By the end of 1918, 35% of Cleveland’s population had contracted either influenza or developed pneumonia
By the end of 1918, 3.5% of Cleveland’s population had contracted either influenza or developed pneumonia. 3,600 people…
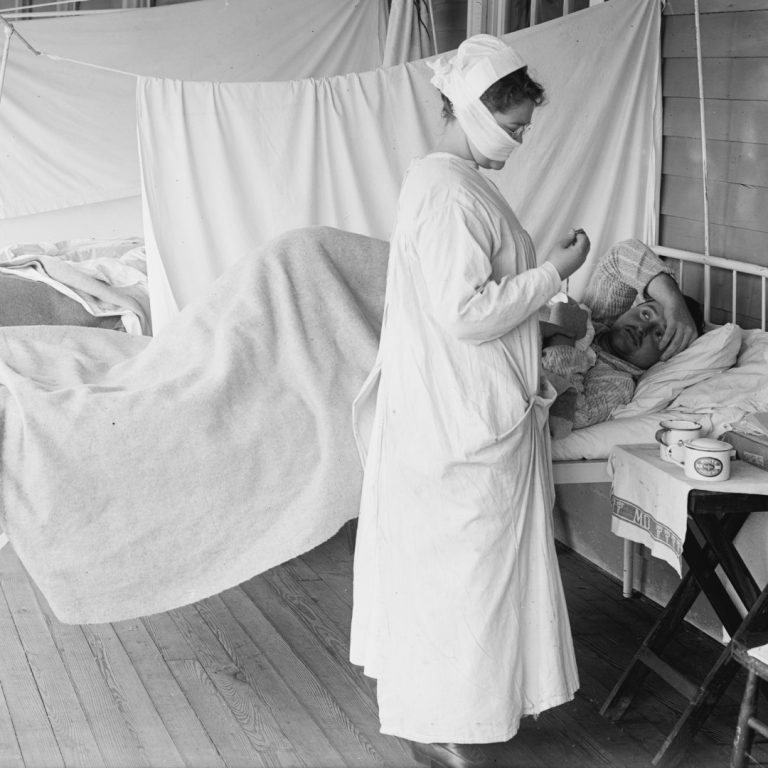
By the end of 1918, 3.5% of Cleveland’s population had contracted either influenza or developed pneumonia. 3,600 people…
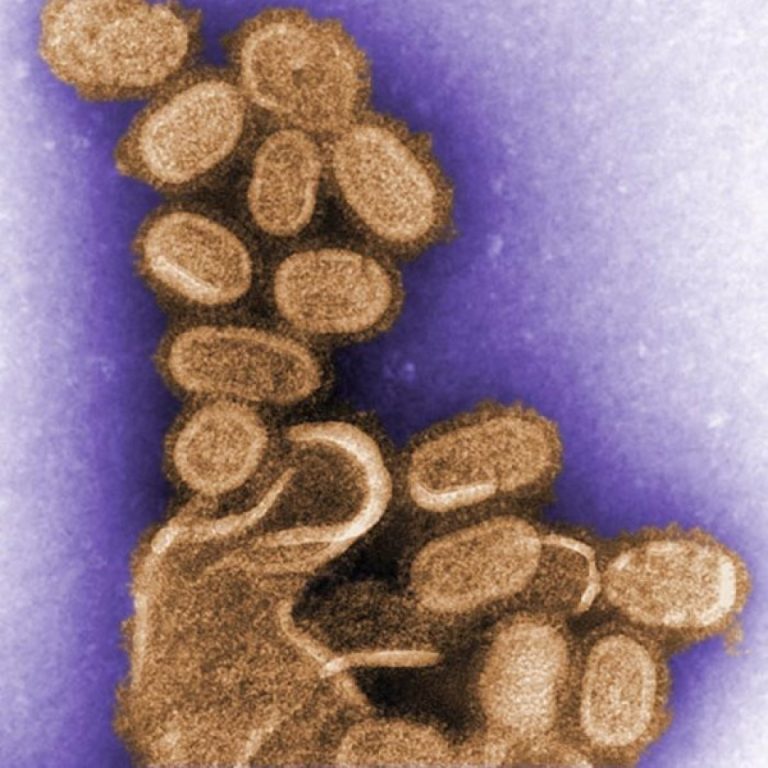
In 1918, by the end of the influenza epidemic in Cincinnati, the death toll had reached 1700 from…

