Masters of acclimation: Octopuses adjust to cold by editing their RNA
On Jul. 25, 2023, U.S. National Science Foundation-supported research, led by Joshua Rosenthal of the Marine Biological Laboratory…

On Jul. 25, 2023, U.S. National Science Foundation-supported research, led by Joshua Rosenthal of the Marine Biological Laboratory…

On Apr. 7, 2023, the U.S. National Park Service reported Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) had been confirmed…
On Feb. 28, 2023, Public Health Delta & Menominee Counties (PHDM) was alerted to three cases of atypical…

On Jan. 19, 2023, researchers at ETH Zurich and the Swiss Federal research institute WSL announced they had…

On Jan. 1, 2023, a study published in the Lancet reported that concentrations of antibiotic residues found in…

On Dec. 7, 2022, scientists reported in Nature an ancient environmental DNA (eDNA) record describing the rich plant…

On Nov. 28, 2022, the U.S. Department of Agricultureメs Research Service, Auburn University’s College of Agriculture, and the…

On Sept. 13, 2022, the National Institutes of Health announced it will invest $130 million over four years,…

On Jul. 27, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that it had identified for…

On April 21, 2022, researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) National Institute for Occupational…

On Jan. 6, 2022, two new studies published in the journal Current Biology showed that environmental DNA (eDNA)…
On Sept. 6, 2021, a genomic analysis of lung cancer in people with no history of smoking has…

On Aug. 30, 2021, the United Nations announced the global phase-out of leaded fuel, a milestone for multilateralism,…
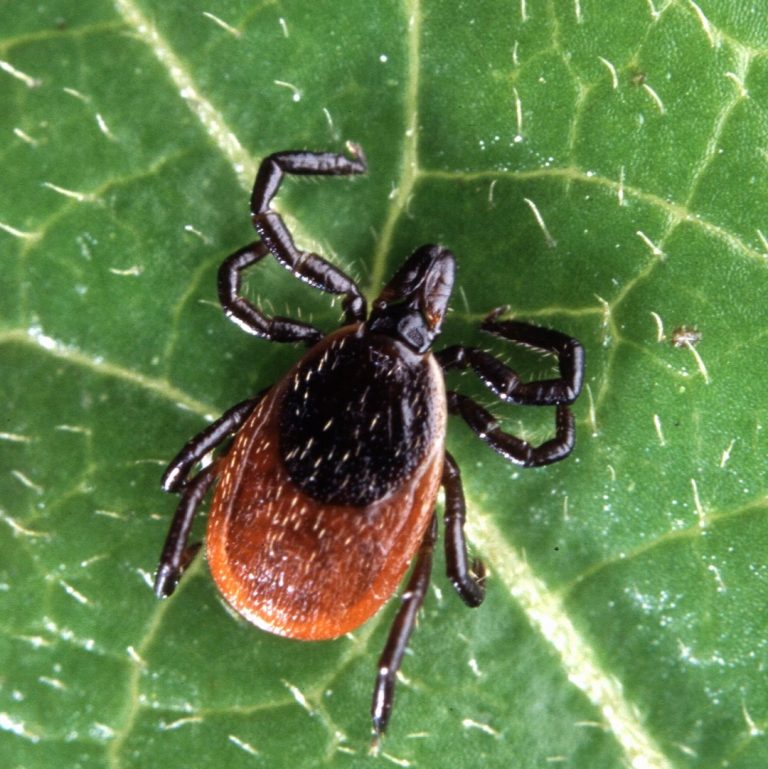

On Mar. 16, 2021, TGen announced a study that suggested ecosystems suitable for harboring ticks that carry debilitating…

On Dec. 21, 2020, the NIH announced that it had awarded eight research grants to develop approaches for…
On Dec. 21, 2020, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) announced a study published in the Proceedings…

On Nov. 18, 2020, Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) announced an initiative that will attempt to discern…

