Albert Hofmann self-tested lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)
On Apr. 16, 1943, Albert Hofmann tested synthesized lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) on himself. LSD-25, as originally known…

On Apr. 16, 1943, Albert Hofmann tested synthesized lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) on himself. LSD-25, as originally known…

In 1943, Leo Kanner, a child psychiatrist at Johns Hopkins University, published the first clinical description of 11…
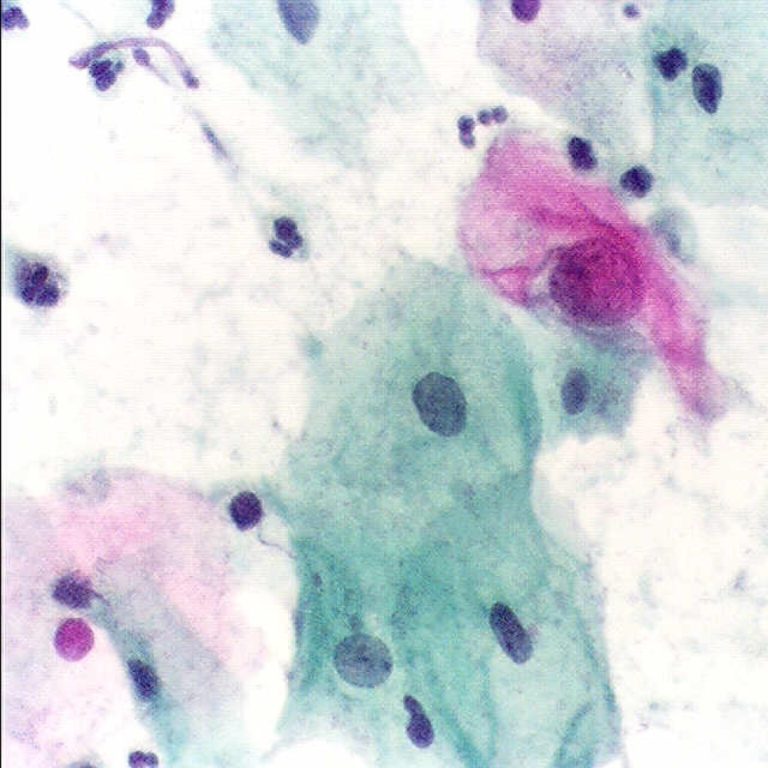
In 1943, George Nicholas Papanicolaou and Herbert Traut published their landmark book “Diagnosis of Uterine Cancer by the…

In 1943, The Detroit Institute for Cancer Research was incorporated with just $483 and 200 shares of General…

In 1942, Dr. William Hutchinson began a 47 year career in Seattle, Washington when he joined the Swedish…

In 1942, Dr. Jonas Salk arrived at the University of Michigan School of Public Health. Techniques earned there…
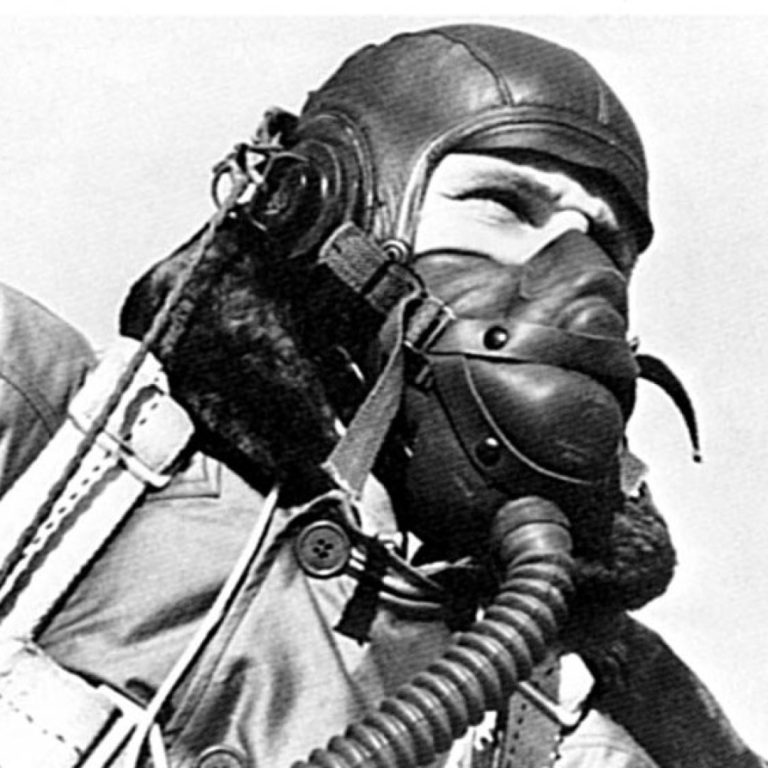