In 1918, Innis Steinmetz, became the first woman to enter the medical school, and 30 years later, the…
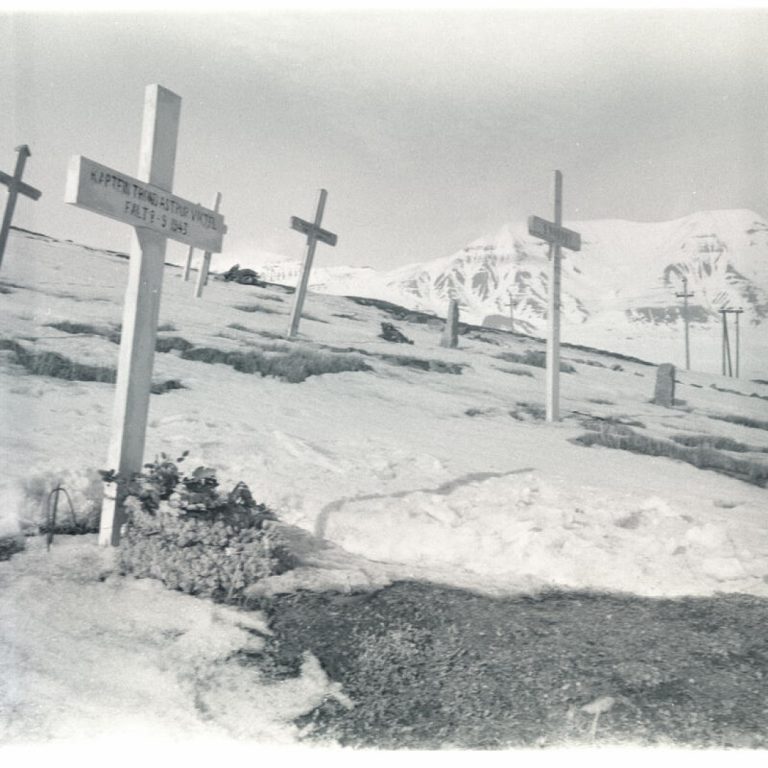

In 1918, It was estimated that about 500 million people or one-third of the world’s population became infected…
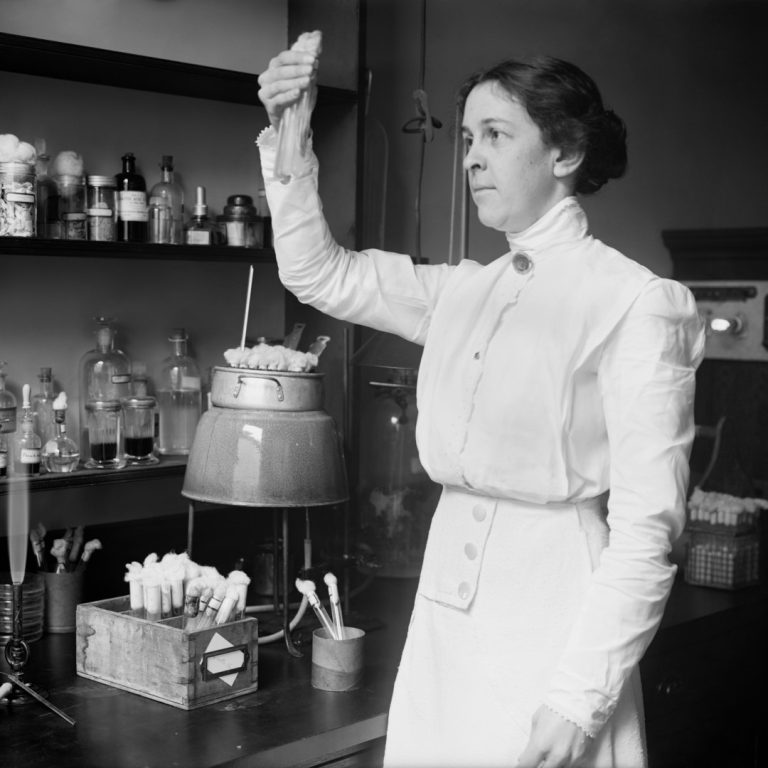

