University of Washington Population Health Initiative received $210 million transformative gift from the Gates Foundation
On Oct. 25, 2016, the University of Washington’s Population Health Initiative received a $210 million gift from the…

On Oct. 25, 2016, the University of Washington’s Population Health Initiative received a $210 million gift from the…

On Jun. 24, 2016, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released the results of its…

On June 22, 2016, President Barack Obama signed the Frank R. Lautenberg Chemical Safety for the 21st Century…

On May 13, 2016, the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) announced a new National…

On Mar. 3, 2016, the University of Oregon (UO) announced receipt of a $10 million gift from Tim…

On Jan. 11, 2016, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) research scientist David J. Smith reported finding that…

On Jan. 29, 2015, a Rutgers University study suggests that pregnant women and young children are more susceptible…
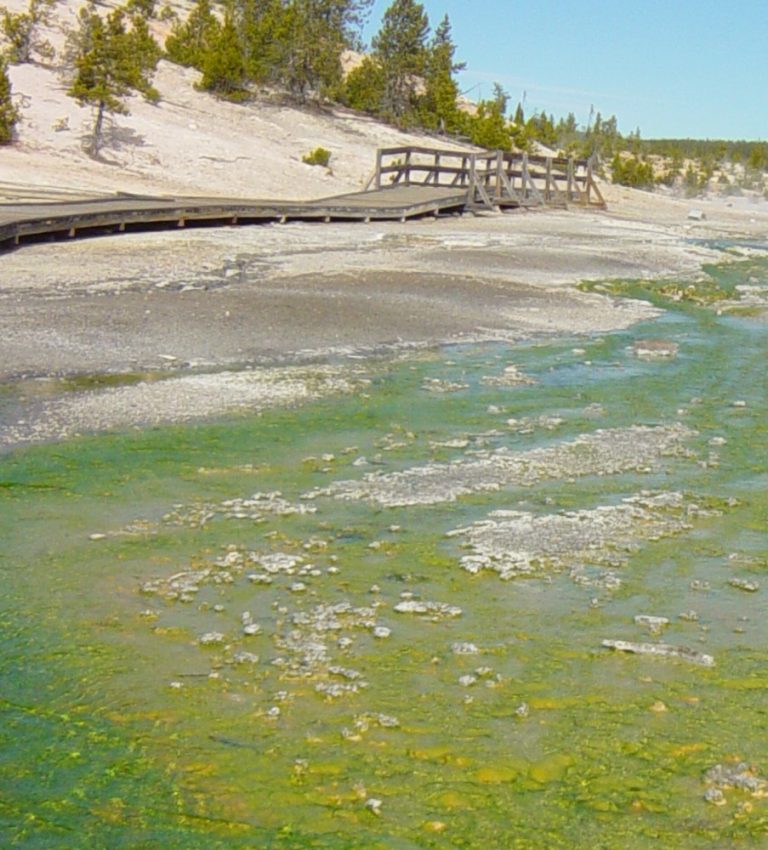

On Sept. 19, 2013, Thomas Brock and Hudson Freeze received the Golden Goose Award for their discovery of…
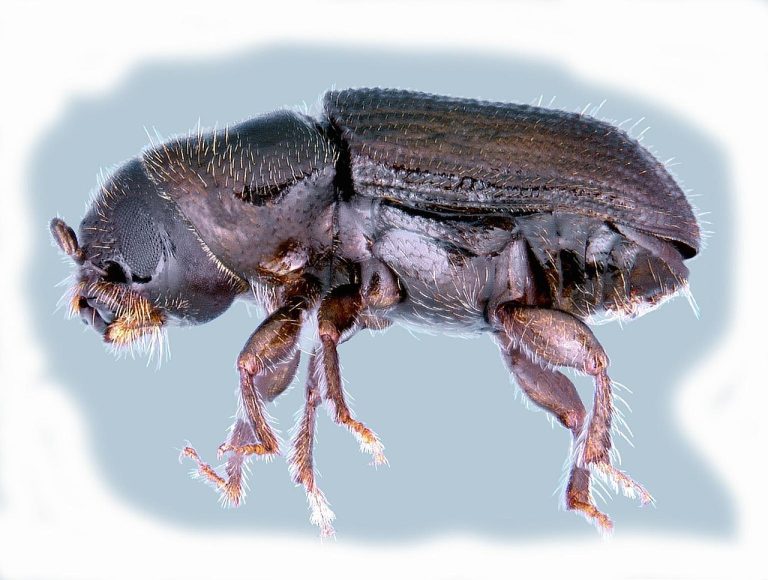

On Mar. 27, 2013, researchers at the University of British Columbia and Canada’s Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre,…