In 1942, the U.S. government with the military secretly tasked a small group of Mayo Clinic physicians and…

In 1942, The Hormel Institute was founded by Jay C. Hormel in Austin to research and find a…

In 1942, the Medical Research Foundation (MRF) was founded by a group of Portland area businessmen and physicians…
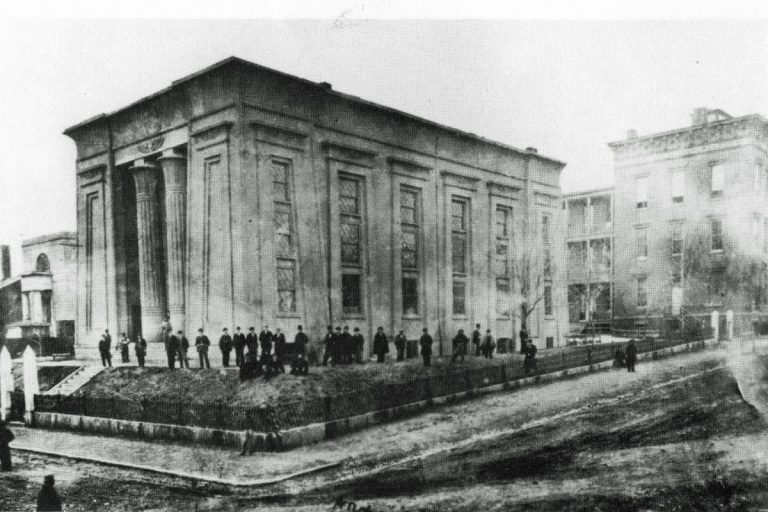

In 1942, the Virginia Agricultural and Mechanical College’s first Ph.D. was awarded to Nathan Sugarman in chemistry. In…
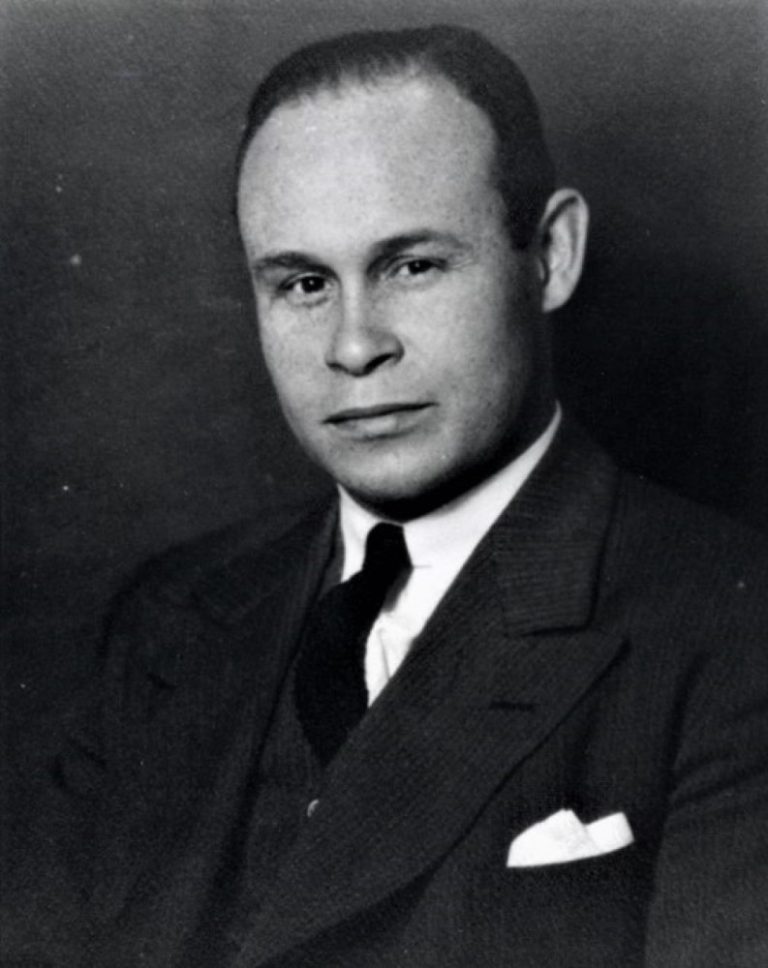