In 1918, Alice C. Evans described the organism that caused undulant fever. Despite severe and persistent criticism of…
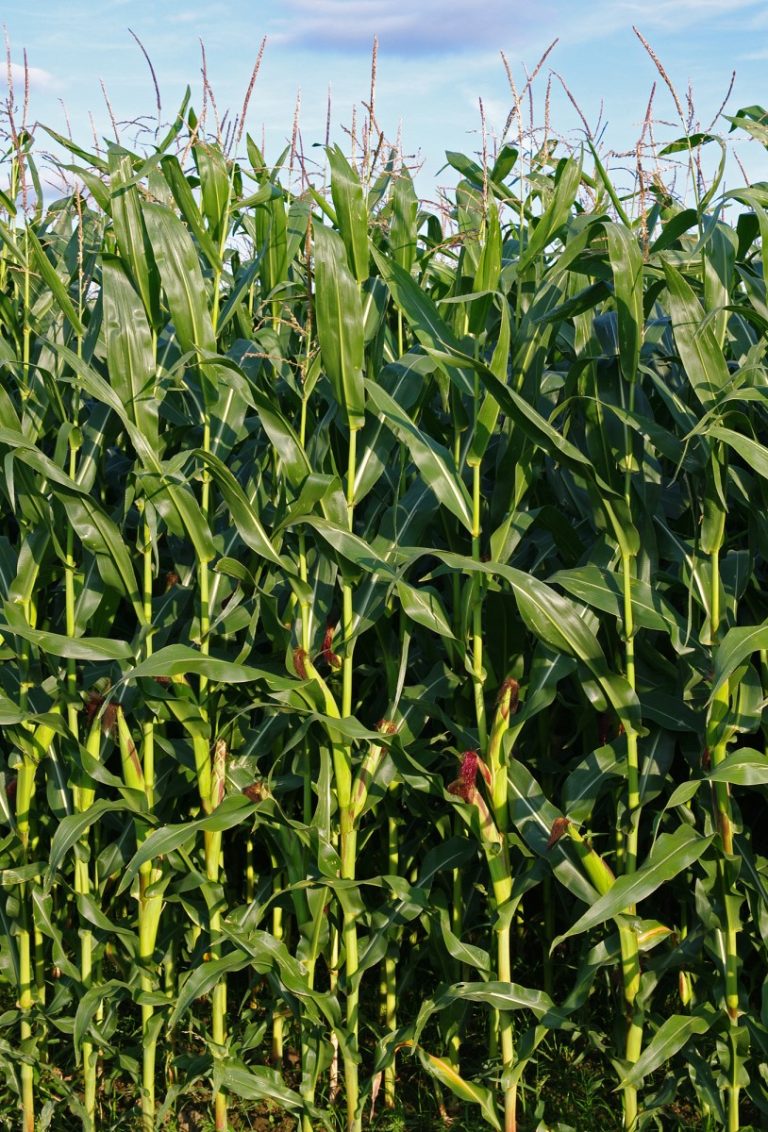

In 1918, geneticist Donald Jones invents the double-cross (the crossing of two single crosses) that moves hybrid corn…

In 1918 Army General Hospital 21, also know as the Fitzsimons Life Science District, became the first medical…

