Moderna confirmed discussions with government of South Korea to supply 40 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine
On Dec. 29, 2020, Moderna confirmed that the Company was engaged in discussions with the government of South…
On Dec. 29, 2020, Moderna confirmed that the Company was engaged in discussions with the government of South…

On Dec. 29, 2020, University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) and Nebraska Medicine announced participation in a clinical…
On Dec. 28, 2020, Novavax announced initiation of PREVENT-19, its pivotal Phase 3 study in the U.S. and…

On Dec. 24, 2020, Inovio Pharmaceuticals announced publication of peer-reviewed Phase 1 clinical data from the first cohort…

On Dec. 24, 2020, AIM ImmunoTech announced that the post-COVID-19 ‘Long Hauler’ portion of the active AMP-511 Expanded…

On Dec. 23, 2020, Moderna announced that Health Canada had authorized its vaccine against COVID-19 for the immunization…

On Dec. 23, 2020, recent tests confirmed mink that tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 at an Oregon farm in…
On Dec. 21, 2020, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) announced a study published in the Proceedings…

On Dec. 21, 2020, the U.S. Dept. of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced that it had begun COVID-19 vaccinations…

On Dec. 21, 2020, Quidel announced that it had received Emergency Use Authorization from the U.S. Food and…

On Dec. 19, 2020, after a transparent, evidence-based review of available data, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices…

On Dec. 18, 2020, the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) announced it was providing advisory services and…

On Dec. 18, 2020, the FDA issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the second vaccine for the…

On Dec. 18, 2020, Eli Lilly announced plans to begin a new pragmatic study of bamlanivimab (LY-CoV555) in…

On Dec. 18, 2020, Moderna announced that the European Commission (EC) had exercised its option to purchase an…
On Dec. 18, 2020, Moderna announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had authorized the emergency…

On Dec. 18, 2020, Moderna announced that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Advisory Committee on…

On Dec. 16, 2020, Novavax announced an Advance Purchase Agreement with the government of New Zealand for the…

On Dec. 15, 2020, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals announced the funding and initiation of an open-label exploratory trial evaluating the…

On Dec. 15, 2020, Inovio Pharma announced the company and a team of scientists from The Wistar Institute,…
On Dec. 14, 2020, the U.S. Dept. of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced that the New Orleans and Bedford,…
On Dec. 14, 2020, Anixa Biosciences announced that it and partner OntoChem GmbH had verified that one of…
On Dec. 14, 2020, Moderna confirmed that the Company had concluded an agreement with the Ministry of Health…
On Dev. 11, 2020, the University of Oxford reported that an Artificial Intelligence test had been shown to…
On Dec. 11, 2020, Moderna announced that the U.S. government has exercised its option to purchase an additional…

On Dec. 10, 2020, Roche announced a partnership with Moderna to utilise the Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S antibody test…
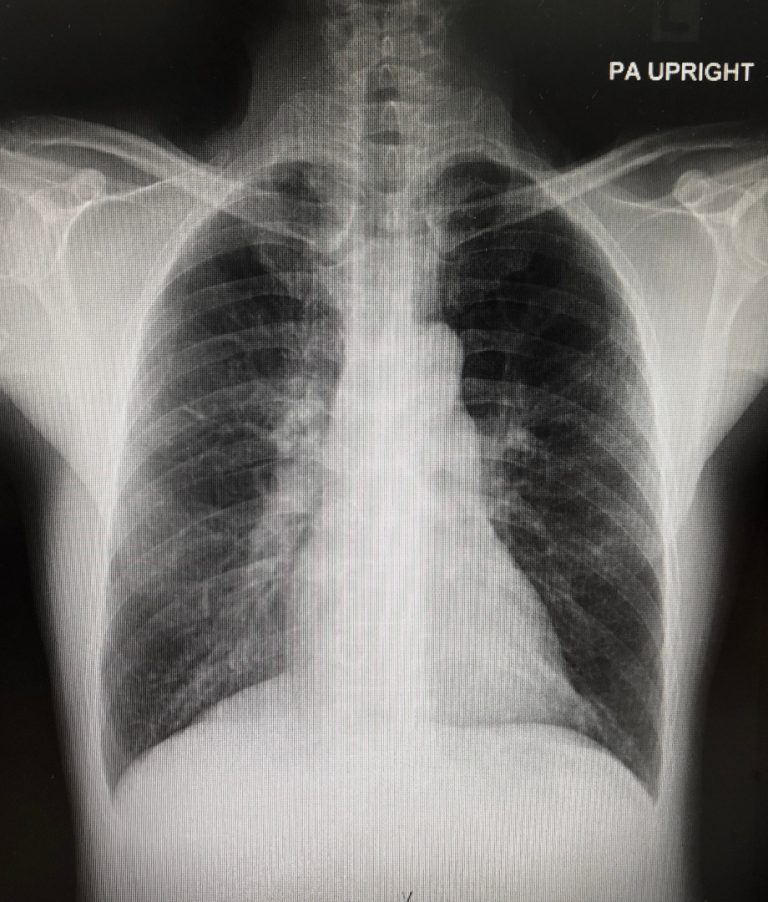
On Dec. 10, 2020, ImmunityBio announced its COVID-19 vaccine candidate protected nasal and lung airways of non-human primates…
On Dec. 10, 2020, Moderna announced that the first adolescent participants had been dosed in the Phase 2/3…

On Dec. 9, 2020, Roche announced a partnership with Moderna to utilise the Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S antibody test…

On Dec. 8, 2020, Moderna announced the Swiss Federal Government had increased its confirmed order commitment from 4.5…