Trubion Pharmaceutical was founded
In 1999, Trubion Pharmaceutical was founded in Seattle as a spin-off from the Pacific Northwest Diabetes Research Institute,…

In 1999, Trubion Pharmaceutical was founded in Seattle as a spin-off from the Pacific Northwest Diabetes Research Institute,…

In 1999, The Indiana University (IU) Cancer Center became an National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated cancer center. Its mission…
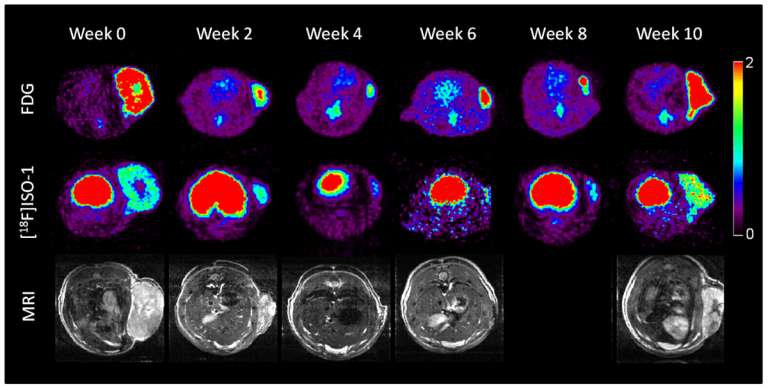
In 1999, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital developed fluorescent molecular probes that fluoresced upon contact with tumor enzymes,…
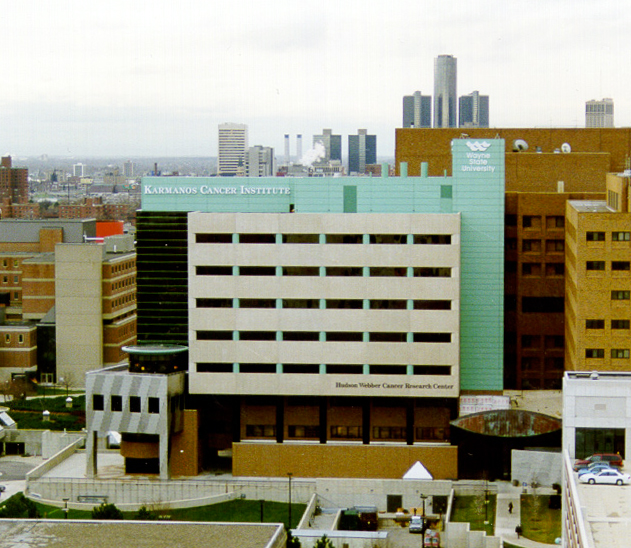

In 1999, the Hudson-Webber Cancer Research Center opened to serve as a ‘translational’ research facility, bridging the gaps…

Dec. 22, 1998, researchers from Barnes-Jewish Hospital in St. Louis announced using a revolutionary system that uses superconducting…
On Sept. 25, 1998, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the monoclonal antibody Herceptin (Trastuzumab) for…

On Sept. 14, 1998, researchers from the Breast Cancer Prevention Trial (BCPT) published a full report and update…
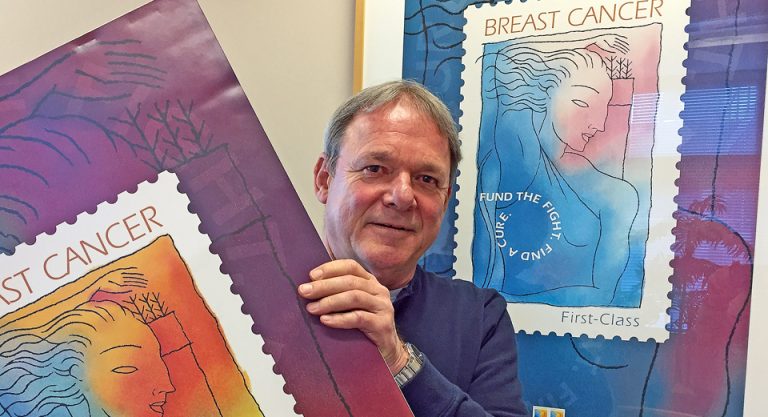

On Jul. 29, 1998, the Stamp Out Breast Cancer stamp was first issued. The driving force behind the…