On May 3, 1917, Alaska Territorial Gov. John Strong signed the bill to create the institution now known…

In 1917, Mather H. Neill discovered that scrotal reactions of guinea pigs with “Mexican” typhus (later known as…

In 1917, Stem rust attacked the U.S. wheat crop, destroying more than two million bushels and forcing Herbert…

In 1917, Hungarian Kark Ereky first coined the word “biotechnology” and in 1919 published “Biotechnology of Meat, Fat…
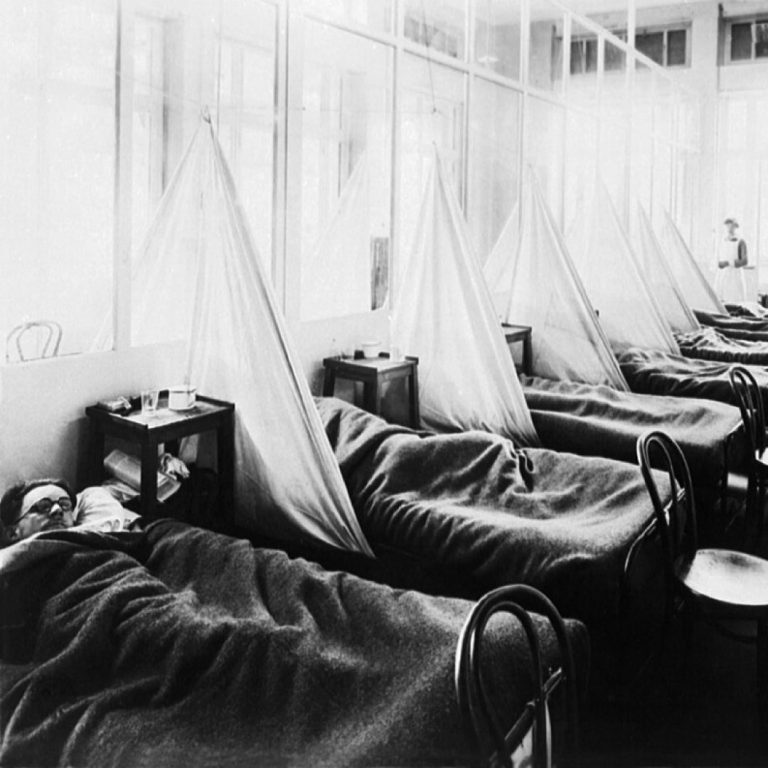
In 1917, when the U.S. entered World War I, Emory University organized a medical unit that would be…
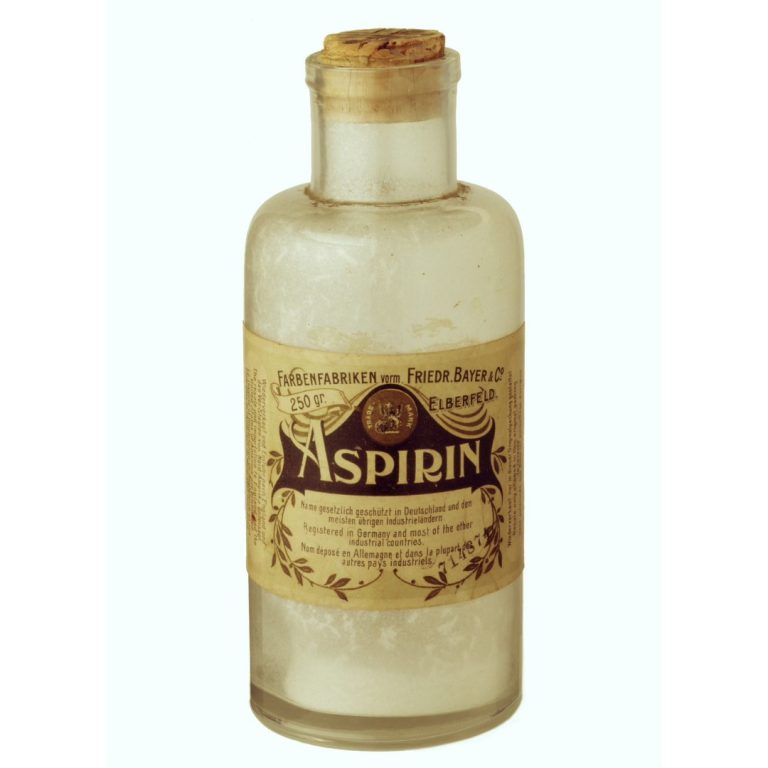

