BioAegis demonstrated Gelsolin therapy can quell the cytokine storm and promote tissue repair
On Apr. 27, 2020, BioAegis Therapeutics announced it had published gene expression data in animal studies where recombinant…
On Apr. 27, 2020, BioAegis Therapeutics announced it had published gene expression data in animal studies where recombinant…

On Apr. 17, 2020, Celdara Medical announced that it had entered into a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement…

On Apr. 15, 2020, FUJIFILM announced that it had expanded its manufacturing capacity at FUJIFILM Toyama Chemical Co.,…

On Apr. 9, 2020, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) confirmed the presence of highly pathogenic H7N3 avian…

On Apr. 9, 2020, FUJIFILM announced initiation of a U.S. phase II clinical trial to evaluate the safety…
On Apr. 8, 2020, Nanomix announced that the company had been awarded $570,000 in funding from Biomedical Advanced…

On Apr. 7, 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved an Investigational New Drug application by…
On Apr. 4, 2020, Mesa Biotech announced the addition of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) to its active influenza…

On Apr. 2, 2020, an international collaboration of virologists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and the vaccine companies…

On Mar. 31, 2020, Cue Health announced that is had been awarded up to $30 million in base…

On Mar. 31, 2020, Emergent BioSolutions announced an agreement with Novavax whereby Emergent provided molecule-to-market contract development and…

On Mar. 31, 2020, FUJIFILM announced initiation of a phase III clinical trial to evaluate the safety and…
On Mar. 26, 2020, Amyris announced that it had completed initial testing of a leading vaccine adjuvant. In…
On Mar. 24, 2020, Novavax announced positive top-line results of its pivotal Phase 3 clinical trial of NanoFlu,…
On Mar. 23, 2020, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis announced they were investigating…
On Mar. 20, 2020, a study was published in JAMA that expands the understanding of influenza-associated complications. Influenza…

On Mar. 19, 2020, Mesa Biotech announced it had been awarded a $561,000 contract from the U.S. Department…
On Feb. 24, 2020, Seqirus announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved the first…
On Dec. 12, 2019, BioAegis Therapeutics announced publication of new research findings with recombinant human plasma gelsolin in…
On Dec. 12, 2019, Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) researchers James Crowe Jr., MD, and colleagues announced they…

On Dec. 11, 2019, Seqirus announced that its cell-based quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIVc) had received approval from Health…
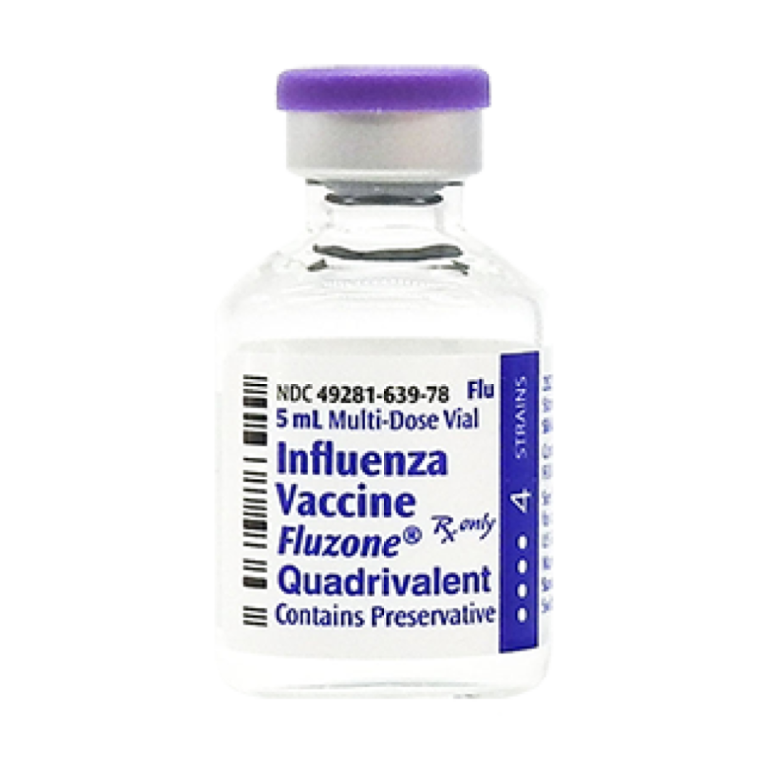
On Nov. 4, 2019, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Fluzone High-Dose Quadrivalent (Sanofi Pasteur) for…

On Oct. 17, 2019, Genentech announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved Xofluza (Baloxavir Marboxil),…
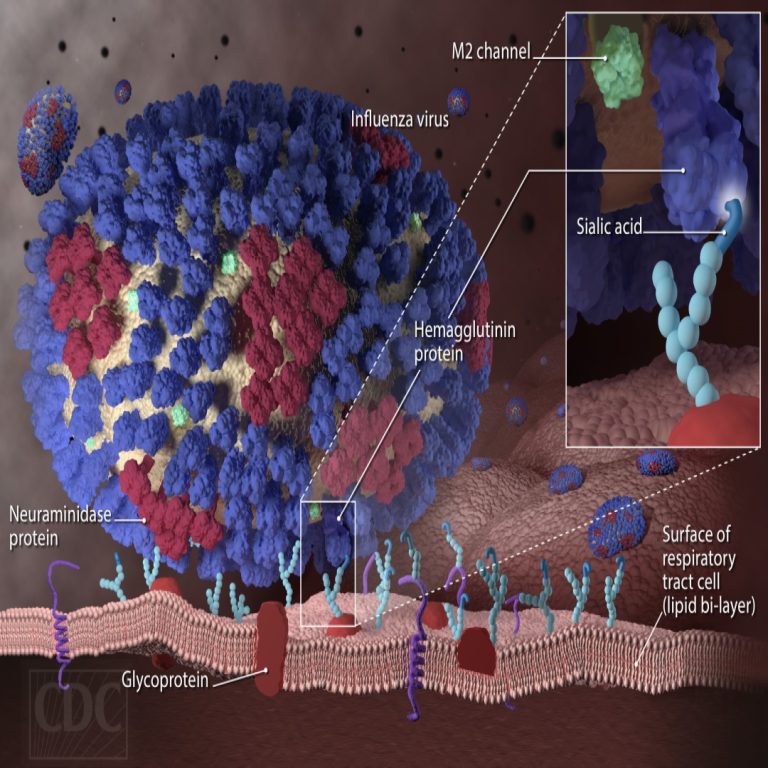
On Sept. 30, 2019, the University of Georgia (UGA) announced it had signed a contract with the National…
On Aug. 23, 2019, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP)…

In Jun. 2019, Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) announced it had funded a $21.9 gene modulation research…

On Jun. 5, 2019, Vaccitech announced that it has administered its pandemic universal influenza A vaccine MVA-NP+M1 (VTP-100)…

On Jan. 23, 2019, U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had approved approved the use of…

On Dec. 5, 2018, Seqirus, a CSL subsidiary, announced real-world data showing that its cell-based quadrivalent influenza vaccine…

On Oct. 24, 2018, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had granted approval of Xofluza…