WHO’s Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System established
Since 1952, global influenza surveillance has been conducted through WHO’s Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS). The…

Since 1952, global influenza surveillance has been conducted through WHO’s Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS). The…

In 1952, the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS) was created by World Health Organization (WHO) to…

On Apr. 7, 1948, the World Health Organization (WHO) was founded and is today the United Nations agency…

In 1948, the World Health Organization (WHO) Influenza Centre was established at the National Institute for Medical Research…

In 1948, Dr. Isabel M. Morgan led a team that successfully inoculated monkeys with a killed-virurs vaccine. From…
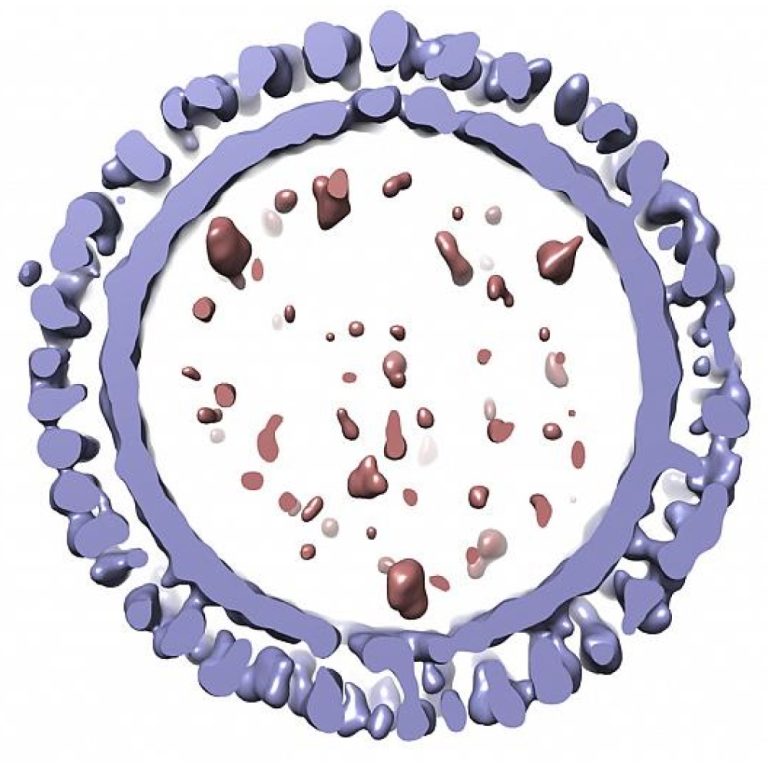
In 1947, during the seasonal flu epidemic, investigators determined that changes in the antigenic composition of circulating influenza…
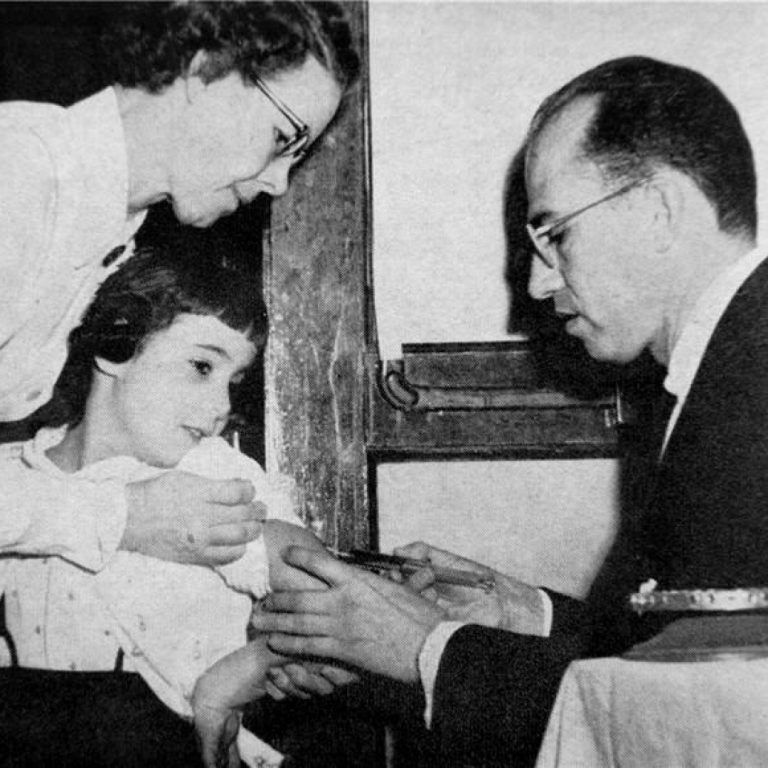
In 1947, Dr. Jonas Salk was recruited from the University of Michigan by Dr. William S. McEllroy, dean…

