U.S. CDC announced International Health Regulations had gone into effect for the U.S.
On Jul. 20, 2007, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced in MMWR that revised…

On Jul. 20, 2007, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced in MMWR that revised…

On Jul. 17, 2007, The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced it was providing states,…

On Jun. 14, 2007, the U.D. of Health and Human Services (HHS) awarded $132.5 million to Sanofi Pasteur…

On Jun. 7, 2007, years before the COVID-19 pandemic swept across the globe, a group of about 100…
On Apr. 17, 2007, Sanofi announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had licensed its H5N1…

On Feb. 1, 2007, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released its long-awaited disease containment strategy…

On Jan. 9, 2007, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had approved a refrigerated form…

On Jan. 9, 2007, the Executive Committee of the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists approved an interim…

On Feb. 6, 2006, Sanofi pasteur announced it had delivered more H5N1 vaccine to the U.S. government including…
On Jan. 17, 2006, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that it had stopped recommending…

On Oct. 7, 2005, a new Federal Medicare rule became effective that required all long-term care facilities to…
On Oct. 7, 2005, Jeffery Taubenberger, AH Reid, AE Krafft, Karen Bijwaard and Thomas Fanning published a report…
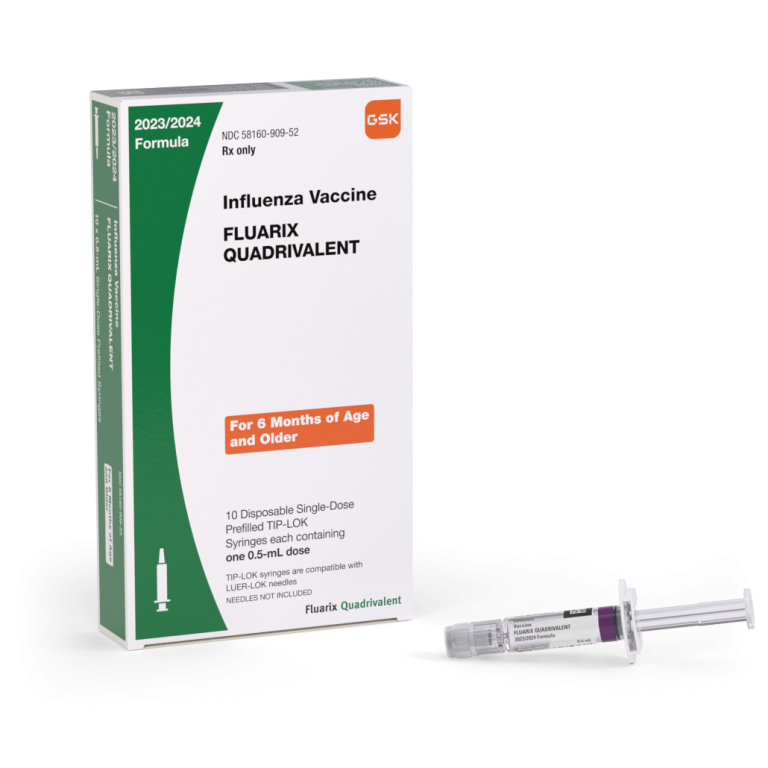
On Aug. 31, 2005, the inactivated, injectable influenza vaccine (Fluarix) by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) was licensed. The vaccine was…
On Apr. 1, 2005, Sanofi pasteur was awarded a five-year $97 million contract from the U.S. Department of…

In 2005 and 2006, the White House Homeland Security Council outlined the National Strategy for Pandemic Influenza to…
On Aug. 25, 2004, a significant shortage of influenza vaccine occurred in the U.S. as a result of…

On May 27, 2004, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) announced it had awarded contracts…

On Oct. 15, 2003, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) voted to recommend that children 6 to 23…

On Jun. 17, 2003, the first nasally administered influenza vaccine (FluMist by MedImmune) was licensed. This live influenza…

In 2003, public health officials reported the re-emergence of H5N1 avian influenza for the first time since an…