On Feb. 4, 1941, the Red Cross began a National Blood Donor Service to collect blood for the…
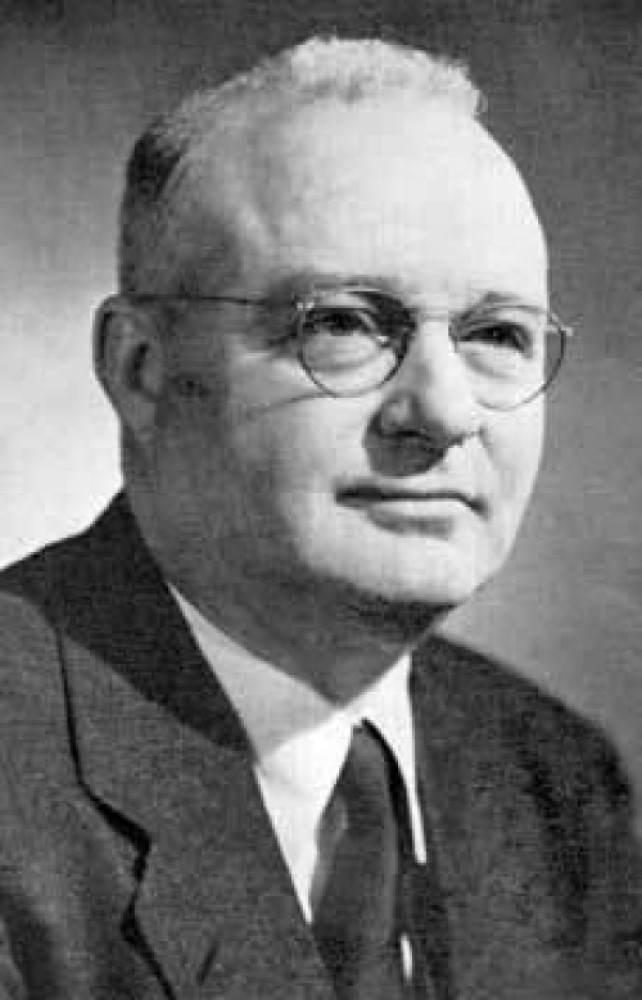

In 1941, the Priestley Medal was awarded to Thomas Midgley by the American Chemical Society “to recognize distinguished…

In 1941, Texas State Cancer Hospital, now known as the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, was…

