Oral polio vaccine types 1 and 2 was developed by Dr. Albert Sabin
In 1962, oral polio vaccine types 1 and 2, developed by Dr. Albert Sabin and grown in monkey…
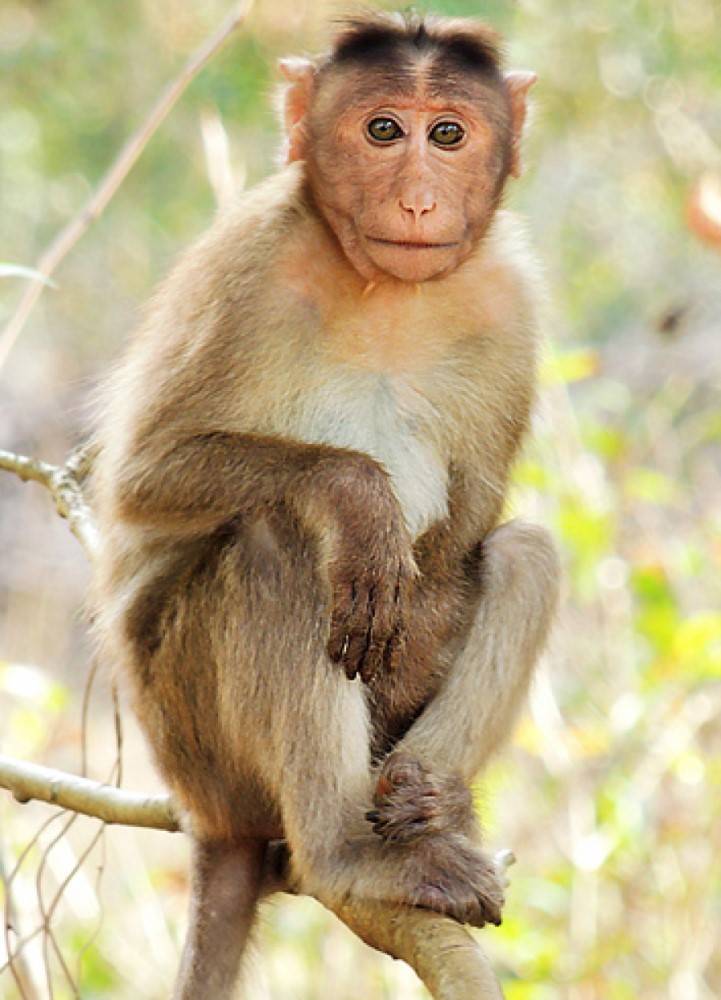

In 1962, oral polio vaccine types 1 and 2, developed by Dr. Albert Sabin and grown in monkey…

In 1962, Joseph Altman of MIT published several papers claiming that adult rats, cats, and guinea pigs all…
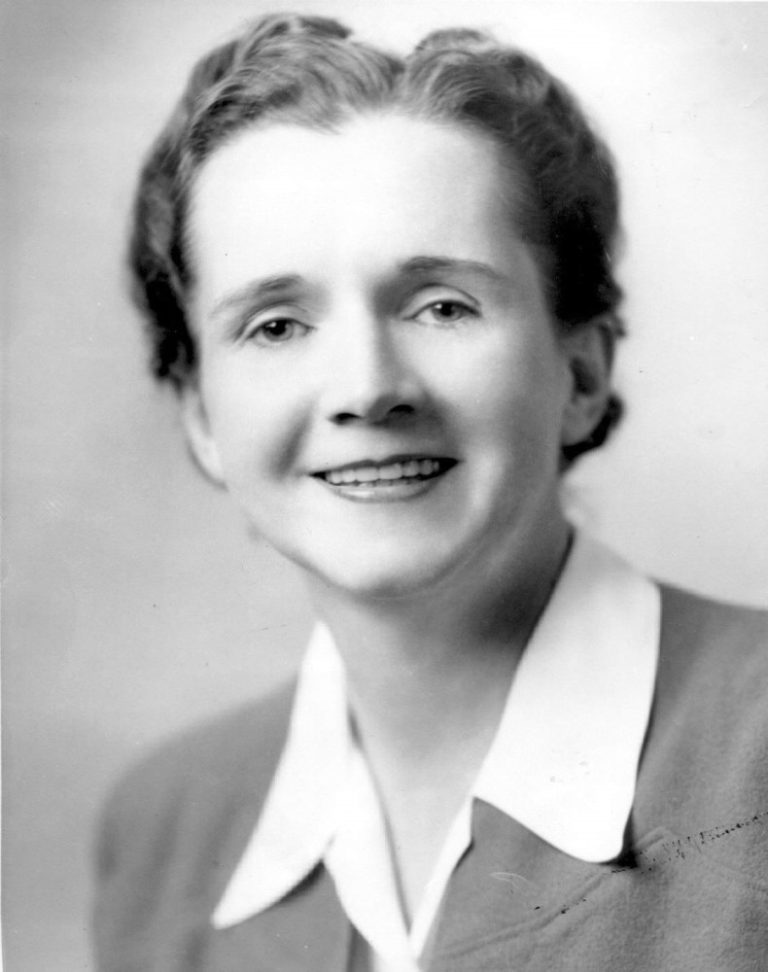

