CDC published ACIP’s 2018-19 influenza vaccination recommendations
On Aug. 24, 2018, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee’s (ACIP)…
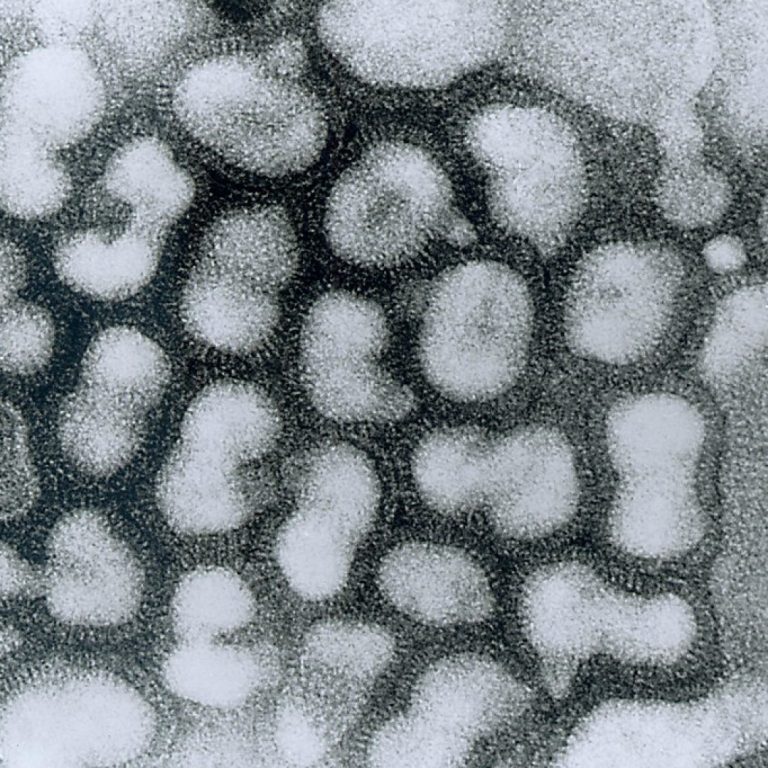
On Aug. 24, 2018, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee’s (ACIP)…

On Jul. 12, 2018, Cue Health announced that is had been awarded up to $30 million in base…
On Jun. 8, 2018, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee…

