The ACIP updated flu vaccine recommendations for 2020-2021
On Sept. 9, 2020, the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) reviewed and agreed with the Advisory Committee…

On Sept. 9, 2020, the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) reviewed and agreed with the Advisory Committee…

On Sept. 8, 2020, LabCorp announced the launch of the first testing method to simultaneously detect COVID-19, influenza…

On Sept. 7, 2020, DiaSorin Molecular announced that it had received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Clearance…
On Sept. 3, 2020, Sanofi and GSK announced the start of the Phase 1/2 clinical trial for their…

On Sept. 3, 2020, BioCryst Pharmaceuticals announced that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) had…

On Sept. 3, 2020, Roche announced that the cobas SARS-CoV-2 & Influenza A/B Test for use on the…
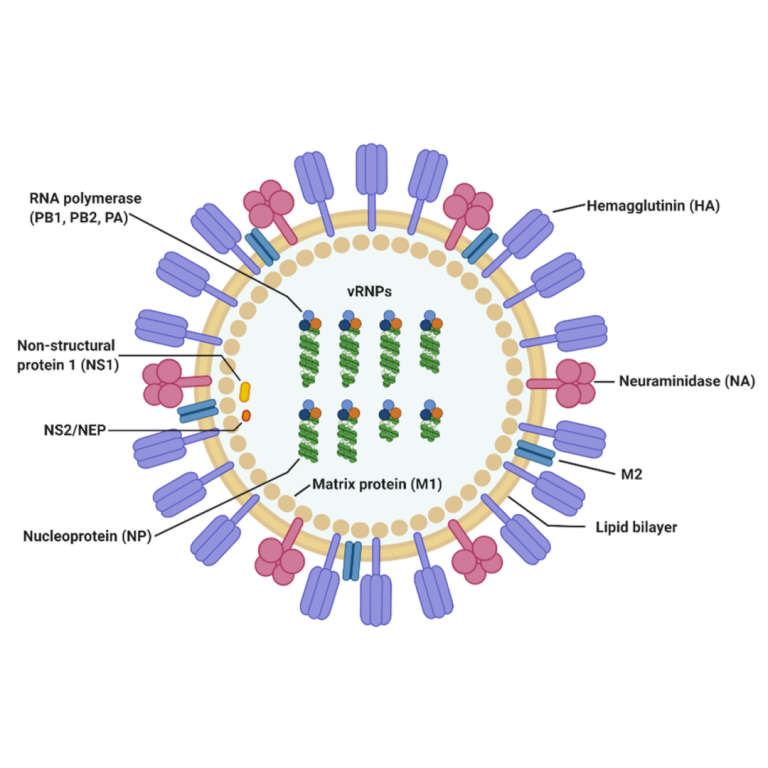
On Sept. 2, 2020, the Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson announced that it had made a…

On Sept. 2, 2020, MicroGEM announced it had been awarded up to $40.9 million by the National Institutes…
On Aug. 21, 2020, the CDC published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) 2020-21 influenza vaccination recommendations. Routine annual…

On Aug. 12, 2020, Celdara Medical announced that the NIH had awarded a Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR)…

On Jul. 31, 2020, Sanofi and GSK announced advanced discussions, with the European Commission for the supply of…

On Jul. 30, 2020, Seqirus announced it had begun shipping its portfolio of seasonal influenza vaccines to customers…
On Jul. 29, 2020, Sanofi and GSK announced an agreement with the UK government for the supply of…
On Jul. 27, 2020, MediciNova announced an agreement with BioComo and Mie University (Mie prefecture, Japan) for joint…

On Jul. 16, 2020, Dynavax Technologies and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai announced they had…

On Jul. 15, 2020, Tevogen Bio announced its intention to evaluate its proprietary antigen-specific T cell technology as…

On Jul. 13, 2020, Tonix Pharmaceuticals announced a new preclinical research and option agreement with Kansas State University…
On Jul. 8, 2020, the European Commission announced regulatory approval for the first adjuvanted quadrivalent influenza vaccine to…

On Jul. 6, 2020, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the third diagnostic test for…

On Jul. 2, 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for…
On Jul. 2, 2020, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced a publication in the…

On Jun. 24, 2020, Sinovac Biotech announced the China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) issued a product license…

On Jun. 23, 2020, scientists at Scripps Research reported that some common strains of influenza have the potential…

On Jun. 11, 2020, Quidel announced it had received funding from the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority…
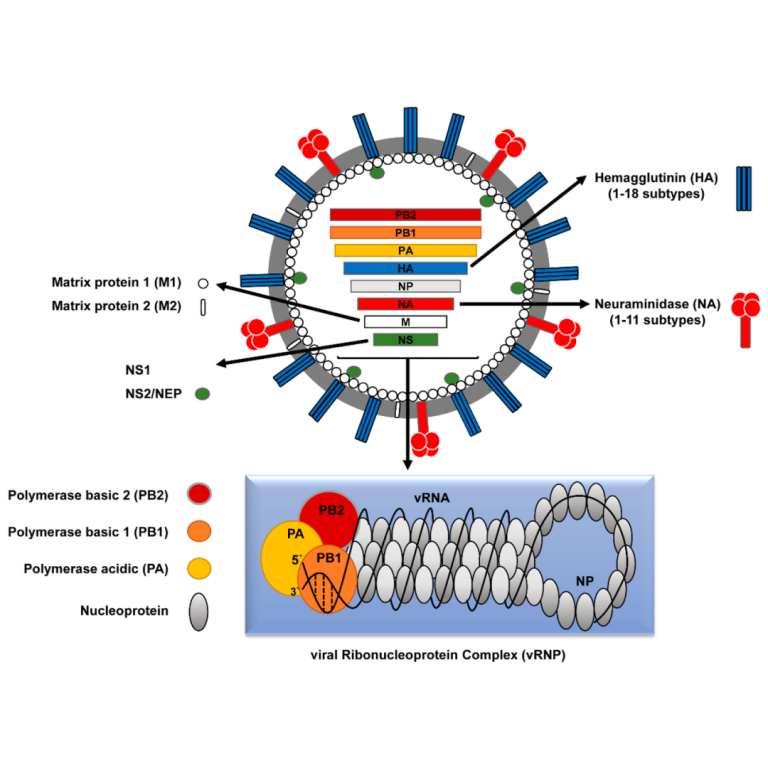
On Jun. 8, 2020, Intravacc and Versatope announced that they have signed a research service agreement to further…

On May 6, 2020, Baxter announced results of the Fluid Response Evaluation in Sepsis Hypotension and Shock (FRESH)…

On May 6, 2020, Predictive Oncology announced the acquisition of Soluble Therapeutics and partnership and licensing of a…
On Apr. 29, 2020, Emory University played a leading role in the government-sponsored clinical trial of the COVID-19…
On Apr. 27, 2020, BioAegis Therapeutics announced it had published gene expression data in animal studies where recombinant…

On Apr. 17, 2020, Celdara Medical announced that it had entered into a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement…