The Harrison Narcotic Act required prescriptions for products exceeding the allowable limit of narcotics
On Feb. 14, 1924, the Harrison Narcotic Act required prescriptions for products exceeding the allowable limit of narcotics…
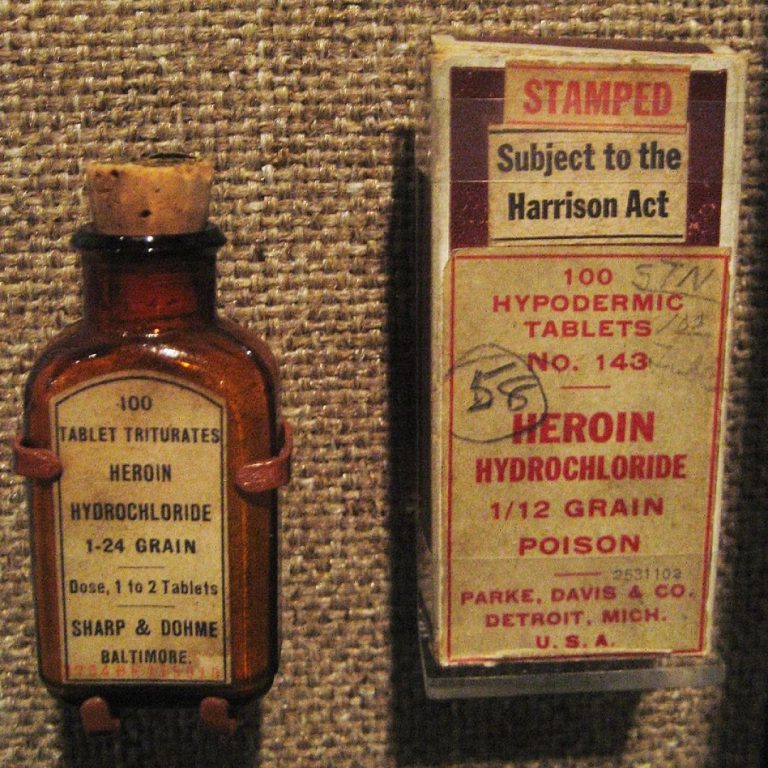
On Feb. 14, 1924, the Harrison Narcotic Act required prescriptions for products exceeding the allowable limit of narcotics…
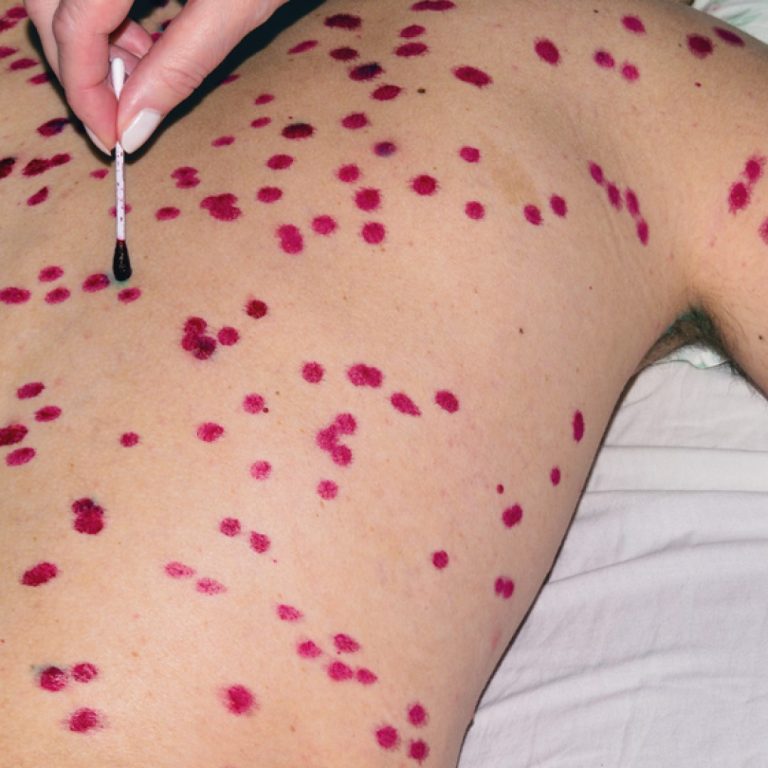
Between 1924-1925, smallpox hit Minnesota and more than five hundred people died – four hundred in the Twin…

In 1924, Roscoe R. Spencer and Ralph R. Parker produced a vaccine against Rocky Mountain spotted fever, the…

In 1924, Leo Rigler was appointed associate professor of radiology at the University of Minnesota. Rigler obtained full…

In 1924, Johnsonᅠ &ᅠ Johnson established first overseas operating company in the United Kingdom.

In 1924, Bristol-Myers’ gross profits topped $1 million and its products were sold in 26 countries. Shares held…
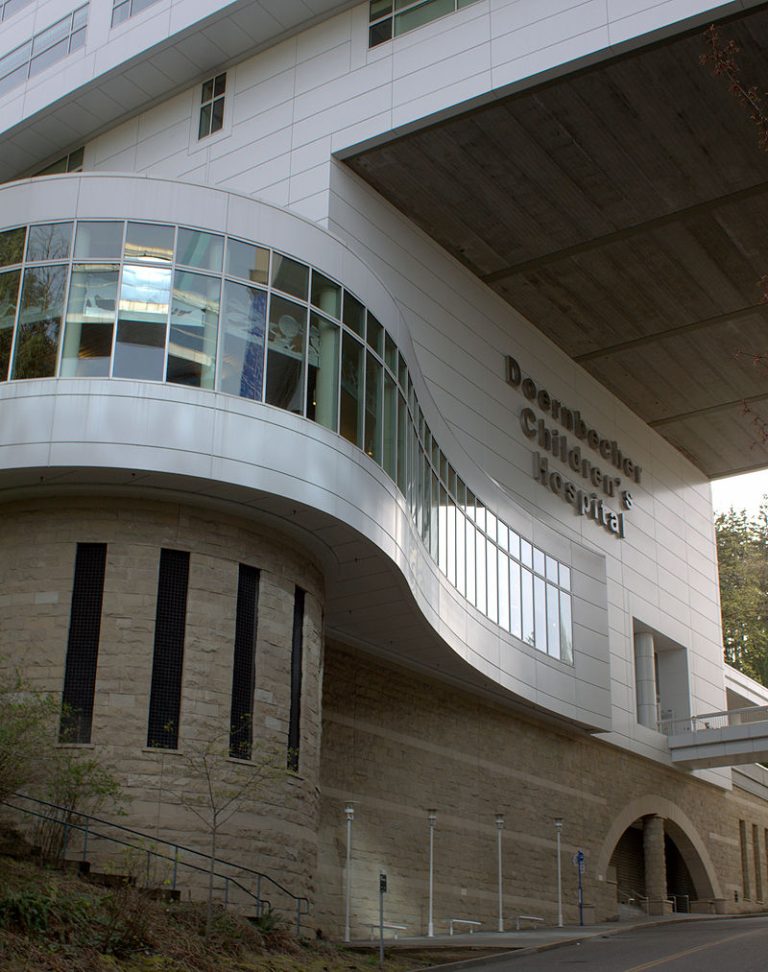

On Oct. 14, 1923, plans were announced for Doernbecher Memorial Hospital for Children. Frank S. Doernbecher was a…
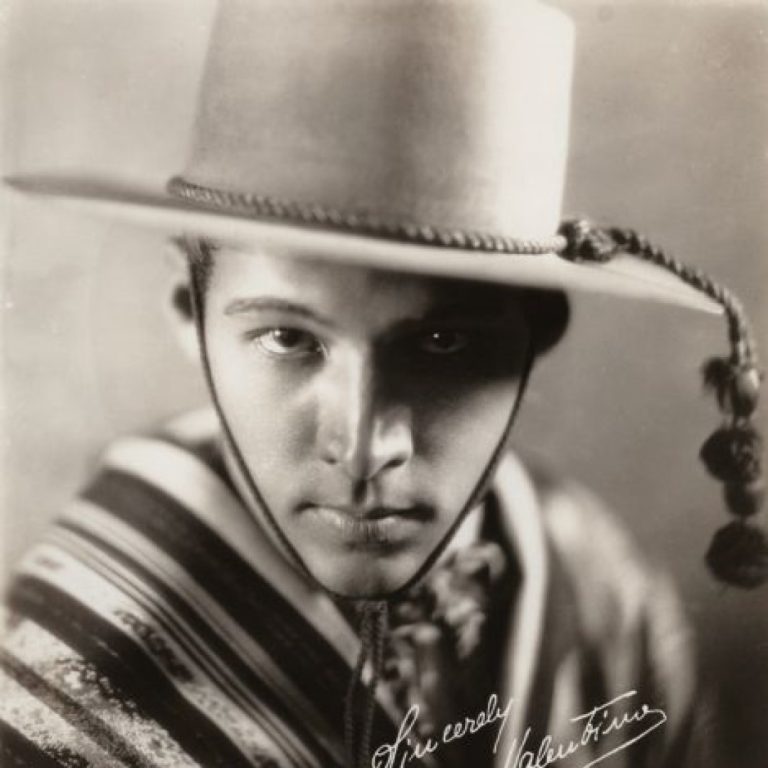