In 1917, the University of Iowa College of Pharmacy secretly produced bootleg aspirin after the war in Europe…
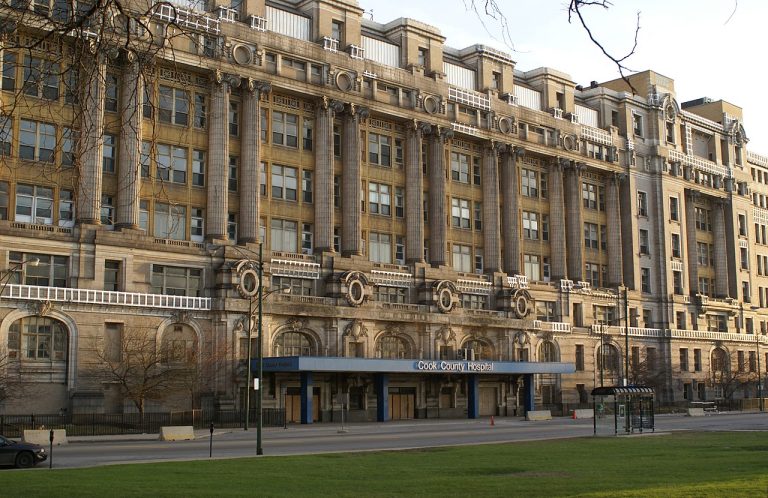

In 1917, the new Cook County Hospital facility opened and is the current Main Building of today’s Hospital….
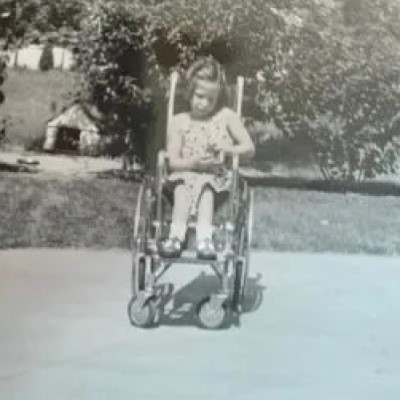

In 1917, the state wide Children’s Development and Rehabilitation Center Service Program was established in the University of…
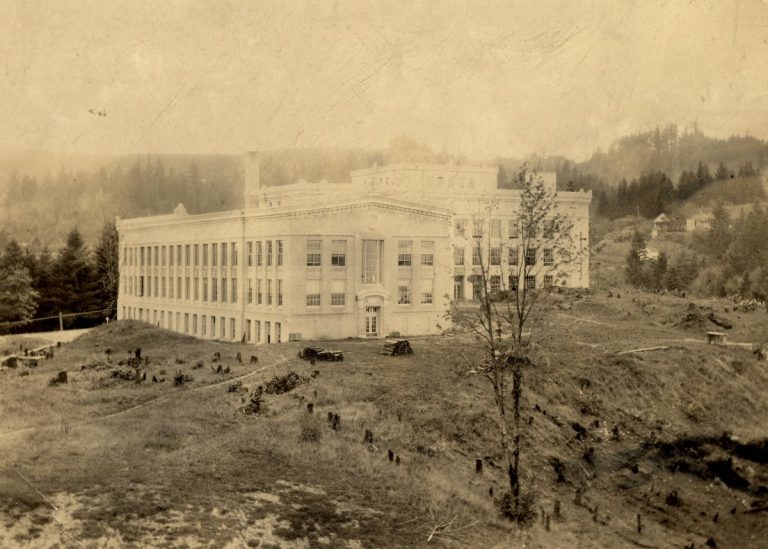