In late 1946, an outbreak of influenza occurred in Japan and Korea in American troops. It spread in…
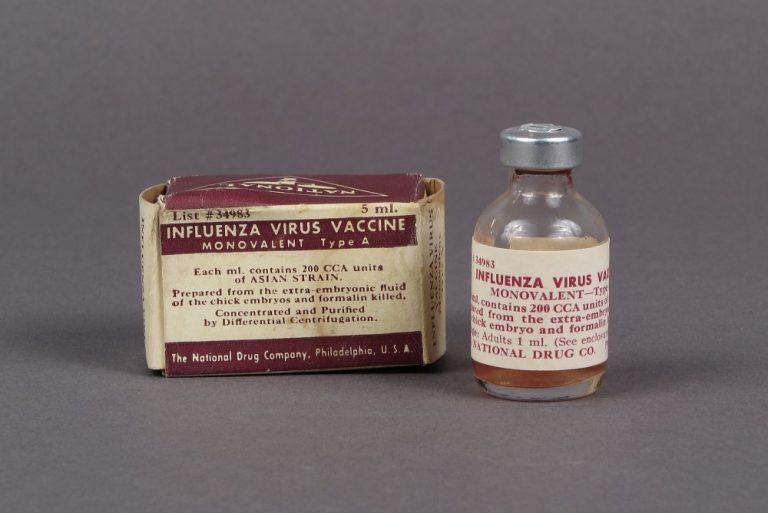
In 1945, the inactivated influenza vaccine was first licensed in the U.S. The first vaccine was an inactivated,…
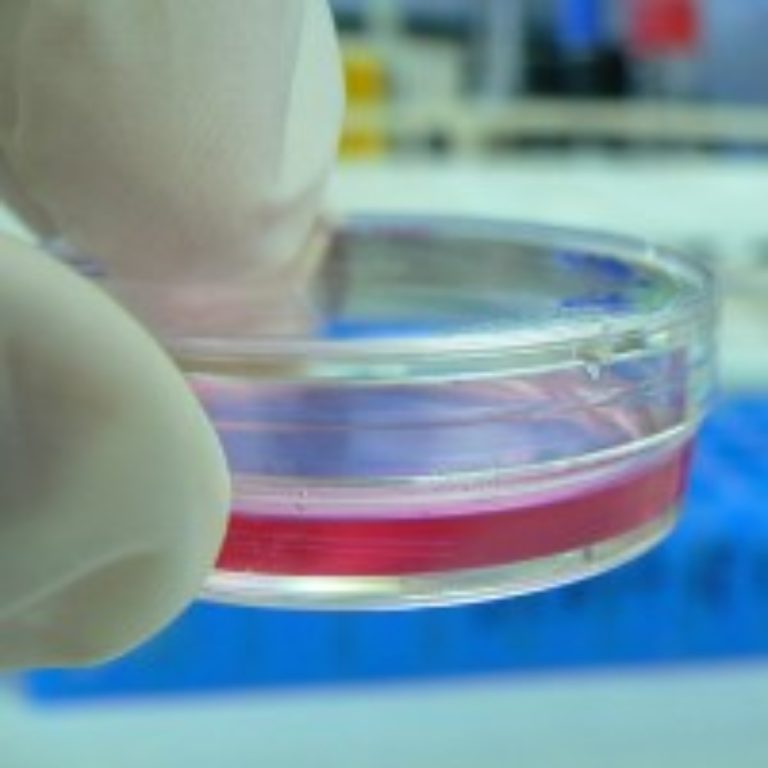
In 1944, the use of cell cultures for virus growth was discovered. This allowed viruses to be cultured…

In 1942, influenza A/B vaccine was introduced to the Armed Forces Epidemiological Board. The vaccine was effective against…

