Yale Cancer Center was awarded a SPORE (Specialized Programs of Research Excellence) grant for translational research
On Oct. 10, 2006, Yale Cancer Center was awarded a SPORE (Specialized Programs of Research Excellence) grant for…
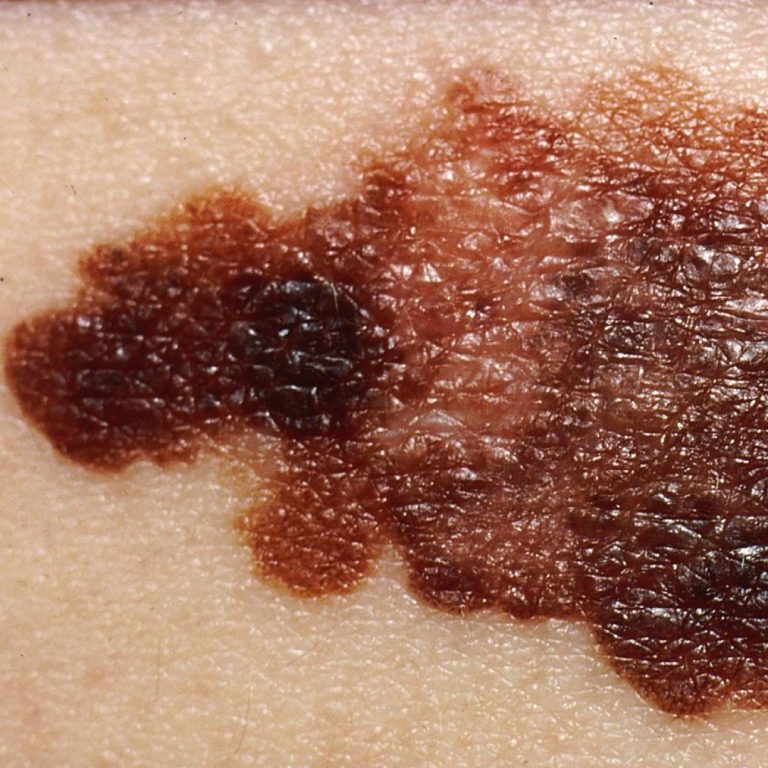
On Oct. 10, 2006, Yale Cancer Center was awarded a SPORE (Specialized Programs of Research Excellence) grant for…

On Sept. 28, 2006, the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute (VBI) opened its new office complex in the National Capital…
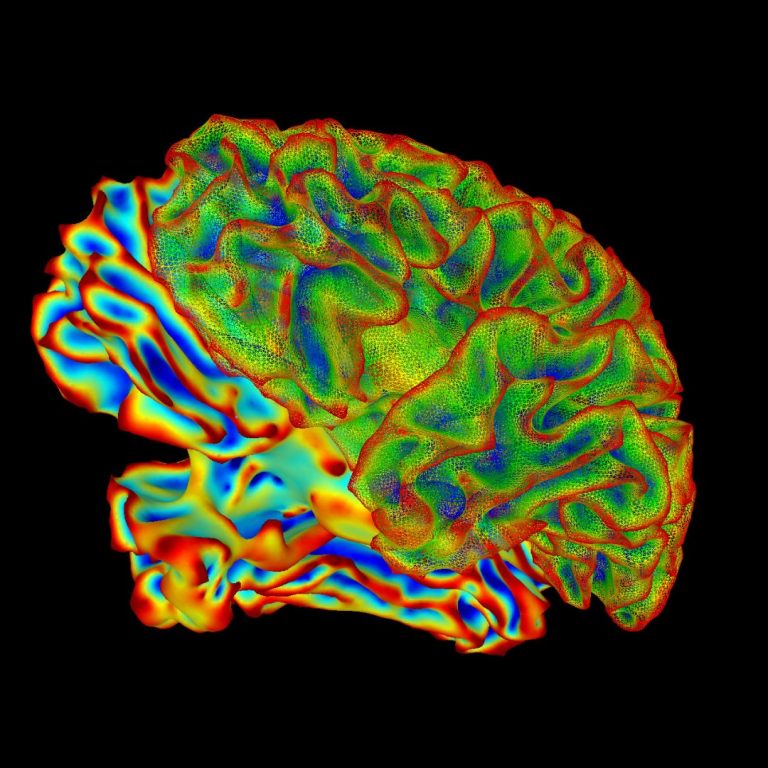
On Sept. 26, 2006, the Allen Institute for Brain Science announced the completion of the groundbreaking Allen Brain…