In 1917, Dr. Kenneth McKenzie the staff surgeon at Oregon-Washington Railroad and Navigation Company persuaded the company to…

In 1917, David Marine, a U.S. physician in Ohio, and his colleagues initiated an iodine prophylaxis program in…
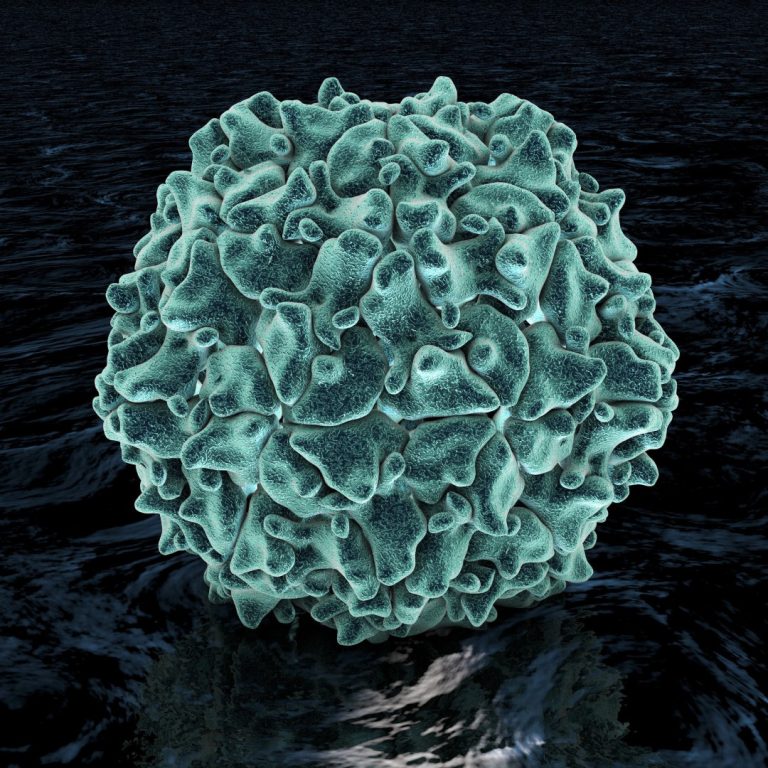
On Jun. 17, 1916, New York City experienced the first large epidemic of polio (poliomyletis), with over 9,000…

On Jan. 10, 1916, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled the Sherley Amendment to the Pure Food and Drugs…

In 1916, the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences (CVM) is an institution that represents…

In 1916, the National Research Council (NRC) was created under the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) charter by…
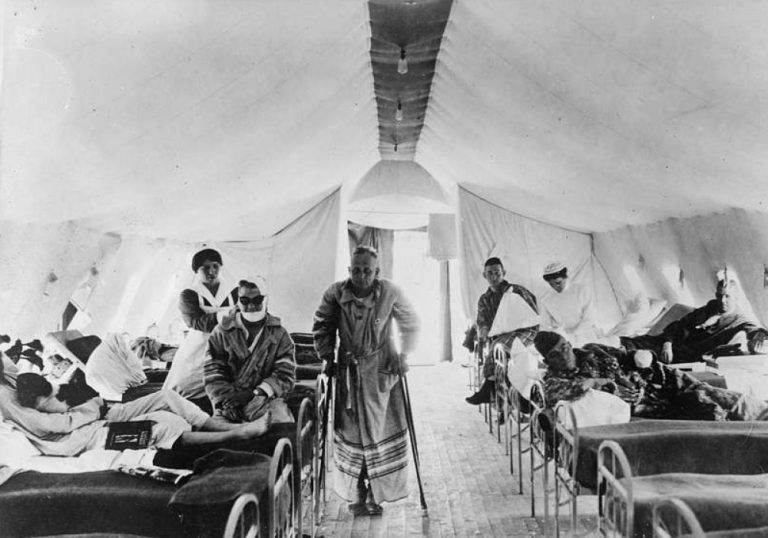
In 1916, During World War I, work by Hygienic Laboratory investigators changed the way smallpox vaccinations were administered…