In 1942, Dr. Jonas Salk arrived at the University of Michigan School of Public Health. Techniques earned there…
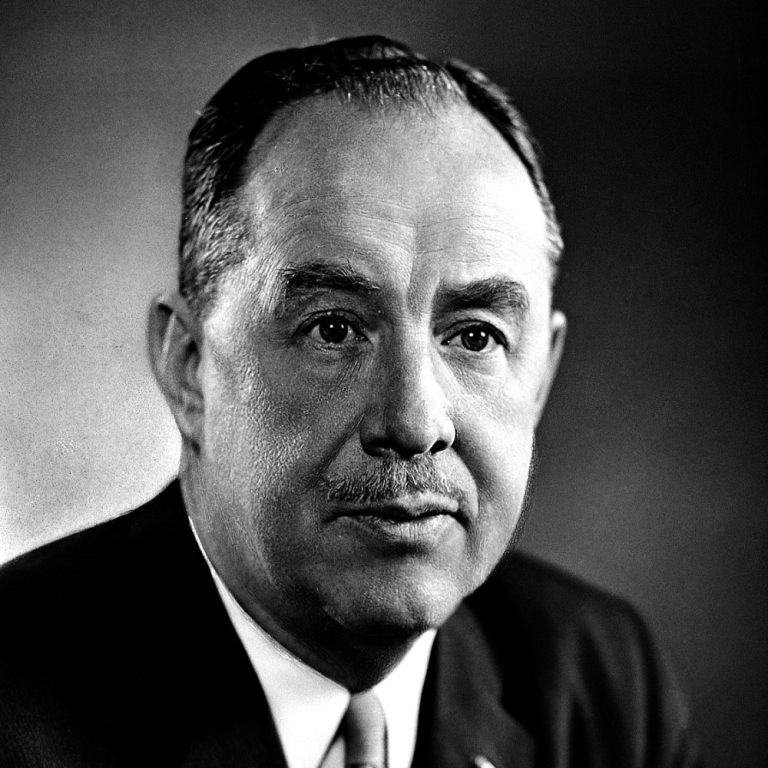

In 1940, Thomas Francis, Jr, MD isolated the influenza B virus from a child in 1940. Francis helped…
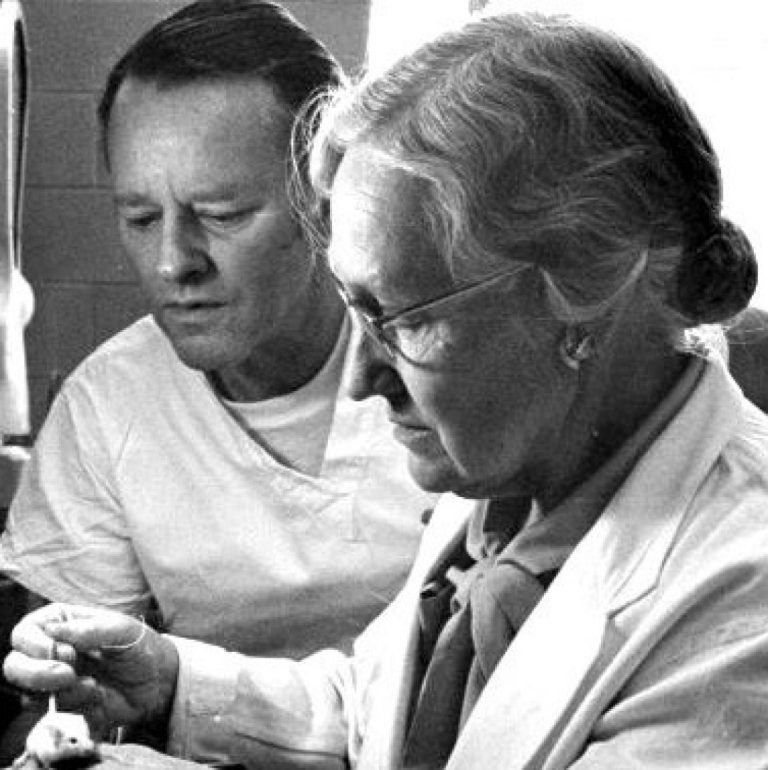

In 1939, Margaret Pittman showed that sulfapyradine was effective against nontype-specific Haemophilus influenzae. Pittman discovered that there are…

