The Harold C Simmons Cancer Center received The National Cancer Institute designation
On Jul. 10, 2015, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) announced it had awarded the UT Southwestern Medical Center’s…

On Jul. 10, 2015, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) announced it had awarded the UT Southwestern Medical Center’s…

On Jul. 7, 2015, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) awarded the Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and…

On Jun. 24, 2015, Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute (SBP) announced that Sanford-Burnham has received a gift…

On Jun. 16, 2015, Ardis Dee Hoven became the first woman president of the World Medical Association (WMA)….

On Jun. 3, 2015, Business leader and University of Southern California (USC) Trustee Rick J. Caruso and his…

On May 6, 2015, Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU and the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National…
On Mar. 27, 2015, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee…

On Mar. 26, 2015, Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, announced plans to invest more than $125…

On Mar. 25, 2015, longtime University of Southern California (USC) benefactors Mark and Mary Stevens donated $50 million…

On Mar. 2, 2015, Dr. Helen Wallace, a world-renowned professor, mentor and advocate known for her passion for…

On Jan. 23, 2015, Novartis announced the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted accelerated approval of…

On Jan. 12, 2015, The Albert Einstein Cancer Center became the only medical institution in New York City,…
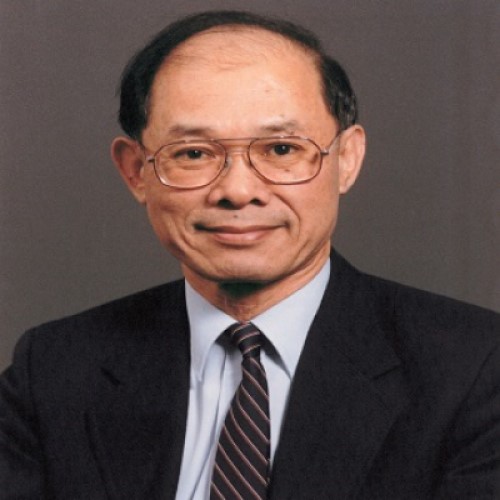

In 2015, Dr. Horace H. Loh received the Society of Chinese Bioscientists in America (SCBA) Lifetime Achievement Award…
On Dec. 18, 2014, the University of Nebraska Medical Center announced it had received a $1.3 million gift…
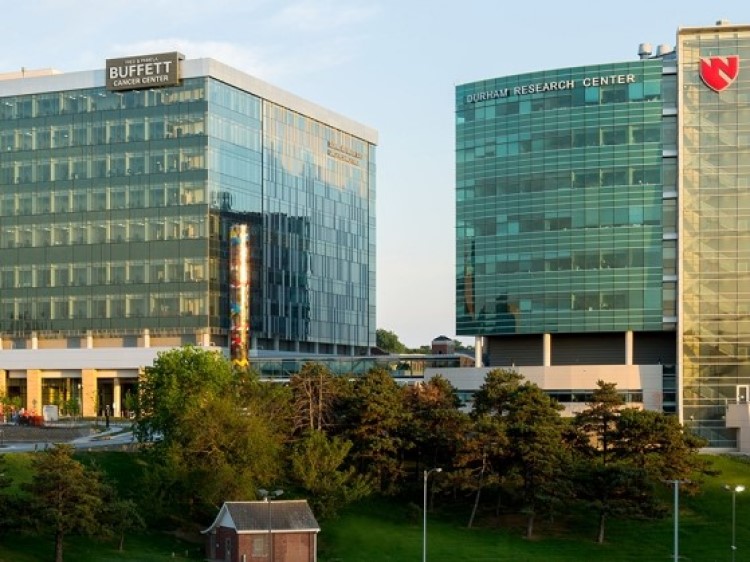

On Dec. 3, 2014, the Fred & Pamela Buffett Cancer Center at the University of Nebraska Medical Center…

On Oct. 21, 2014, the Jackson Laboratory (JAX) announced that technology investor David Roux and his wife Barbara…

On Oct. 13, 2014, the University of Minnesota’s Children’s Hospital was renamed the University of Minnesota Masonic Children’s…
On Oct. 9, 2014, a landmark study led by Douglas Melton from Harvard University successfully generated functional, mature human…

On Oct. 7, 2014, The Jackson Laboratory opened a state-of-the-art genomics research center on the campus of the…
On Sept. 19, 2014, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention”s (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP)…

On Aug. 21, 2014, Mark McAndrew, a resident of McKinney, Texas, gave $2.4 million to the University of…

On Aug. 4, 2014, the Allen Institute for Brain Science, California Institute of Technology, New York University School…

On Jul. 7, 2014, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) announced a $50 million gift from Jim and Marilyn…

On Jul. 1, 2014, Genentech entered into an agreement to acquire Seragon Pharmaceuticals, a privately held biotechnology company…

On Jun. 20, 2014, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Immunization Practices Advisory Committee…

On Jun. 17, 2014, Grifols opened state-of-the-art North Fractionation Facility (NFF) in Clayton, NC, where production capacity of…

On Jun. 2, 2014, Omeros received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Omidria for use in…

On Apr. 14, 2014, Stanford Medicine researchers announced a study that found a gene variant puts women at…
On Jan. 9, 2014, DNA was isolated from a 165-year-old intestine of a cholera victim from Philadelphia – …

On Nov. 20, 2013, researchers at the University of Toronto’s Institute of Biomaterials & Biomedical Engineering and the…