On Sept. 15, 2006, the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation (OMRF) celebrated it’s 60th anniversary. More than 600 people…

On Sept. 8, 2006, BD (Becton, Dickinson) announced an agreement to acquire the 93.5% of the outstanding shares…
On Aug. 14, 2006, National Cancer Institute (NCI) researchers announced they had found a unique pattern of activity…

On Aug. 1, 2006, the Frances Langford Heart Center opened its doors bringing open-heart surgery and interventional cardiology…
On Jul. 18, 2006, the Fred Hutchinson Business Alliance announced that the E. Donnall Thomas Medal of Achievement…

On Jun. 27, 2006, the U.S. Surgeon General released a report on the harmful health consequences of involuntary…
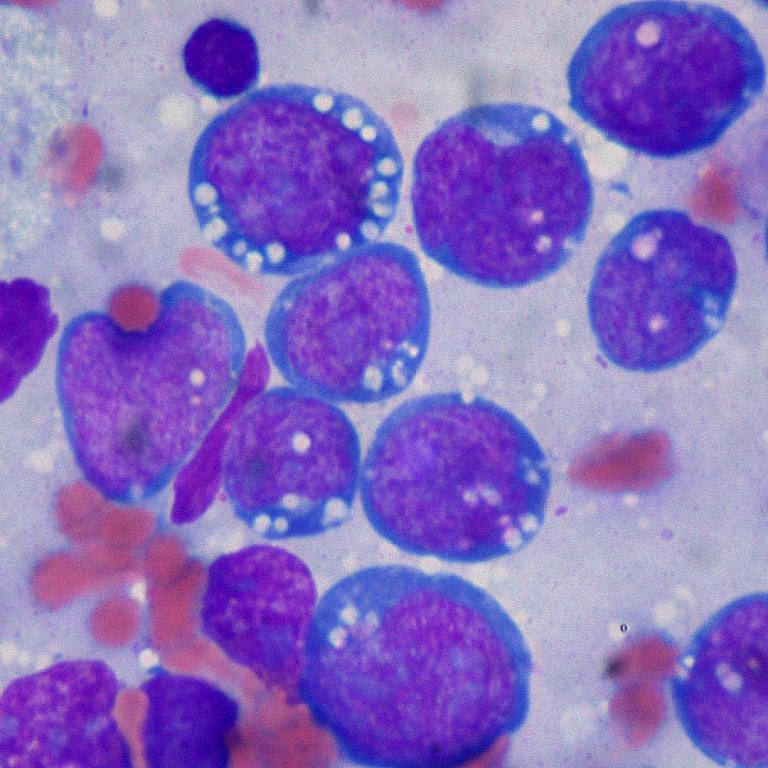
On Jun. 7, 2006, gene profiling, a molecular technique that examines many genes simultaneously, can accurately distinguish between…
On May 23, 2006, the Trial Assigning IndividuaLized Options for Treatment (Rx), or TAILORx, was launched to examine…

On May 5, 2006, the Cancer Research Initiative was established in South Carolina, between MUSC, University of South…

On Mar. 22, 2006, the Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington School of Medicine in St….