In 1916, the first AACR publication, The Journal of Cancer Research, was launched in 1916. The journal was…
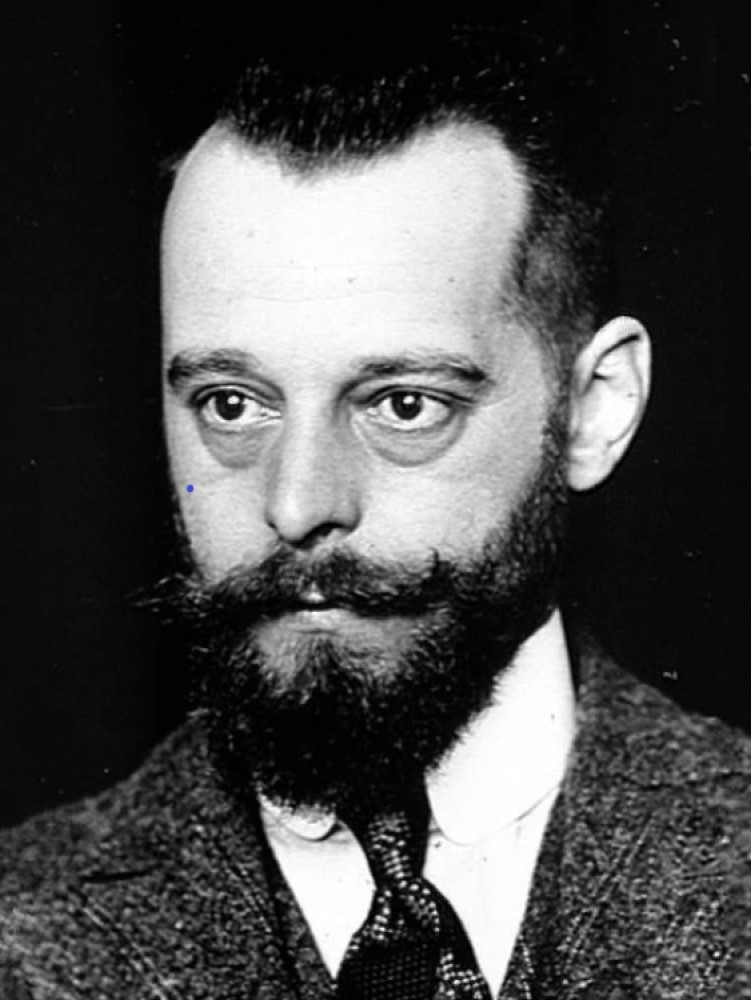

In 1916, French-Canadian bacteriologist Felix-Hubert D’Herelle discovered viruses that prey on bacteria and named them bacteriophages or bacteria…

In 1916, George Harrison Shull accepted a professorship at Princeton University. At his instigation, Princeton University Press began…

In 1916, Guillain-Barr syndrome (GBS), also known as Landry-Guillain-Barr-Strohl syndrome, was described. Its incidence in North America and…

In 1916, the Hancock Agricultural Research Station, a 412-acre vegetable research farm, was founded in central Wisconsin. The…

On Aug. 14, 1915, Hans Lundbeck founded a company in Copenhagen, Denmark, which dealt in everything from machinery…

In 1915, Yamagiwa Katsusaburo, a Japanese pathologist, was the first to prove chemical carcinogenesis when he gave coal…
In 1915, Richard Lewishon found that sodium citrate added to freshly drawn blood prevents clotting (coagulation). This discovery…