On Jun. 25, 2012, the Rocky Mountain Biological Laboratory (RMBL) announced the unveiling of its Legacy Campaign, a…
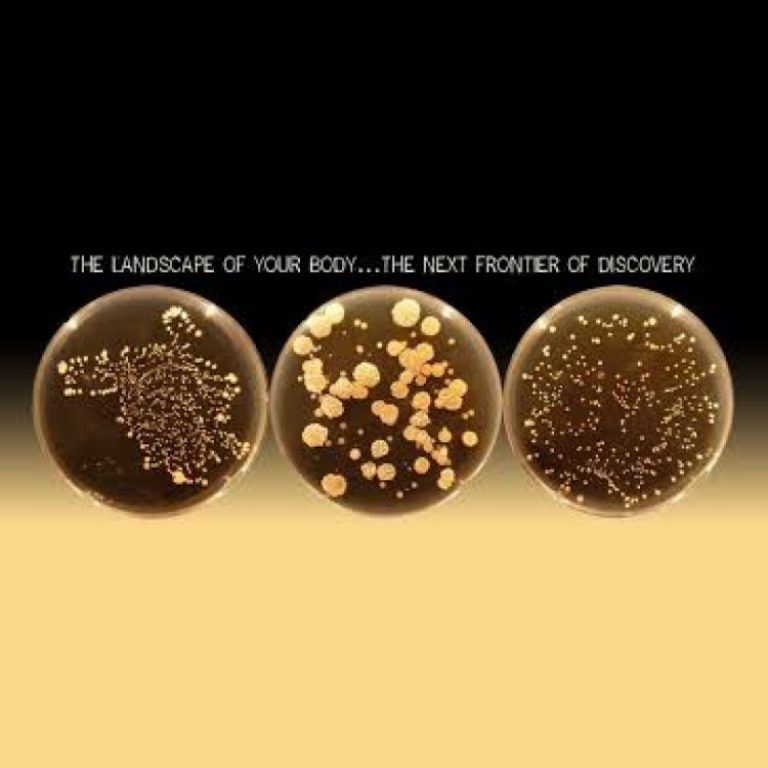
On Jan. 3, 2011, the Belly Button Biodiversity project was launched to investigate the microbes inhabiting our navels…

On Dec. 31 2010, In a meeting report from the Terabase Metagenomics Workshop in Snowbird, Utah, the Vision…
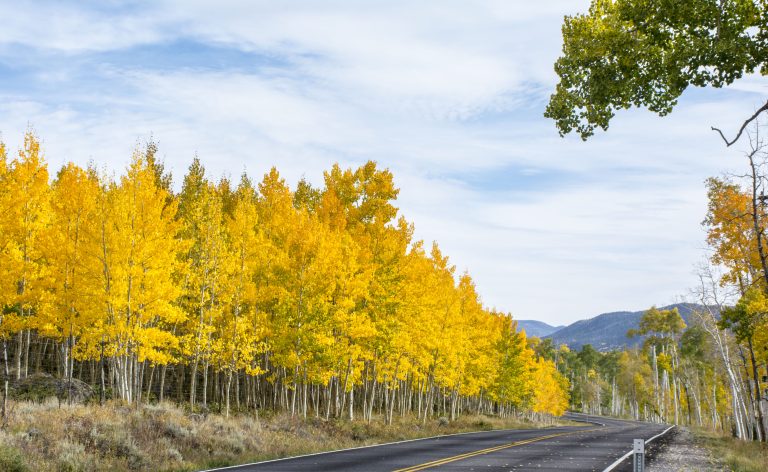

On Sept. 30, 2010, Utah State University geneticist Karen Mock announced that testing of a forest-size collection of…
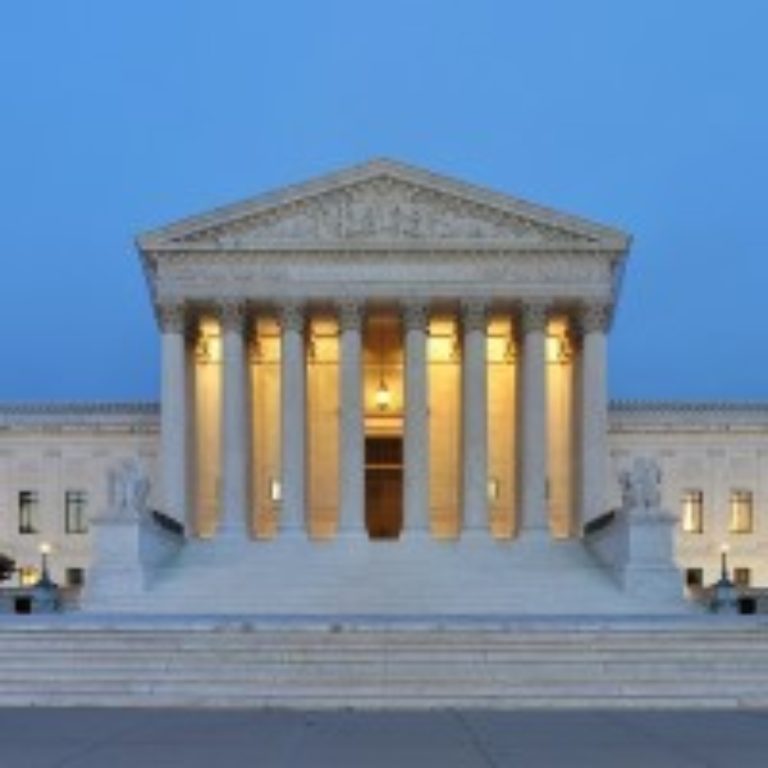