On Jun. 16, 1998, University of Washington Medicine, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and Seattle Children’s announced the…

In March 1998, the Stop TB Initiative was established following a meeting of the First Ad hoc Committee…

On Feb. 10, 1998, the Cook County Board of Commissioners took the final steps in the approval process,…
In 1998, Tamoxifen, created with the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line established by Karmanos, was revealed to reduce…

In 1998, The Case Cancer Center (Case CCC) was recognized as an National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated comprehensive cancer…
In 1998, the Neurological Sciences Institute (NSI) joined the university as its fifth research unit. NSI researchers conduct…
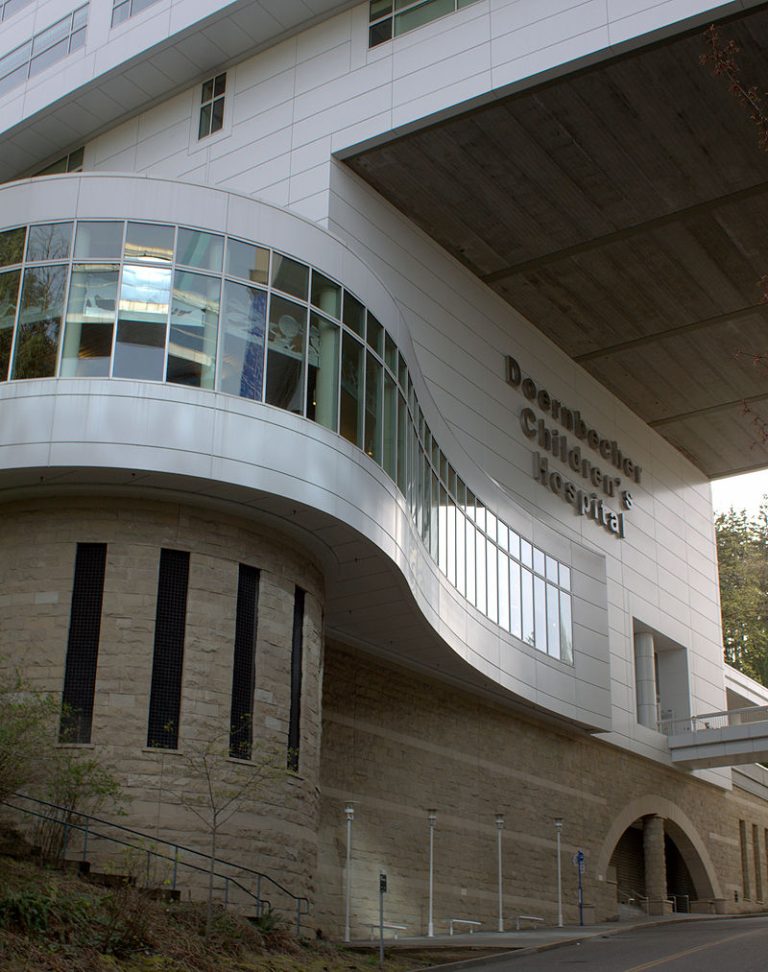

In 1998, Doernbecher Children’s Hospital’s new state-of-the-art pediatric medical complex was opened. Built with private funding and bond…
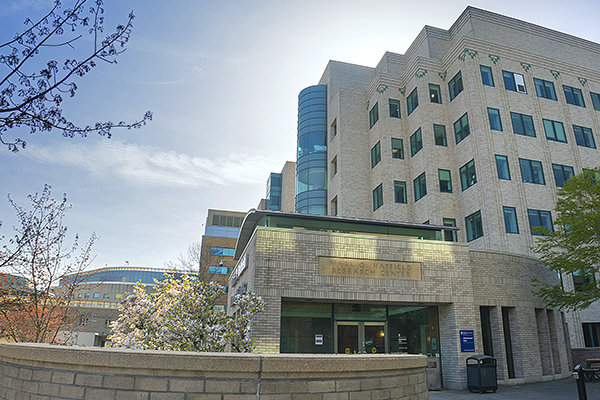

In 1998, The Mark O. Hatfield Research Center was dedicated. The center houses a variety of basic and…

In 1998, Chicago Mayor Richard M. Dale proclaimed November “National Sarcoidosis Awareness Month” in Chicago. The National Sarcoidosis…
In 1998, some research caused concern that hepatitis B vaccination might be linked with multiple sclerosis (MS), a…