On Mar. 8, 2006, World Kidney Day, a joint initiative between the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) and…

On Feb. 23, 2006, groundbreaking was held for the first building of the North Carolina Research Campus (NCRC),…

On Jan. 31, 2006, Dan Duncan, founder of Enterprise Partners, an energy company in Houston, announced a donation…
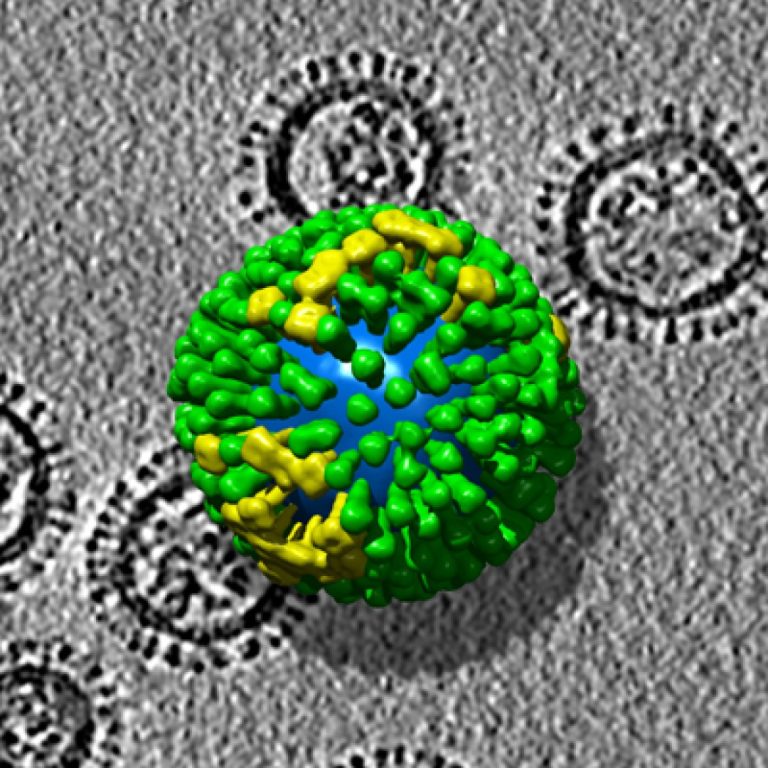
On Jan. 17, 2006, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that it had stopped recommending…

On Jan. 17, 2006, researchers at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) announced the development of a…
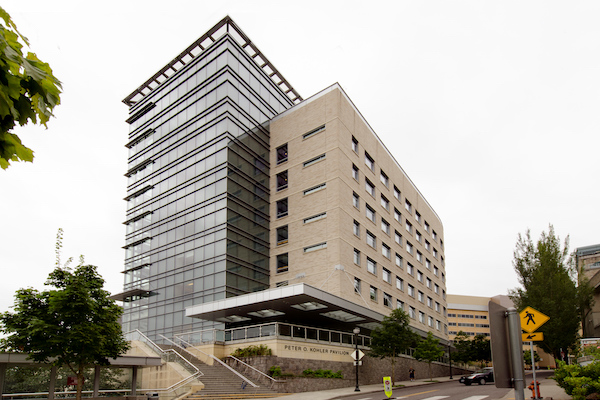

In 2006, The OHSU Peter O. Kohler Pavilion opened as state-of-the-art patient care facility on Marquam Hill in…
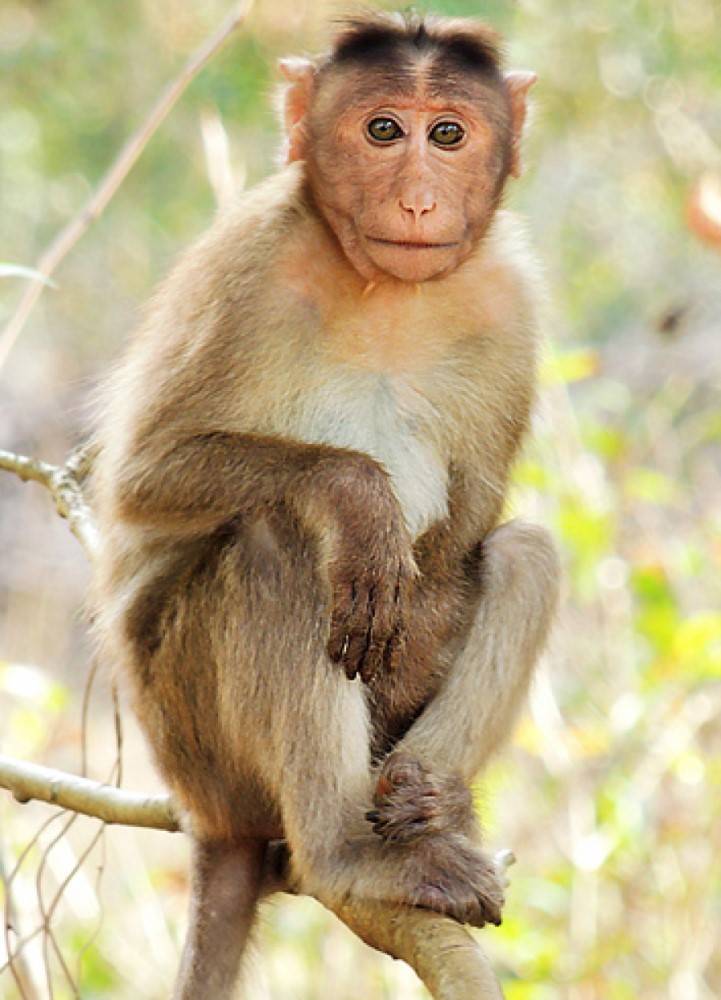