In 1941, the Medical College of Virginia Hospital (MCV West Hospital) opened to national acclaim. The largest donation…
On Sept. 6, 1940, Karl Habel produced an improved, killed rabies vaccine that eliminated foreign brain tissue that…
On Jun. 14, 1940, Charles Armstrong and V. H. Haas published Immunity to the Lansing Strain of Poliomyelitis…
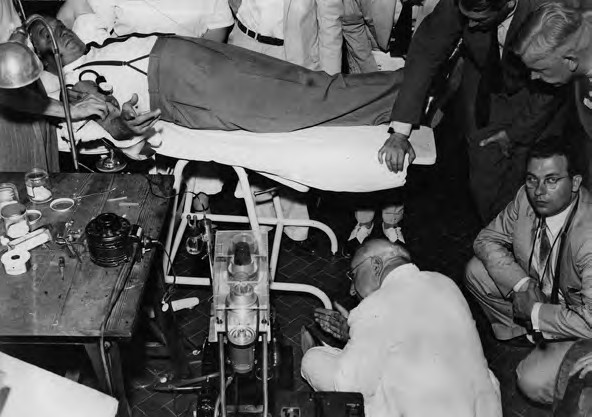
In 1940, Edwin Cohn, a professor of biological chemistry at Harvard Medical School, developed cold ethanol fractionation, the…
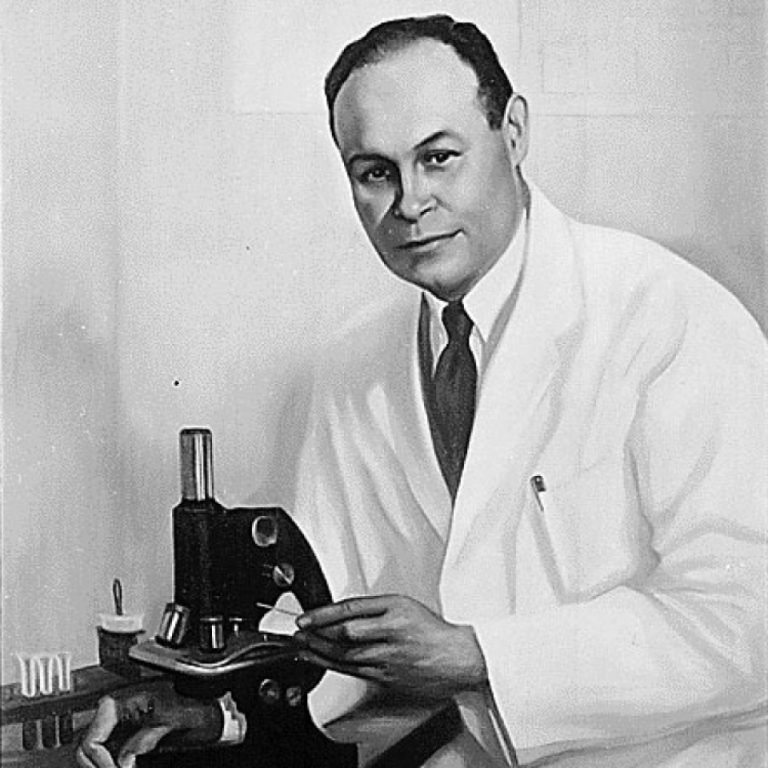

In 1940, Charles R. Drew, MD, an African American surgeon and Howard University researcher, began an early blood…
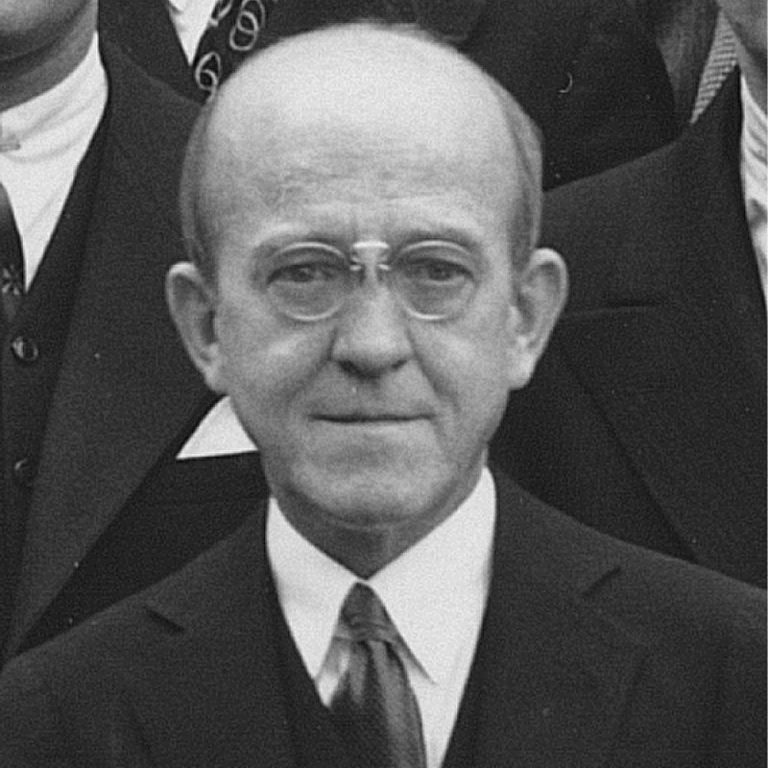