In 1998, the The Prostate Centre at VGH, now known as the Vancouver Prostate Centre, was founded. The…

In 1998, National Cancer Institute (NCI) awarded the City of Hope Cancer Center NCI-comprehensive cancer center designation. City…

In 1998, The Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center received a $5 million gift from local philanthropist Henrietta Lee which…
In 1998, Cancer incidence rates showed first sustained decline since the National Cancer Institute (NCI) began keeping records…
In 1998, the Mammography Quality Standards Reauthorization Act (MQSA) was passed by the U.S. Congress and continued the…
In 1998, the Pediatric Rule was implemented that required drug manufacturers to study the efficacy and safety of…

In 1998, Yale Cancer Center researchers discovered the gene, Survivin, which is linked to the detection of some…

In 1998, Harvard Medical School-based scientists established the Institute of Chemistry and Cell Biology (ICCB), to facilitate the…

On Nov. 11, 1997, the Universal Declaration on the Human Genome and Human Rights was adopted unanimously and…
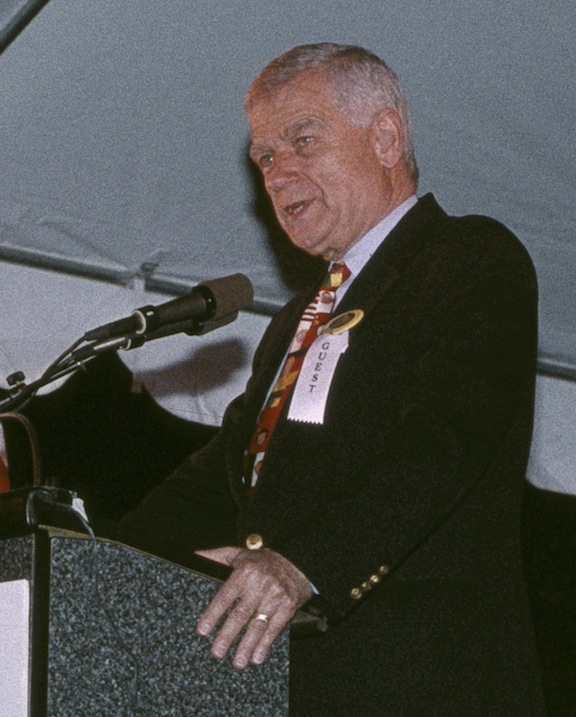

On Nov. 4, 1997, Vice President Al Gore and Senator Mark O. Hatfield attended groundbreaking ceremonies for the…
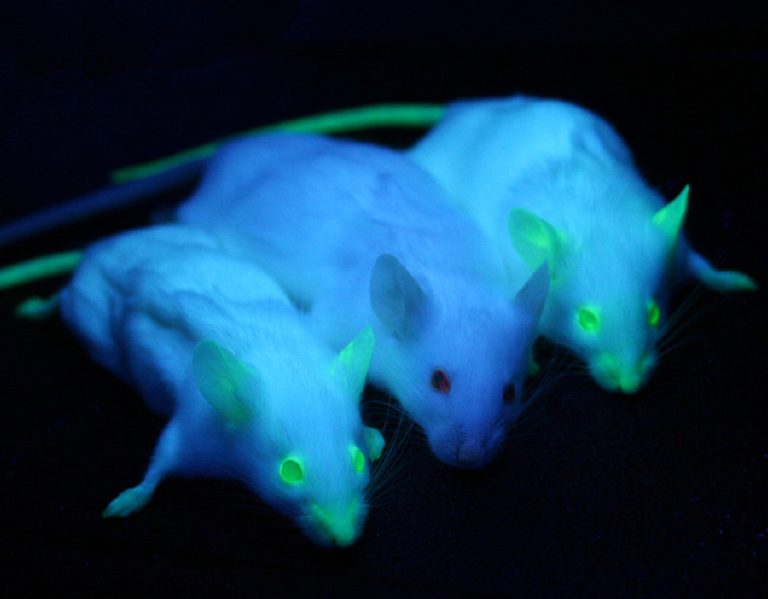

On Oct. 9, 1997, Stanford researchers announced that in a series of experiments performed in mice and rats,…
On Aug. 13, 1997, the Stamp Out Breast Cancer Act (PL 105-41) was signed into law by President…