Mice bred to more closely resemble a genetic variation in humans help target an annual outbreak: the flu
On Feb. 21, 2012, as part of a national collaboration, Oregon Health & Science University researchers were studying…

On Feb. 21, 2012, as part of a national collaboration, Oregon Health & Science University researchers were studying…
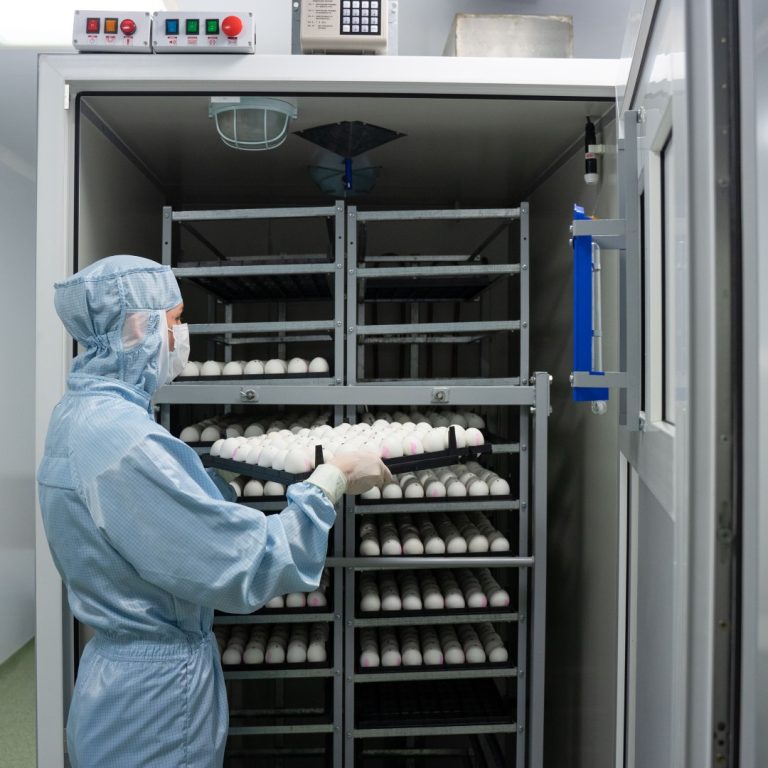

In 2012, vaccines containing cell-cultured virus became available. Even though eggs continued to be the primary means of…
On Dec. 30, 2011, Pfizer announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted approval of…

On Jun. 11, 2011, scientists in China reported the isolation of 2 novel reassortant highly pathogenic avian influenza…

On Aug. 10, 2010, WHO Director-General Dr Margaret Chan announced that the H1N1 influenza virus had moved into…
On Feb. 24, 2010, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) recommended universal Influenza vaccination for those 6 months…
On Jan. 29, 2010, the Bill and Melinda Gates announced that their foundation will commit $10 billion over…
On Dec. 23, 2009, the FDA approved high-dose inactivated influenza vaccine (Fluzone High-Dose) for people ages 65 years…
On Nov. 16, 2009, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended a single dose of…

On Oct. 24, 2009, President Barack Obama declared the swine flu (N1n1) outbreak a national emergency. The declaration…
On Sept. 15, 2009, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved four Influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Monovalent…

On Jul. 31, 2009, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) updates the 2008 recommendations regarding the use of…

On Jun. 23, 2009, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced advanced development contract for…
On Jun. 11, 2009, the Dr. Margaret Chan, Director-General World Health Organization (WHO), declared the world was at…

On May 22, 2009, the U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services (HHS) directed $1 billion toward development…
On Apr. 15, 2009, a novel influenza A virus (then referred to as ‘swine origin influenza A virus’)…

On Apr. 15, 2009, infection with the new influenza A virus (then referred to as ‘swine origin influenza…

On Apr. 15, 2009, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) identified the novel H1N1 influenza…

In Apr. 2009, physicians used point of care rapid immunoassay tests to provide influenza results within 15 minutes…

On Jan. 15, 2009, the U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services (HHS) awarded Novartis a $487 million…

In 2009, Drs. Judith James and Linda Thompson at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation (OMRF) helped develop an…

On Jun. 15, 2008, Australia announced it had approved the first locally made vaccine to protect humans from…

On Feb. 27, 2008, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) voted to expand influenza…

In 2008, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)…

In 2008, the Influenza Reagent Resource (IRR) was established by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)…

On Dec. 12, 2007, Merck voluntarily recalled 1.2 million doses of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccines due…

On Oct. 26, 2007, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) voted to recommend the use of FluMist, the…
On Sept. 28, 2007, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved an Australian-made influenza vaccine called Afluria…

On Sept. 20, 2007, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved use of FluMist nasal-spray influenza vaccine…
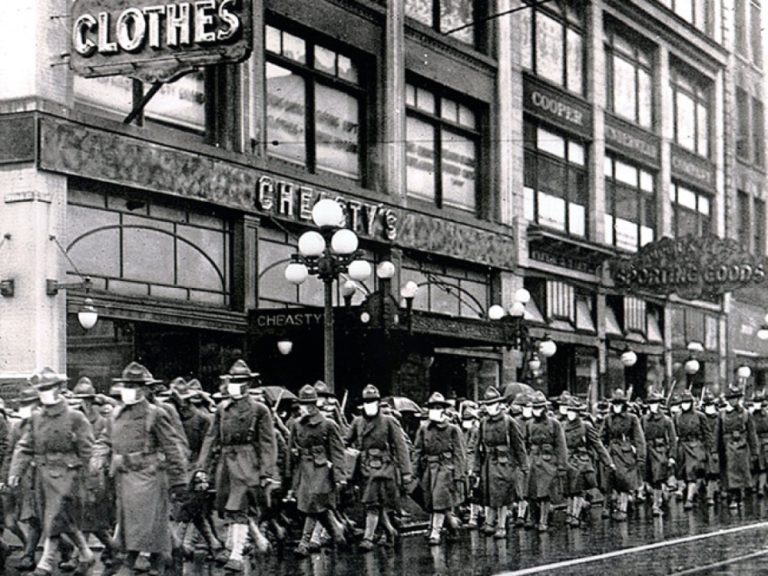

On Aug. 8, 2007, JAMA reported that research demonstrated a strong association between early, sustained, and layered application…