In 1940, American Oswald Avery precipitates a pure sample of what he calls the transforming factor; he has…
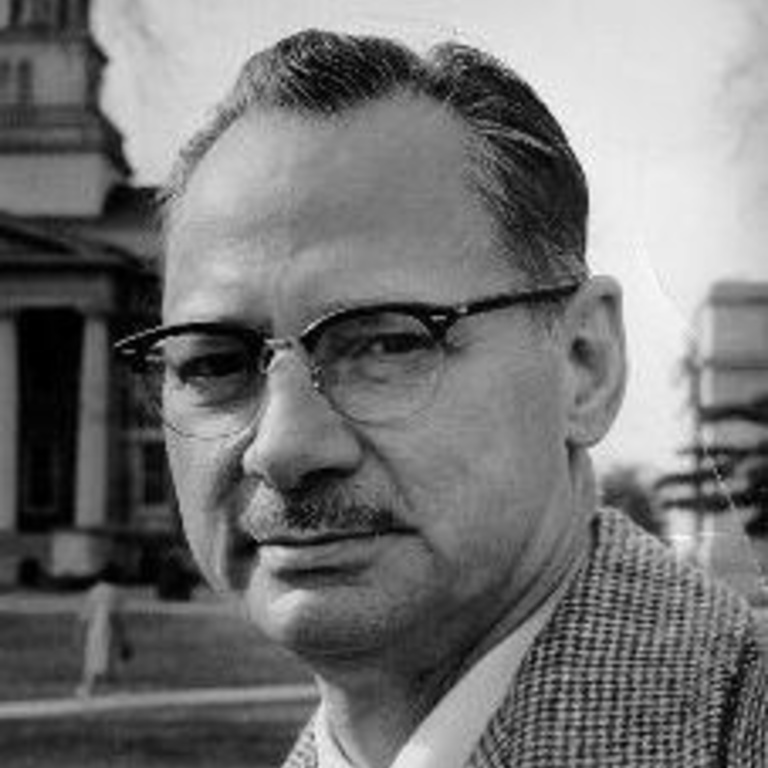