On May 30, 1923, movie star Rudolph Valentino visited Seattle’s Children’s Orthopedic Hospital during his only known visit…

In 1923, the Priestley Medal, named for Joseph Priestley, was awarded for first time by the American Chemical…

In 1923, Dr. Frederick Banting and Dr. J. MacLeod win the Nobel Prize for their work isolating insulin.
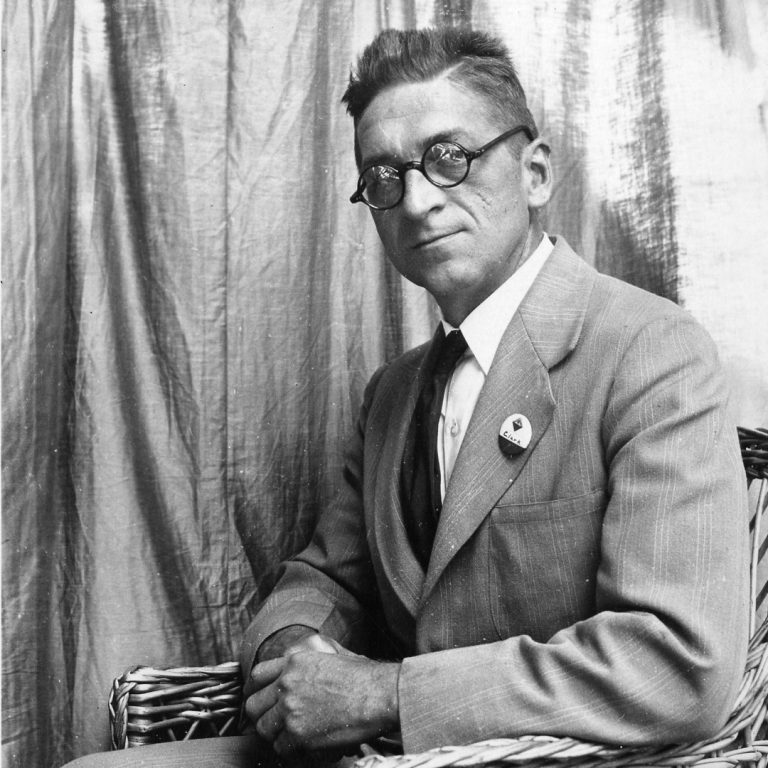

In 1923, William Mansfield Clark from the U.S. Department of Agriculture alerted the public to the dangers of…

In 1923, Atherton Seidell was a renowned research chemist who developed a physiological test for the activity of…

In 1923, more than 50,000 foreign plants had been introduced into the United States since 1862 by the…
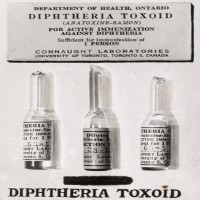
In 1923, diphtheria toxoid was licensed; prepared from the inactivated bacterial toxin that has lost its toxicity but…