In 1938, Thomas Francis, Jr., MD and Jonas Salk, MD served as lead researchers at the University of…
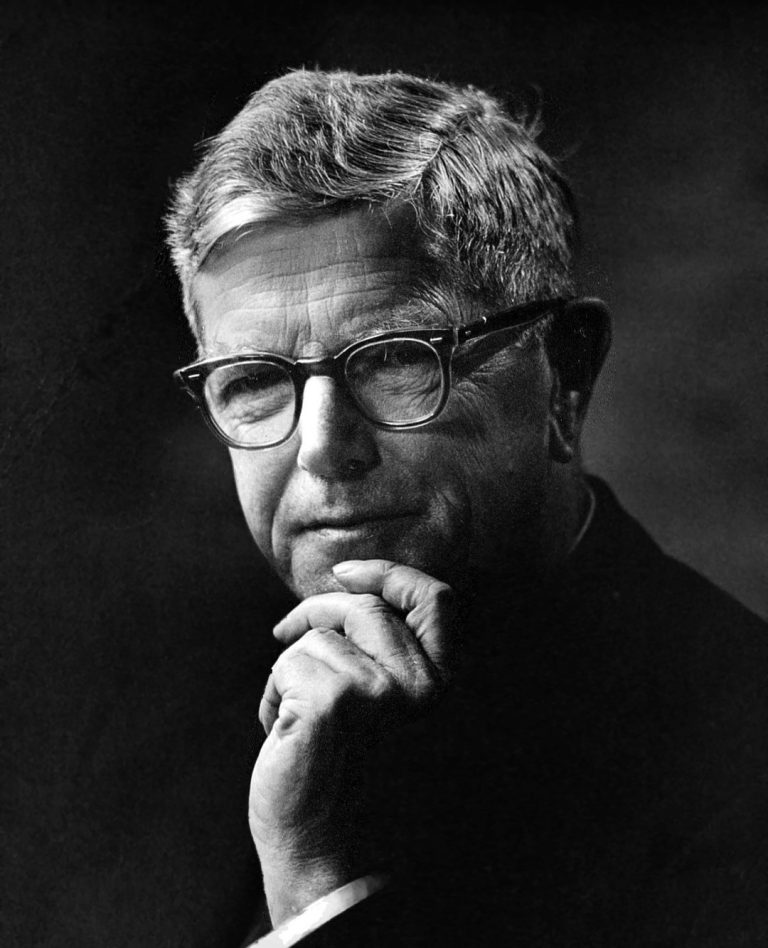

In 1936, Sir Macfarlane Burnet discovered that influenza virus could be grown in embryonated hens’ eggs. This led…

In 1931, Rockefeller Institute investigator Richard Shope published the first of three landmark papers that established the etiology…
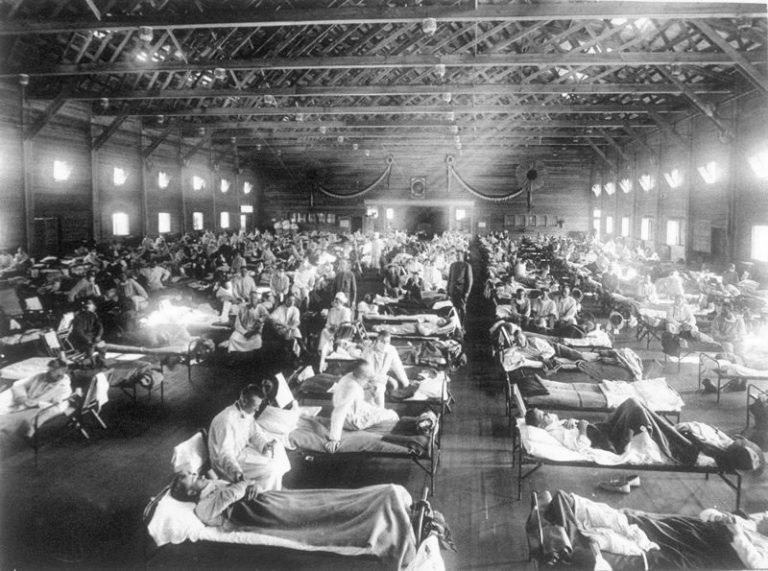
By April 1919, following upticks in influenza over winter, the final tally for New Orleans stood at 54,089…
in 1919, by the end of the influenza epidemic in Omaha, almost 1,200 people had died, with a…
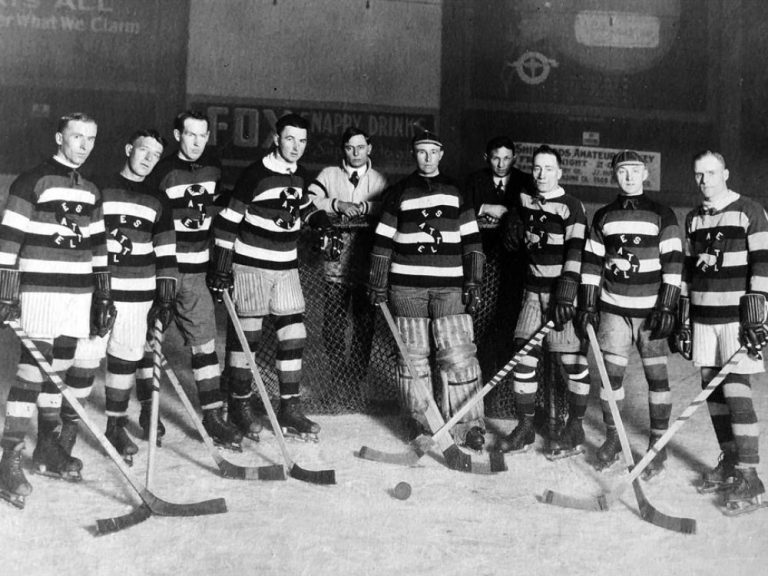