In 1940, Wendell Johnson at the University of Iowa pioneers the fields of speech pathology and audiology. Throughout…
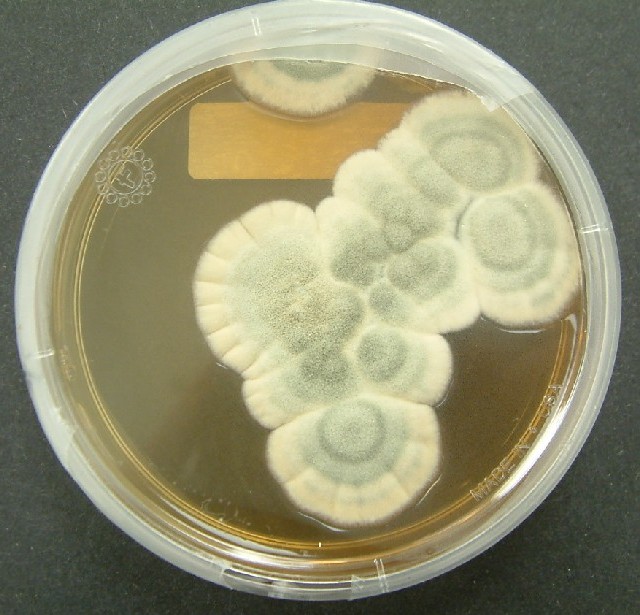
In 1940, Howard Florey, Ernst Chain and others in England discover how to purify and preserve penicillin. The…
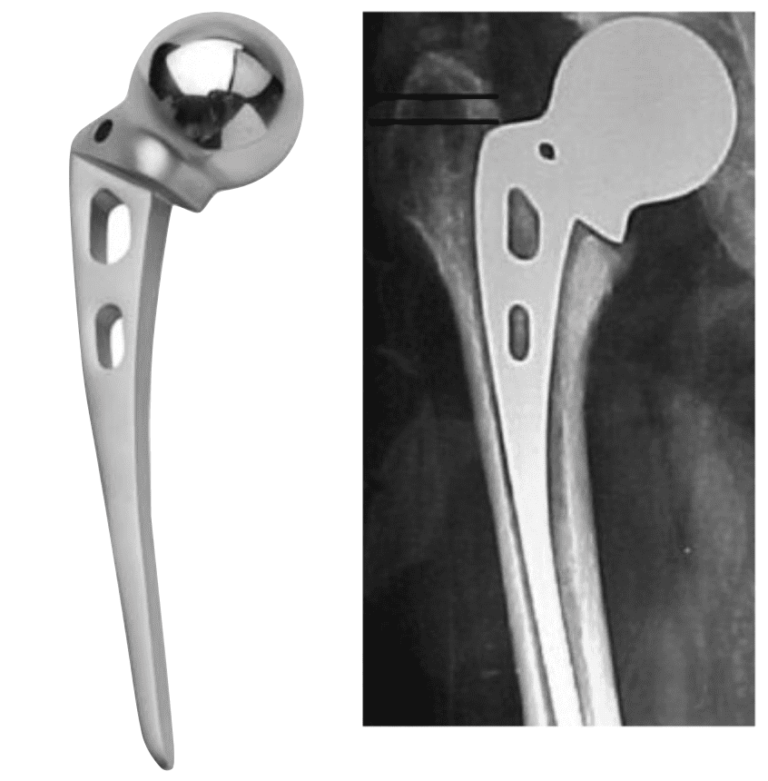
On Sept. 28, 1940, Dr. Austin T. Moore, an American surgeon at Johns Hopkins hospital, and Harold Ray…
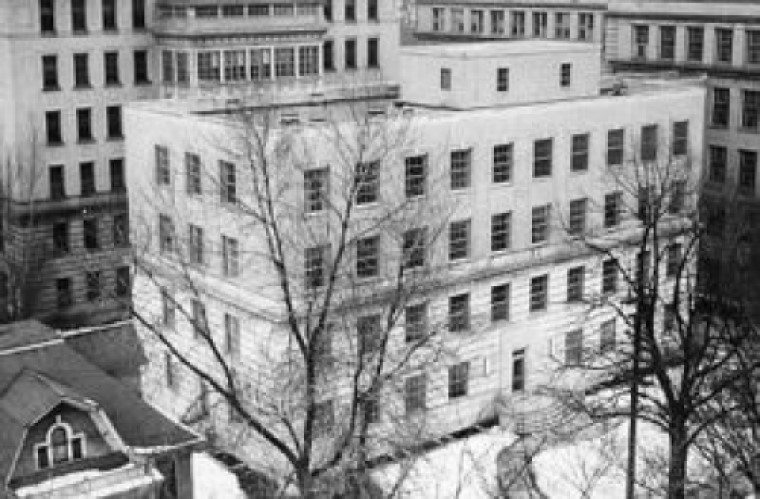

In 1940, the McArdle Memorial Laboratory was founded in Madison. McArdle Lab was one of the first basic…
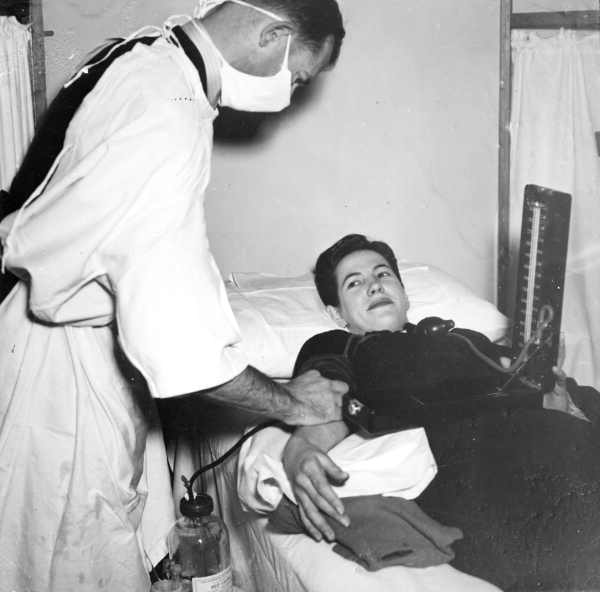
In 1940, the U.S. government established a national blood collection program. That same year the National Research Council…
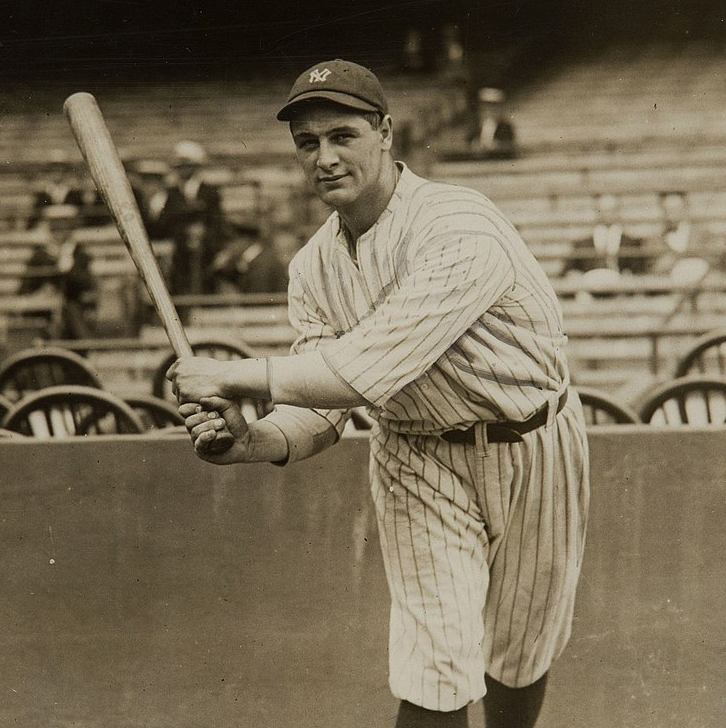

