CDC study showed 2019-20 flu vaccine effectively prevented hospitalizations and emergency visits in children
On Jan. 27, 2021, a U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) study found that the 2019-2020…
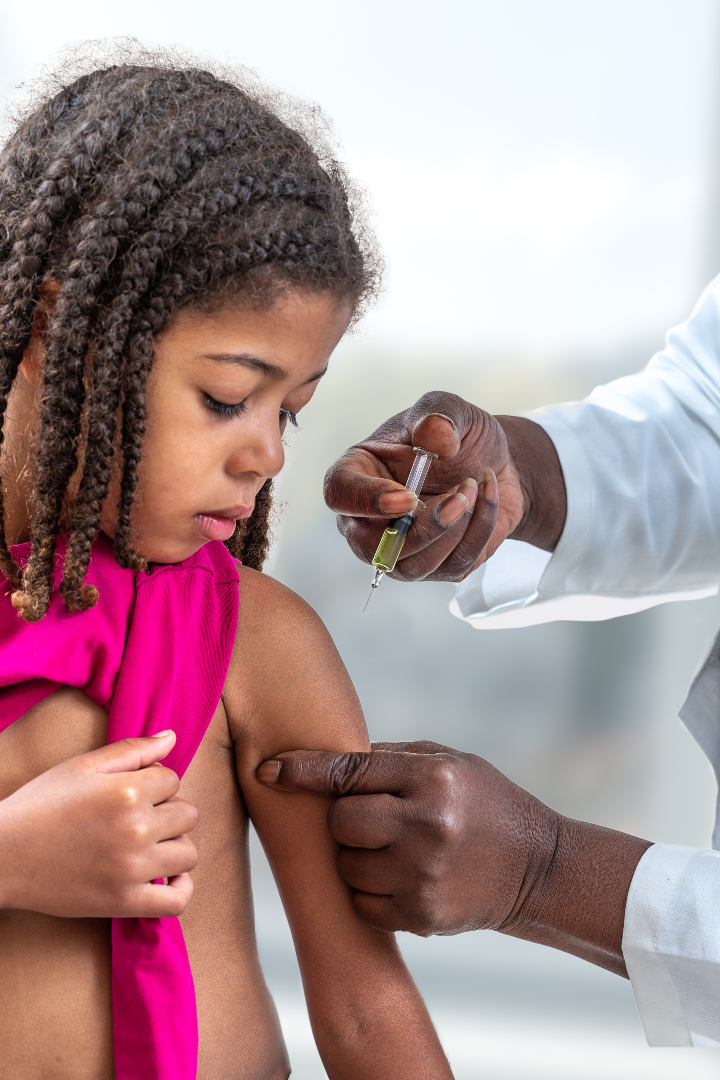
On Jan. 27, 2021, a U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) study found that the 2019-2020…

On Jan. 11, 2021, Roche announced that the European Commission (EC) had approved Xofluza (baloxavir marboxil) for the…
On Jan. 11, 2021, Moderna announced that it was expanding its pipeline of innovative vaccines with three new…

On Jan. 7, 2021, Twist Bioscience announced it would supply the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention…

On Dec. 21, 2020, Quidel announced that it had received Emergency Use Authorization from the U.S. Food and…

On Dec. 7, 2020, an universal influenza virus vaccine, which produces antibodies that target the part of the…

On Dec. 4, 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorized the first diagnostic test for at home collection…
On Dec. 4, 2020, it was reported in JAMA that high-dose influenza (commonly known as flu) vaccines are…
On Nov. 24, 2020, Roche announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved a supplemental…

On Nov. 23, 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) expanded the approved indication for Genentech’s Xofluza…

On Nov. 20, 2020, the ‘European Food Safety Authority reported that within the past month more than 300…
On Nov. 19, 2020, XBiotech announced data for its breakthrough candidate therapy for treating infections of influenza and…

On Nov. 17, 2020, Celdara Medical announced that the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID) of…

On Nov. 16, 2020, Aegis Sciences announced that it had launched a combined test for SARS-CoV-2 and influenza…
On Nov. 13, 2020, Roche announced that the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human…
On Nov. 6, 2020, Mesa Biotech announced it had been awarded a contract up to $13 million from…
On Nov. 2, 2020, Novavax announced the expansion of its Maryland campus to accommodate the company’s rapid growth…

On Oct. 26, 2020, PerkinElmer announced that its PKamp Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Panel had received clearance to be…

On Oct. 21, 2020, CerTest Biotec, along with BD (Becton, Dickinson), announced that the VIASURE SARS-CoV-2 (N1 +…
On Oct. 20, 2020, BioReference Laboratories, an OPKO Health company, announced that it was accepting specimens for a…
On Oct. 15, 2020, scientists from the University of Oxford’s Department of Physics announced they had developed an…

On Oct. 8, 2020, Moderna announced an agreement for a commitment of up to $56 million from the…

On Oct. 7, 2020, Sonic Healthcare USA announced that it had launched a multiplex RT-PCR assay that combined…

On Oct. 6, 2020, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced funding of a patch…

On Oct. 5, 2020, Vaxxas announced a $22 million United States government award to support the deployment of…
On Oct. 2, 2020, Quidel announced that it had received Emergency Use Authorization from the U.S. Food and…
On Sept. 30, 2020, Quest Diagnostics announced three different test options for healthcare providers across the U.S.to aid…
On Sept. 30, 2020, BD (Becton, Dickinson) announced its rapid, point-of-care, SARS-CoV-2 antigen test for use on the…

On Sept. 21, 2020, XBiotech announced it was developing a new breakthrough candidate therapy it calls FLUVID for…
On Sept. 18, 2020, Sanofi and GSK finalised and signed an advanced purchase agreement with the European Commission…