On Jan. 1, 2003, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) encouraged that children 6 to 23 months…
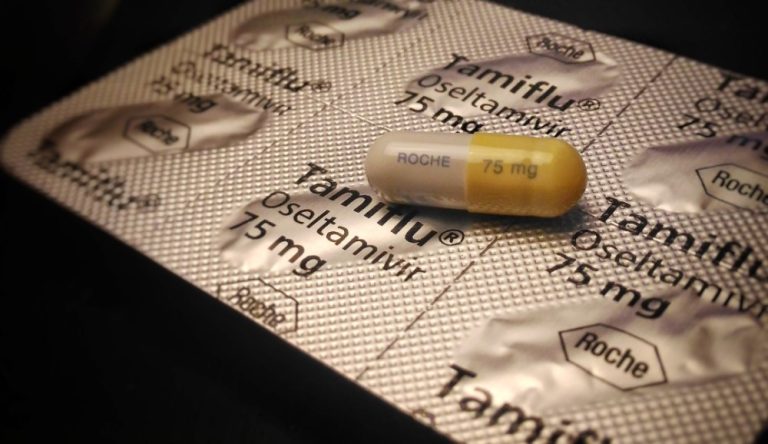
On Oct. 27, 1999, Hoffmann-La Roche and Gilead Sciences announced that Roche’s TAMIFLU (oseltamivir phosphate) had been approved…
On Oct. 27, 1999, Hoffmann-La Roche and Gilead Sciences announced that Roche’s TAMIFLU™ (oseltamivir phosphate) has been approved…

In April 1999, a pandemic planning framework was published by the World Health Organization (WHO) that emphasized the…

In 1998, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) began surveillance of swine for influenza virus in the U.S….

In 1997, FluNet, a global web-based tool for influenza virological surveillance was launched. It is a critical tool…

In 1997, the H5N1 bird flu incident in Hong Kong was the first known instance of a purely…
On Oct. 2, 1996, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed a combined Hib conjugate and hepatitis B…
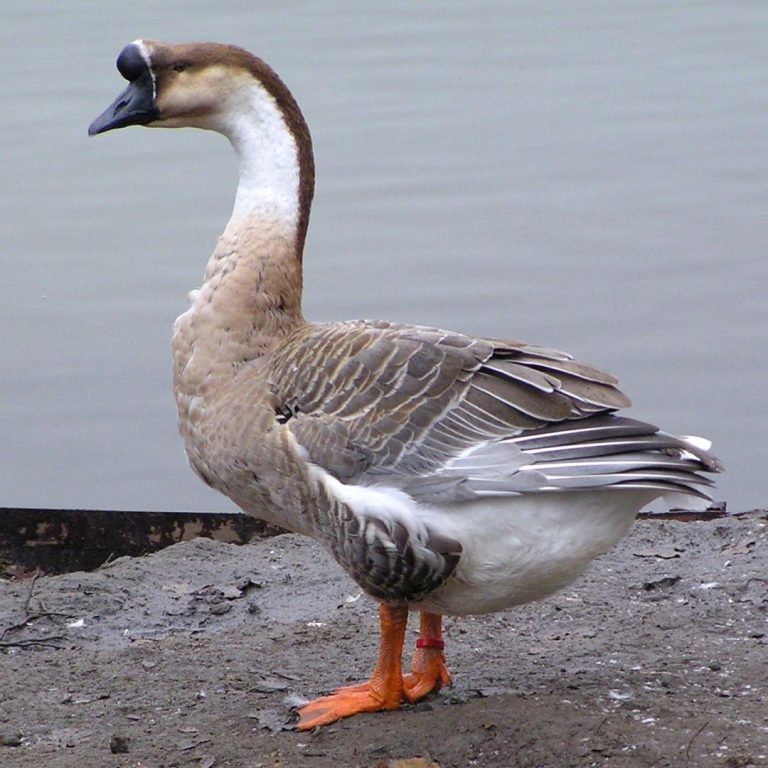

In 1996, A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996 (H5N1), the precursor of the highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza viruses (HPAIVs) was identified in…

In 1995, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP), American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Association of Family…