In 1962, Silent Spring, a book by marine biologist Rachel Carson, galvanized the first generation of environmentalists. Silent…

In 1962, the birth of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) in Mexico was an experiment…
In 1962, President John F. Kennedy signed the Vaccination Assistance Act into law. It allowed the CDC to…

In 1962, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) launched the 122 Cities Mortality Reporting System….

On Oct. 21, 1961, the Atomic Energy Commission issued a construction permit for the University of Missouri Research…

On Oct. 6, 1961, the National Congress on Medical Quackery convened in Washington, D.C. sponsored jointly by the…

In September 1961, U. S. Congress authorized the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to conduct a study of…

On Aug. 23, 1961, The Committee on the National Medal of Science was established by President John F….

On Jul. 1, 1961, pioneering immunologist Frank Dixon and four of his colleagues (William Weigle, Joseph Feldman, Charles…

On Jun. 22, 1961, the North Carolina Award for Science, the stateメs highest civilian honor, was established by…

On May 25, 1961, President John F. Kennedy in his historic message to a joint session of the…

On Apr. 25, 1961, Biochemist Dr. Hans Neurath became the first University of Washington School of Medicine faculty…

On Mar. 2, 1961, President Kennedy swore in Luther Leonidas Terry as U.S. Surgeon General. The landmark Surgeon…

In 1961, the Priestley Medal was awarded to Louis P. Hammett by the American Chemical Society “to recognize…

On Jan. 12, 1961, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) established the Laboratory of Viral Oncology, a new intramural…

On Jan. 10, 1961, External D&C No. 15, a red color additive widely used in cosmetics before it…

In 1961, Raymond U. Lemieux established a research program at the University of Alberta (UA). UA researchers in…

In 1961, the CDC expanded its reach into chronic disease by investigating a cancer cluster in Illinois.

In 1961, The Cook County Hospital Fantus Out-Patient Clinic moved to Harrison and Winchester Streets.

In 1961, Johnsonᅠ&ᅠJohnson acquired Janssen Pharmaceutica in Belgium. Its founder, Dr. Paul Janssen, is recognized as one of…

In 1961, Medtronic relocated its headquarters to a 15,000-square-foot facility in St. Anthony Village in Minneapolis. The new…

In 1961, Congress established National Poison Prevention Week to raise awareness, reduce unintentional poisonings, and promote poison prevention….

In 1961, The University of Missouri College of Veterinary Medicine teaching hospital was constructed, and a diagnostic laboratory…
In 1961, platelet concentrates were recognized for reducing the mortality from hemorrhage in cancer patients.

In 1961, Parks Medical Electronics, founded in 1961 by Loren Parks, is the world’s oldest manufacturer of Doppler…

In 1961, Marshal Nirenberg and others prove the triplet code is how the information to make proteins is…

In 1961, E.R. Squibb & Sons marketed the worldメs first electronic toothbrush in 1961. By 1990 more than…

In 1961, UPOV, the International Union for the Protection of New Varieties of Plants, was negotiated in Paris,…