On Nov. 3, 2020, a study published in JAMA Network Open showed that children from poorer neighborhoods performed…
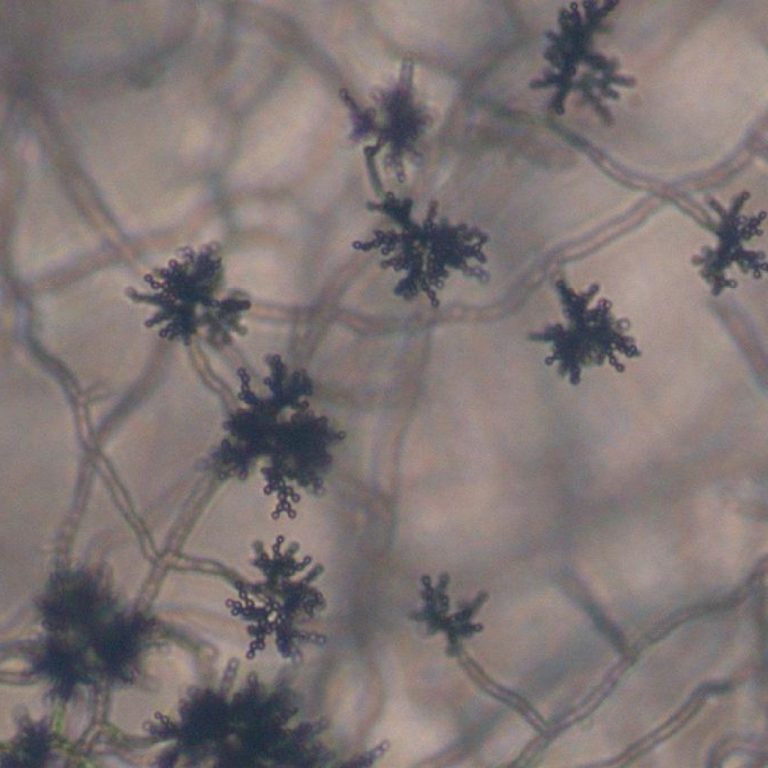
On Sept. 23, 2020, the USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) announced that a harmless airborne fungus, Cladosporium sphaerospermum…

On Aug. 31, 2020, in a study published in PNAS, researchers used conservation biology and genomics to discover…

On Jul. 15, 2020, in collaboration with the Guangdong CDC, Hunan CDC, Sun Yat-Sen University and Southeast University,…
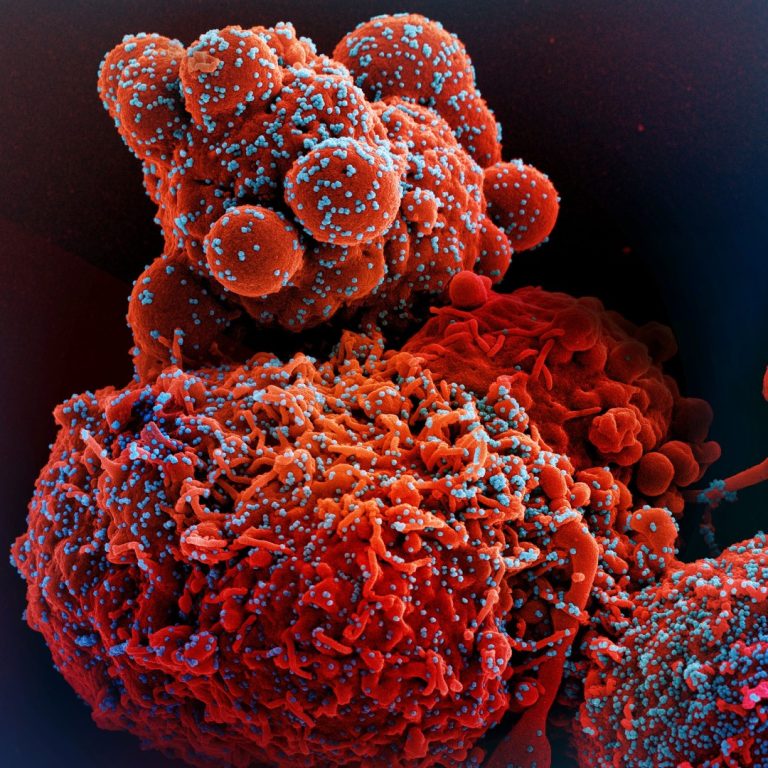
On May 8, 2020, the Rice University COVID-19 Research Fund Oversight and Review Committee announced it had funded…
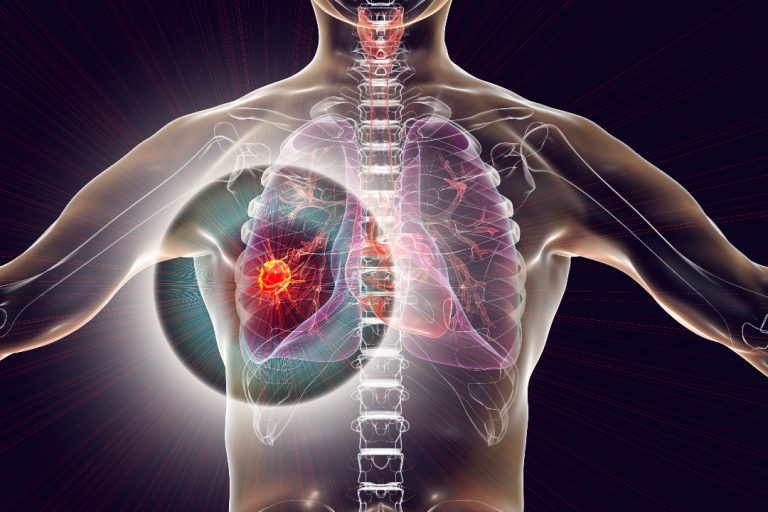
On May 5, 2020, the U.S. Dept. of Veterans Affairs (VA) announced the Airborne Hazards and Open Burn…