On Jul. 4, 1939, baseball legend Lou Gehrig delivered the famous speech bidding farewell to the ballpark and…
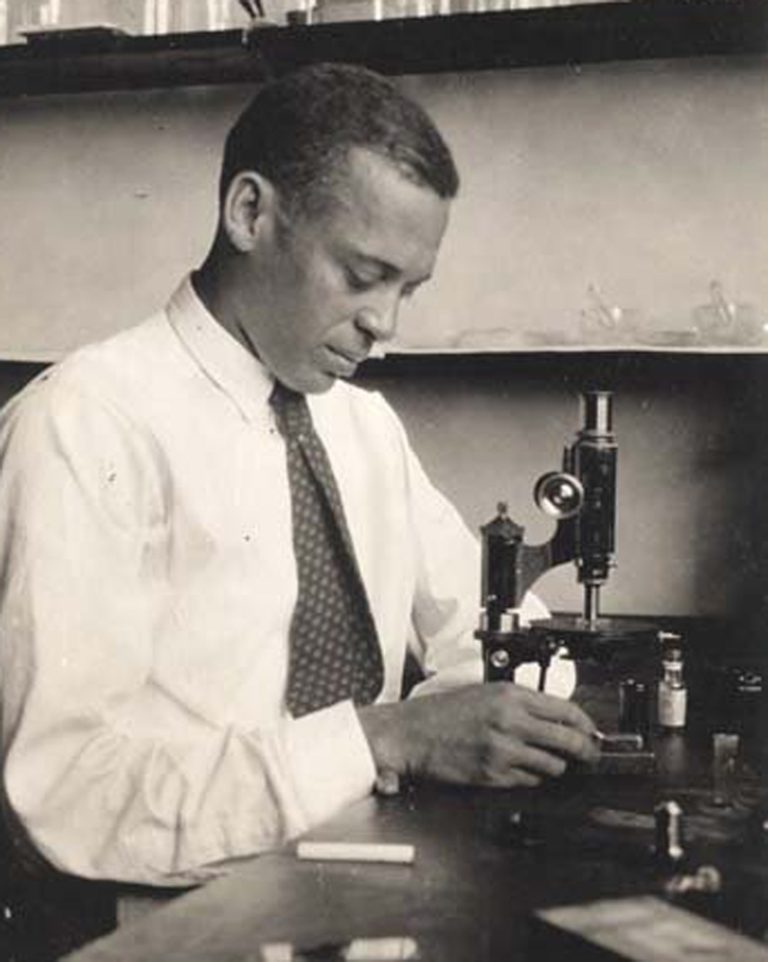

