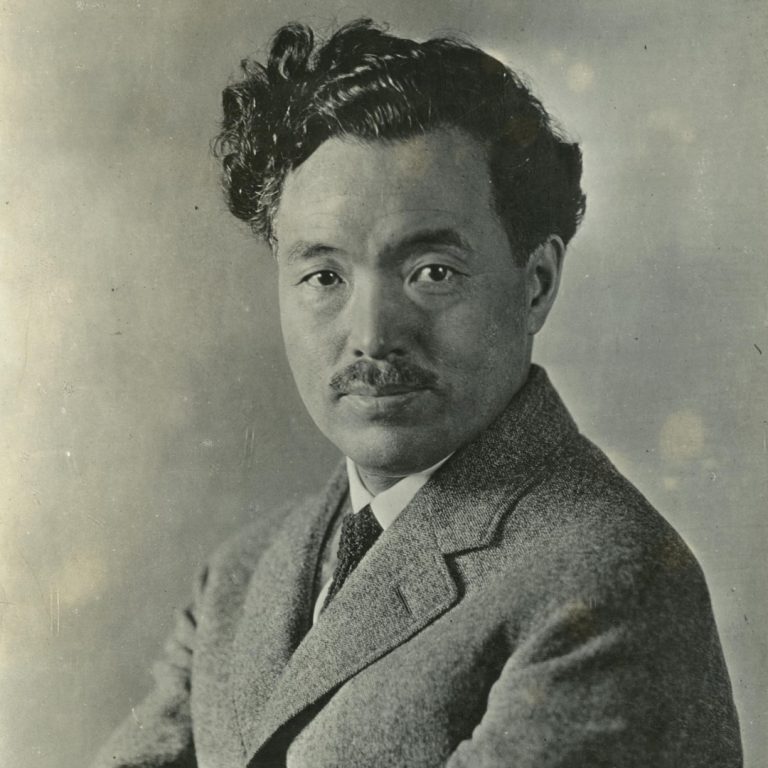
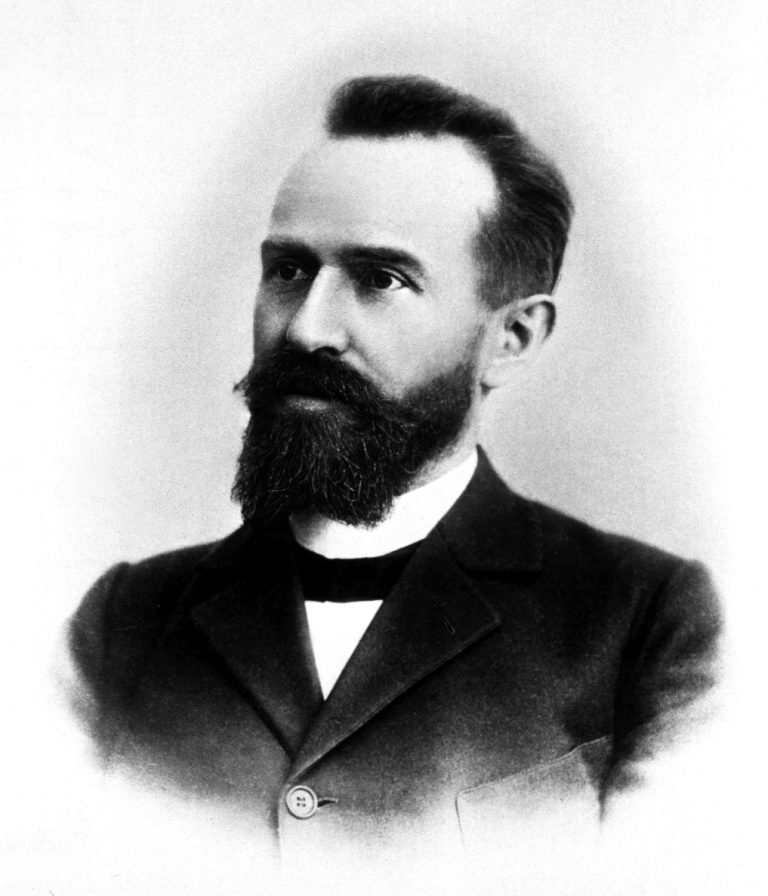
Japanese immunologist and bacteriologist Hideyo Noguchi discovered that Treponema pallidumᅠ (syphilitic spirochete) was the cause of syphilis
In 1913, Japanese immunologist and bacteriologist Hideyo Noguchi discovered that Treponema pallidum (syphilitic spirochete) was the cause of…