On Apr. 1, 1919, the Stanley Cup playoffs between the Montreal Canadians and the Seattle Metropolitans ended tied…
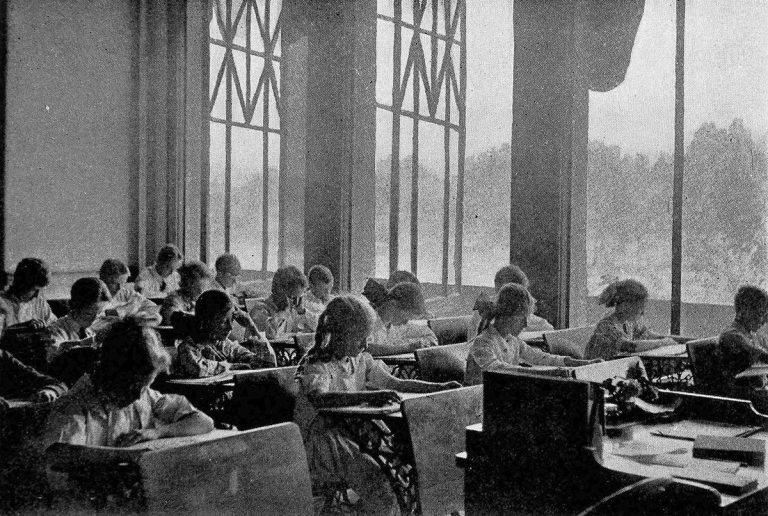

On Jan. 2, 1919, Denver slowly returned to normal after its flu epidemic, and schools reopened. School teachers…
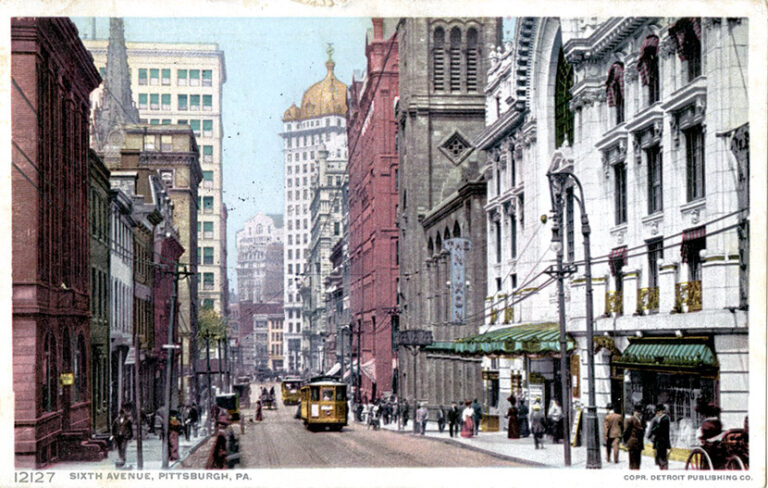