In 2006, Texas Biomed researchers published a genetic linkage map for the rhesus monkey. In 1999, Texas Biomed…

In 2006, Robert C. Byrd Biotechnology Science Center officially opened. The center was constructed with a grant of…

In 2006, the Board of Trustees of the Northwest Lions Foundation for Sight & Hearing renamed Northwest Lions…
In 2006, the Malaria Atlas Project (MAP) was founded as an international research collaboration that tracks the global…
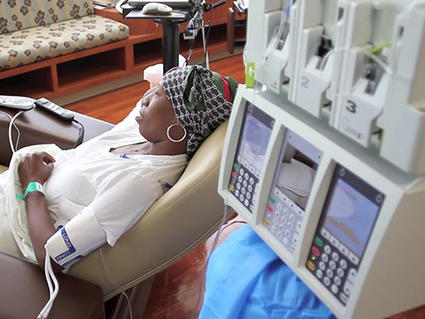
In 2006, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) launched the TAILORx trial to determine whether gene expression patterns in…

In 2006, the Science Foundation Arizona (SFAz), a 501(C)(3) non profit, was initiated by the three statewide CEO…

In 2006, San Diego Consortium for Regenerative Medicine was established as a California non-profit corporation and a 501(c)(3)…
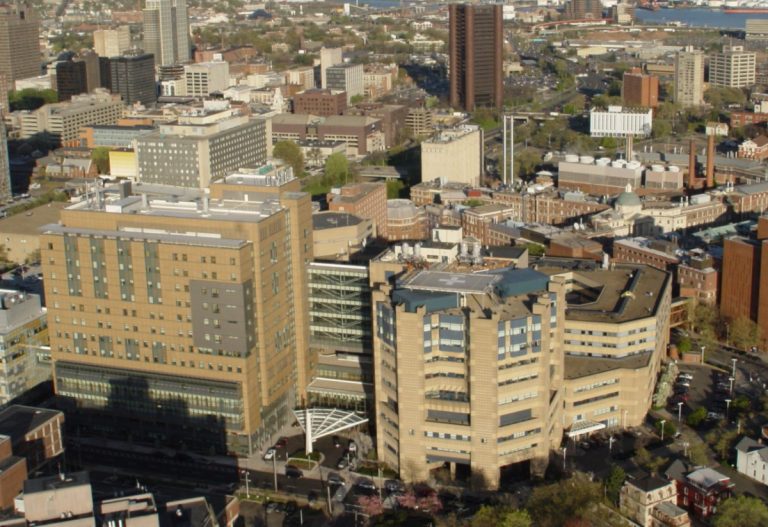

On Aug. 31, 2022, Yale New Haven Hospital (YNHH) broke ground on the $838 million, 505,000 square foot…

On Dec. 13, 2005, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the National Human Genome Research Institute launched a…

On Dec. 12, 2005, the U.S. Congress approved the passage of the Food Allergy Labeling and Consumer Protection…

On Dec. 7, 2005, results from several studies presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium validated that…