On Jun. 1, 2018, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) issued a committee opinion on maternal…
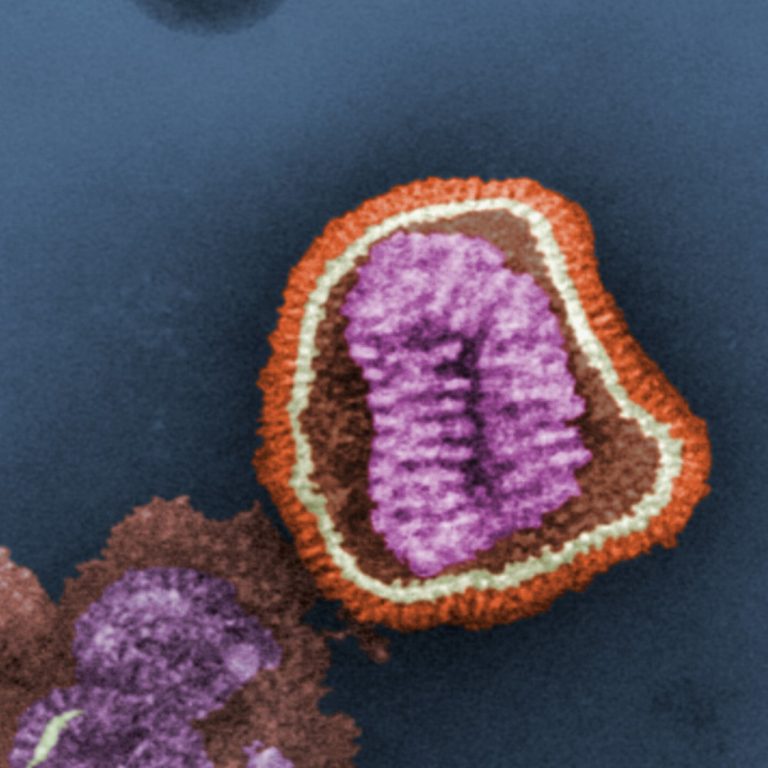
On Apr. 23, 2018, Medigen Vaccine Biologics and GC Pharma entered an exclusive distribution agreement for GCC’s quadrivalent…
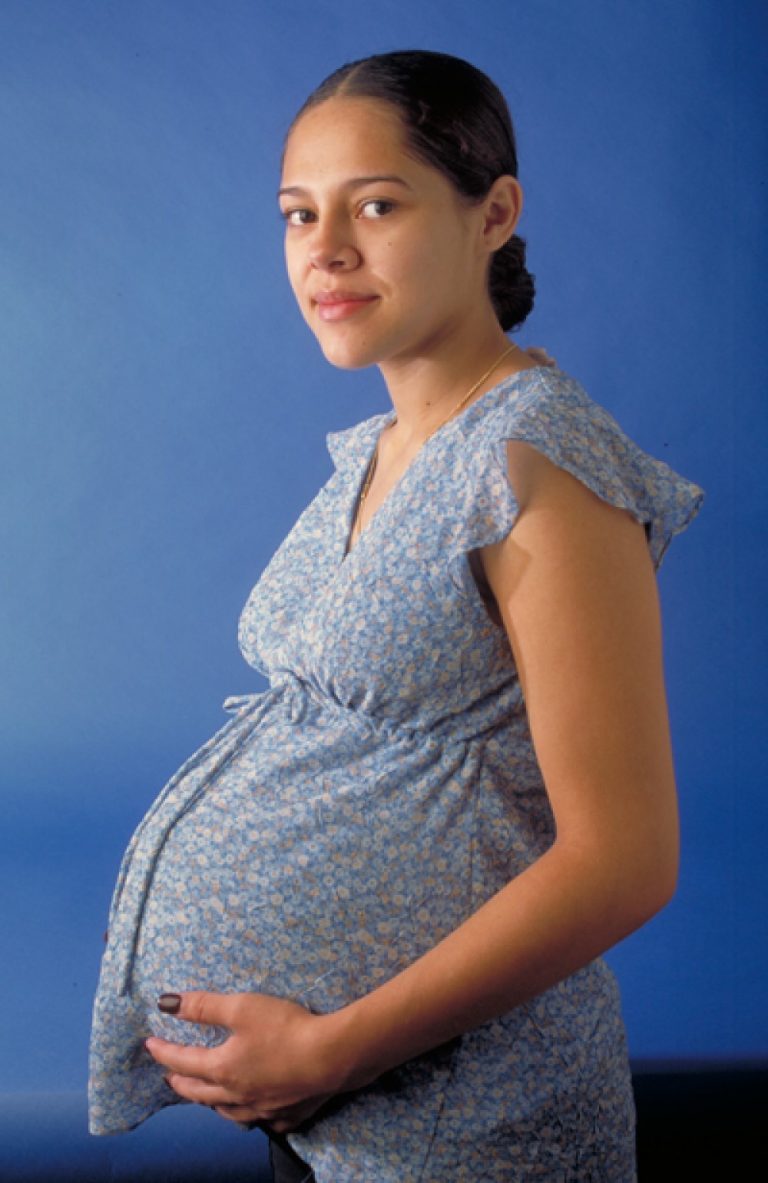

On Apr. 1, 2018, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists released a committee opinion on influenza vaccination…
On Jan. 11, 2018, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved an expanded indication for the four-strain…

On Jan. 9, 2018, armed with 1940s-vintage flu vaccine technology and supported by only anemic funding for developing…

On Aug. 25, 2017, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee…

On Aug. 7, 2017, Seqirus announced that the accelerated development of cell-based manufacturing technology at its state-of-the-art manufacturing…

On Jun. 15, 2017, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) published the nations’s updated Pandemic…

On Apr. 21, 2017, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published updated guidelines for use…

On Dec. 14, 2016, reports from China and South Korea painted a picture of spreading H5N6 avian flu…
On Nov. 18, 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved extending the age range for use…

On Aug. 29, 2016, Seqirus announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved AFLURIA® QUADRIVALENT…

On Aug. 26, 2016, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published 2016-17 influenza vaccination recommendations….

On Jun. 22, 2016, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP)…

On Nov. 25, 2015, Seqirus announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved Fluad™ (Influenza…

On Aug. 14, 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) published “Recommendations on Vaccine Hesitancy” in a special issue…

On Dec. 22, 2014, BioCryst Pharmaceuticals announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved RAPIVAB (peramivir…
On Dec. 12, 2014, Sanofi Pasteur announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved the supplemental…
On Feb. 28, 2014, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee…

On Aug. 1, 2014, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) initiated the Global Heath Security…

On Jul. 2, 2013, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) partnered with Association of Public…

On Jun. 20, 2013, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted 13 to 0, in favor of…

On Jun. 10, 2013, Sanofi Pasteur announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved the supplemental…

On Mar. 26, 2013, GlaxoSmithKline and the Texas A&M University System announced that the U.S. Department of Health…

On Dec. 14, 2012, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had approved GlaxoSmithKline’s quadrivalent formulation…

On Nov. 20, 2012, the FDA approved a seasonal flu vaccine produced by Novartis using animal cell culture…
On Nov. 20, 2012, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had approved first seasonal influenza…