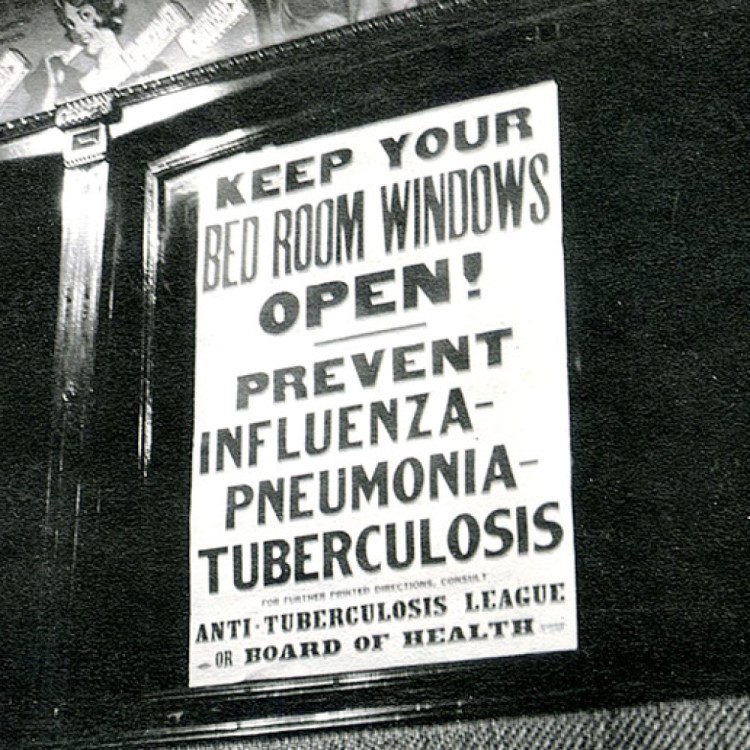
Jan. 1, 1919, brought an increase in the influenza epidemic in Philadelphia and Pittsburgh. With the disease having…
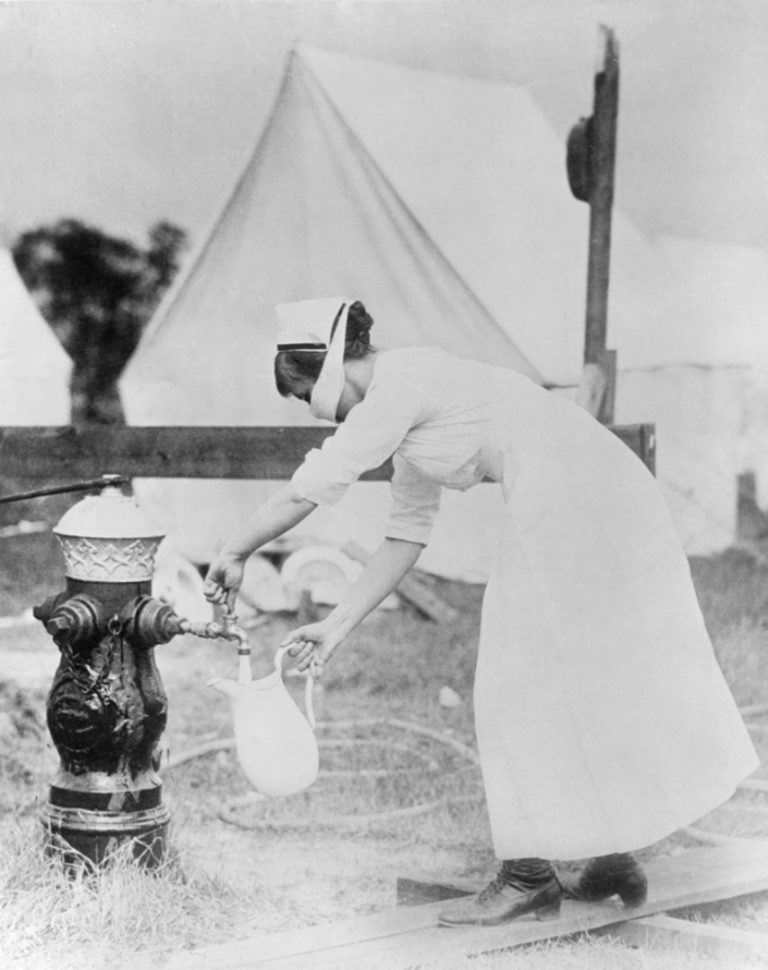