On Mar. 29, 2020, a study by UNMC/Nebraska Medicine/NSRI researchers provides new evidence of SARS-CoV-2 environmental contamination in…

On Dec. 13, 2019, the Masonic Cancer Center joined the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Study, Human…

On Nov. 30, 2018, Sean Norman, associate professor of environmental health sciences and director of the Molecular Microbial…
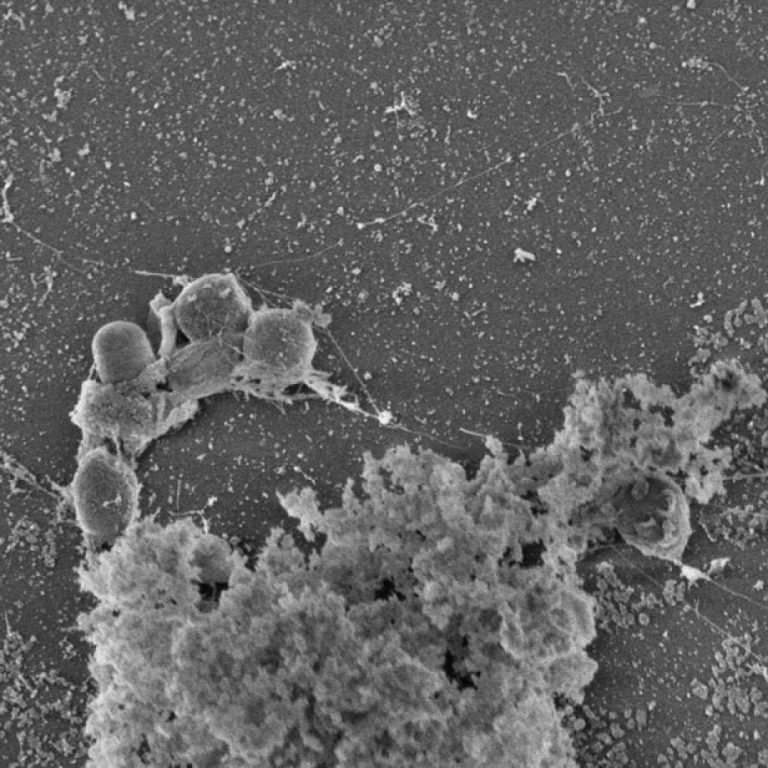
On May 2, 2018, Reed College announced that bio major Morgan Vague ’18 had isolated and bred three…

On Jan. 19, 2018, Yale evolutionary geneticist Gunter Wagner received the 2018 Daniel Giraud Elliot Medal from the…

On Nov. 1, 2017, a study from the Earth Microbiome Project reported the most extensive snapshot ever of…

On Oct. 25, 2016, the University of Washington’s Population Health Initiative received a $210 million gift from the…