In 1939, embryologist E.E. Just published The Biology of the Cell Surface, and pioneered ideas about the importance…
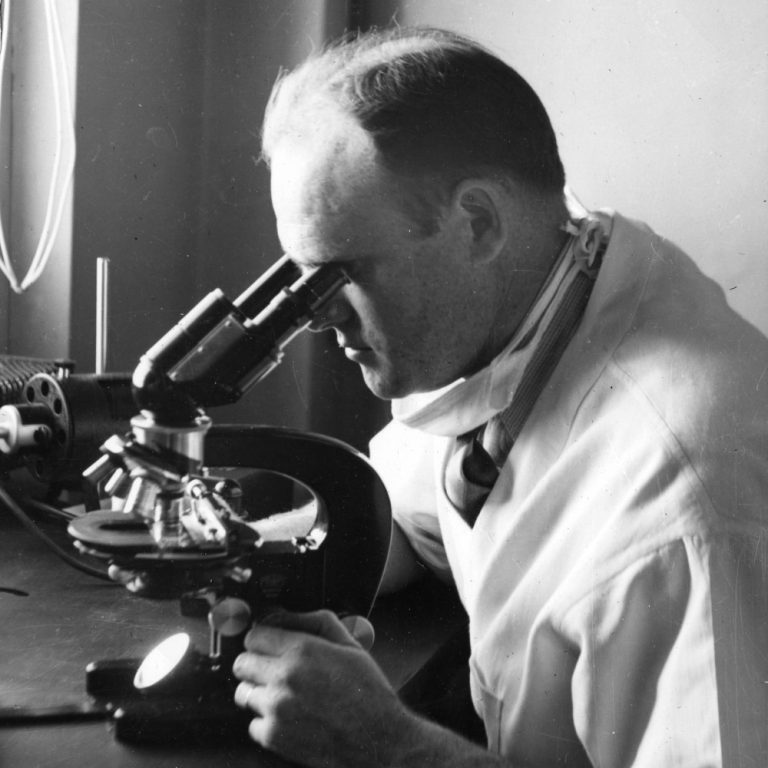

On Dec. 23, 1938, Herald R. Cox published: Use of Yolk Sac of Developing Chick Embryo as Medium…
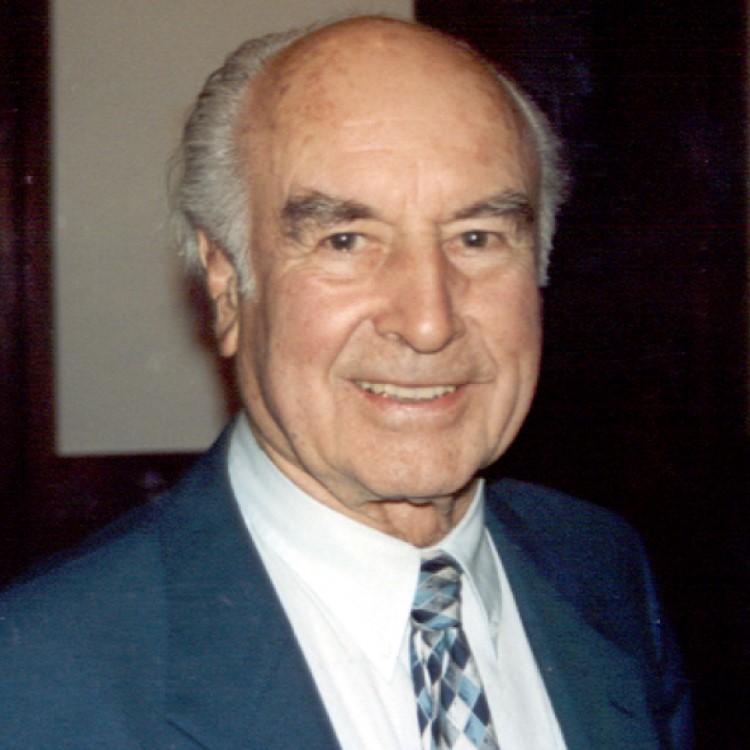

On Nov. 16, 1938, Albert Hofmann at Sandoz synthesized lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). LSD-25, as originally known when…

On Nov. 5, 1938, the British Columbia Cancer Institute, BC Cancer’s first cancer treatment centre officially opened in…

On Jun. 25, 1938, the U.S. Congress passed the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act with new provisions….