On Jun. 21, 2010, the U.S. Supreme Court lifted a nationwide ban on cultivation of biotech alfalfa by…
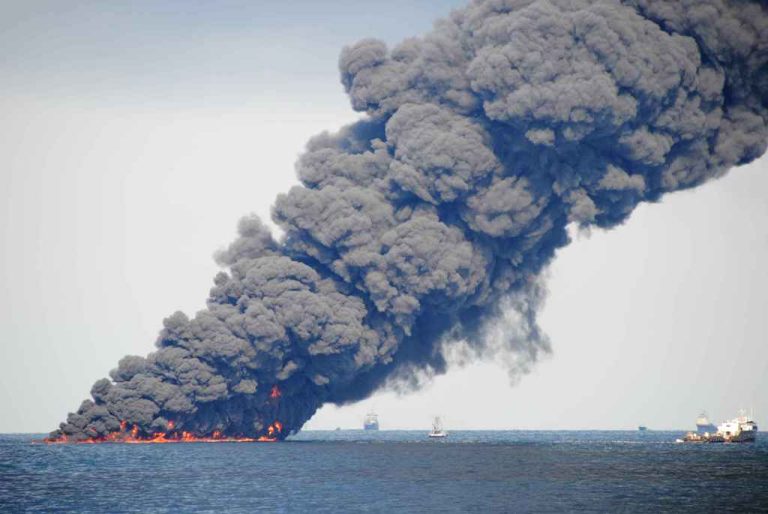

On May 28, 2010, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) received a request for a…

On Oct. 13, 2009, environmentalist and former genetics professor David Suzuki received the Right Livelihood Award for his…

In 2009, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) addressed widespread asbestos contamination in Libby, Montana….

On May 13, 2008, the U.S. Congress passed the Breast Cancer and Environmental Research Act which amended the…

On Jun. 27, 2006, the U.S. Surgeon General released a report on the harmful health consequences of involuntary…

On Jan. 17, 2006, researchers at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) announced the development of a…

On Aug. 29, 2005, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) responded to the crises presented…

In 2005, the Georgia Legislature passed the Smoke Free Air Act, banning indoor smoking in publicly accessible buildings,…

Apr. 14, 2004, the National Center for Vermiculite and Asbestos-Related Cancers was established in Michigan in response to…

On Apr. 10, 2000, the Oregon Health Science Centers (OHSU) Center for Research on Occupational and Environmental Toxicology…

On Nov. 21, 1997, the FDA Modernization Act (FDAMA) was signed into law, amending the Food, Drug and…
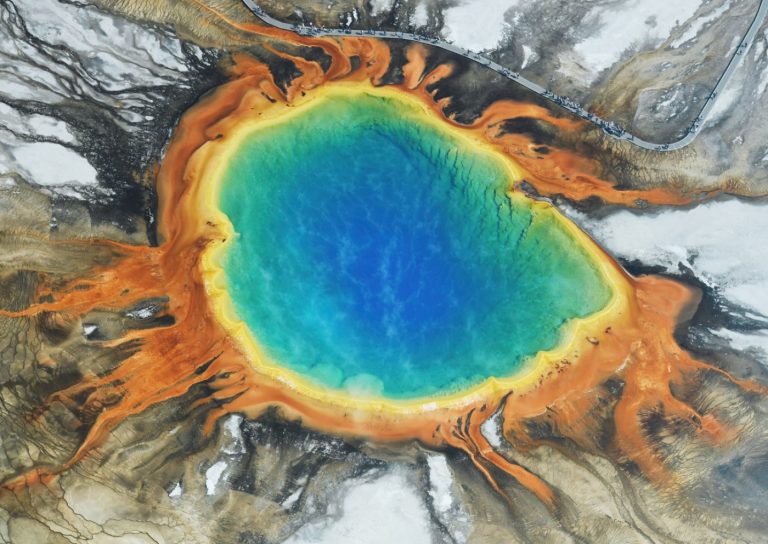

In August 1997, Thomas Brock and undergraduate student Hudson Freeze published their discovery of Thermus aquaticus, which they…

In 1997, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and Chinese scientists found that occupational exposure to benzene is associated…

Dec. 5, 1996, marked the first time that all home buyers and tenants have the right to know…

On Jan. 29, 1996, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Administrator Carol M. Browner took the last steps concluding a…
In 1996, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found evidence of tobacco smoke exposure in…