By late February of 1919, Louisville experienced a third wave of influenza cases, but finally began to return…

By 1919, after the end of its second winter influenza wave, Boston had experienced an excess death rate…

In Jan. 1919, Birmingham experienced a third wave in influenza cases and deaths.
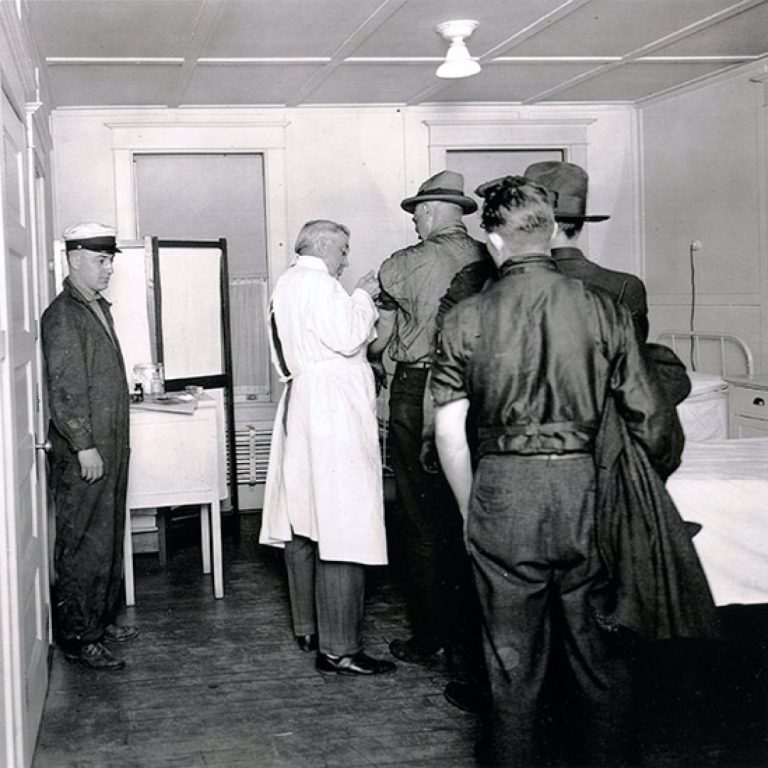

In 1919, Washington, D.C. suffered spikes in influenza cases throughout the remainder of 1918, and into early February…

In 1919, the University of Oregon in Eugene introduced the state’s first professional courses in nursing. The courses…
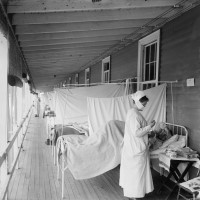
In 1919, influenza cases dwindled through the winter of 1918, yet persisted into April 1919 sporadically. About 9…
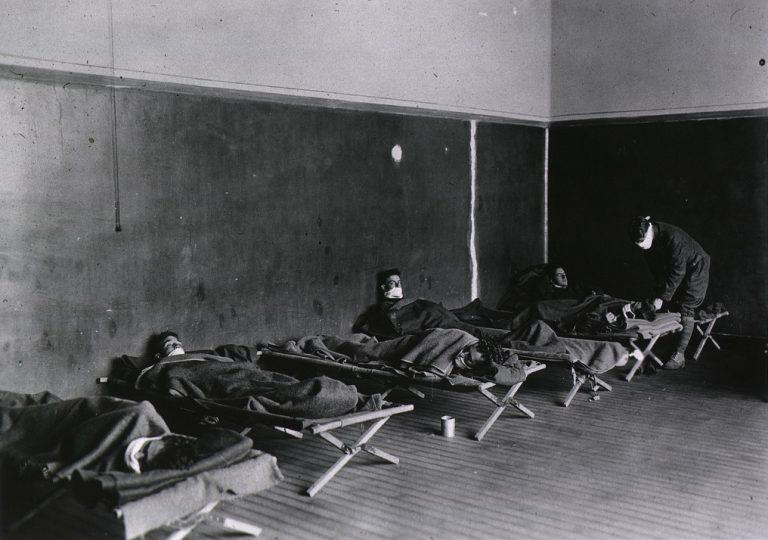
On Dec. 30, 1918, Kansas City schools reopened as the influenza epidemic waned. The New Year came and…

On Dec. 24, 1918, on Christmas Eve, with the epidemic across Nebraska still raging, the state Board of…