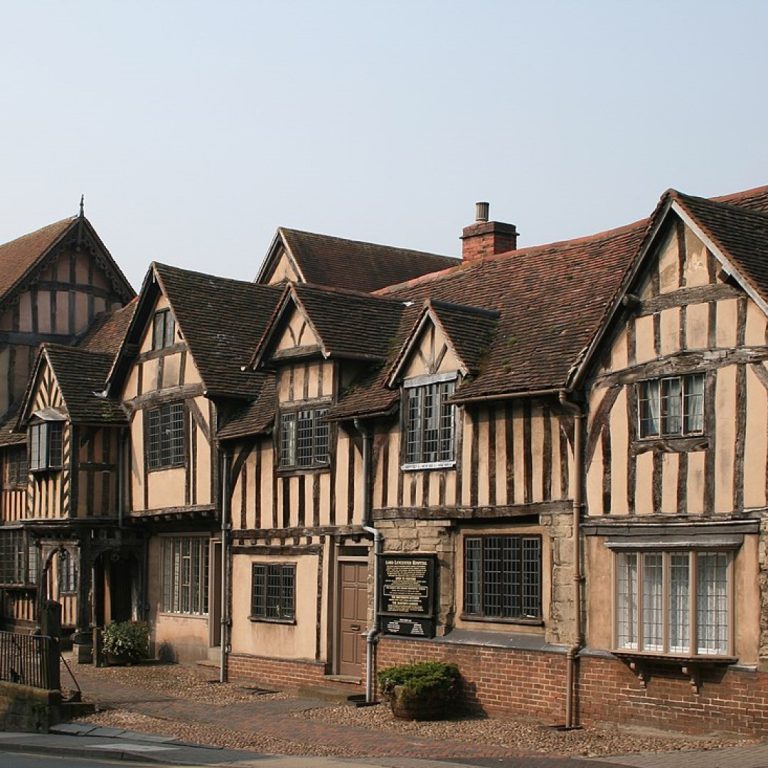

From 1050-1350 marked a particularly active phase of the disease that made necessary the introduction of large-scale specialist…
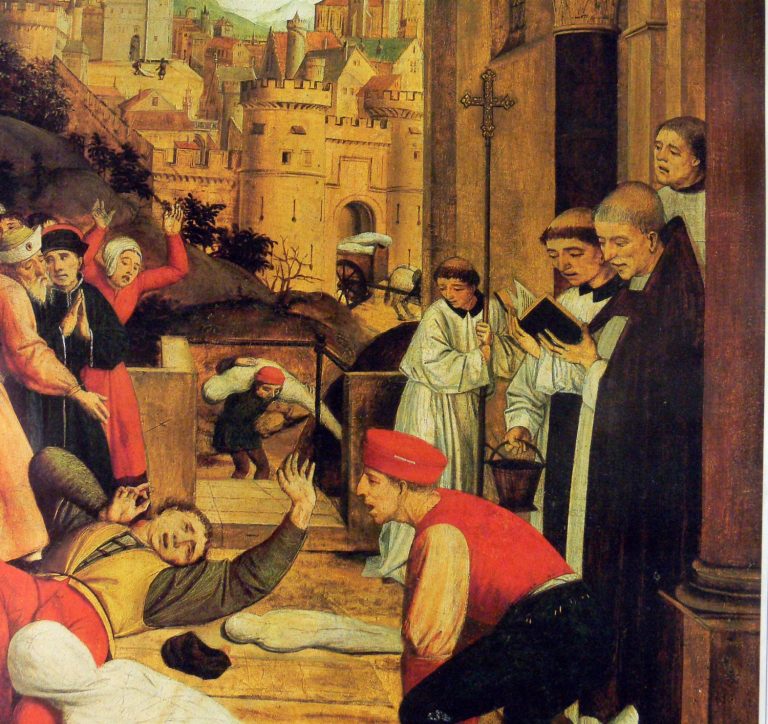

In 541, an outbreak of bubonic plague (yersina pestis), a bacterial disease later named the Black Plague or…

In 470, Atossa, daughter of Cyrius the Great became the first women in recorded history to be diagnosed…

The Edwin Smith Surgical Papyrus, dated to 3,000-2,500 B.C., and possibly attributable to Imhotep, the Egyptian physician-architect, provided…

Around 8000 BCE, Potatoes, the world’s most widely grown tuber crop, were first cultivated for food in area…

Early Chinese medical writings in approximately 3600 B.C. were the first to record the decreases in goiter size…