In 1923, General John J. Pershing signed the order creating the Army Medical Center on the same campus…
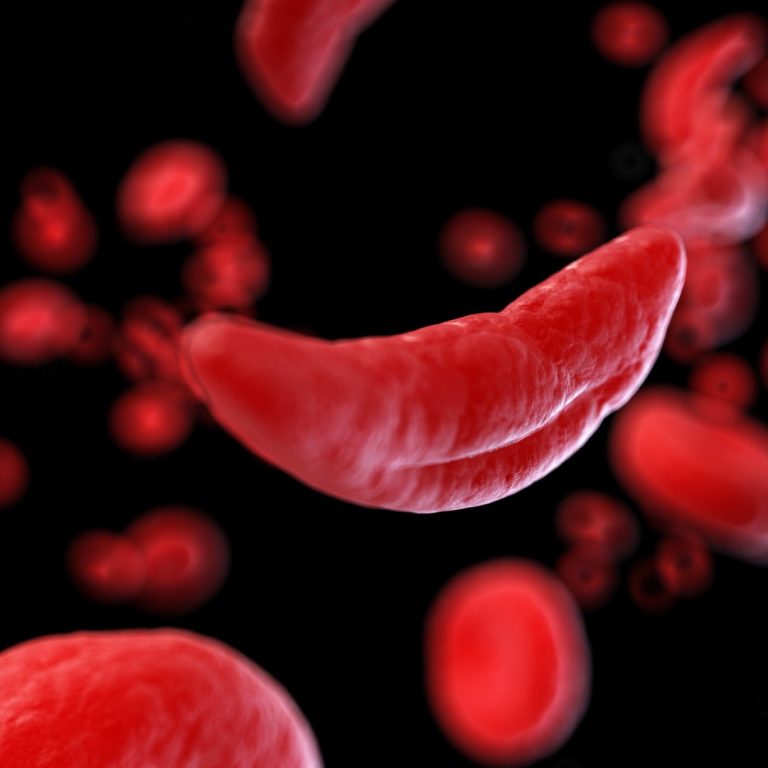
In 1923, Dr. Virgil P. Sydenstricker published the first documented case of sickle cell disease, with full autopsy…

In 1923, Eli Lilly and Company introduced Iletin, the world’s first commercially available insulin product.

In 1923, Eliot Cutler performed the worldメs first successful heart valve surgery at the Peter Bent Brigham Hospital,…

In 1923, Multnomah County Hospital opens on the Marquam Hill campus and contracts with the medical school to…

On Nov. 10, 1922, Carl Voegtlin, J. M. Johnson, and Helen Dyer announced they had co-published an article…

On Sept. 10, 1922, the Arkansas Childrenメs Home Society moved into the newly-named ‘C.A. Forney-Smith Receiving Home.’ The…
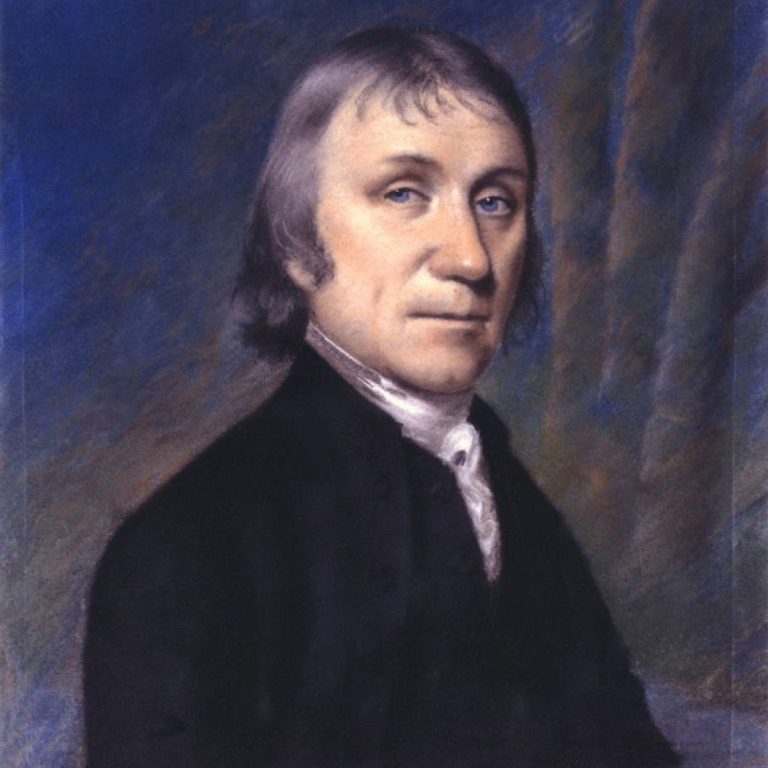

In 1922, the Priestley Medal, named for Joseph Priestley, was awarded for first time by the American Chemical…

In 1922 the Alaska Agricultural College and School of Mines was founded. The College grew quickly, and in…
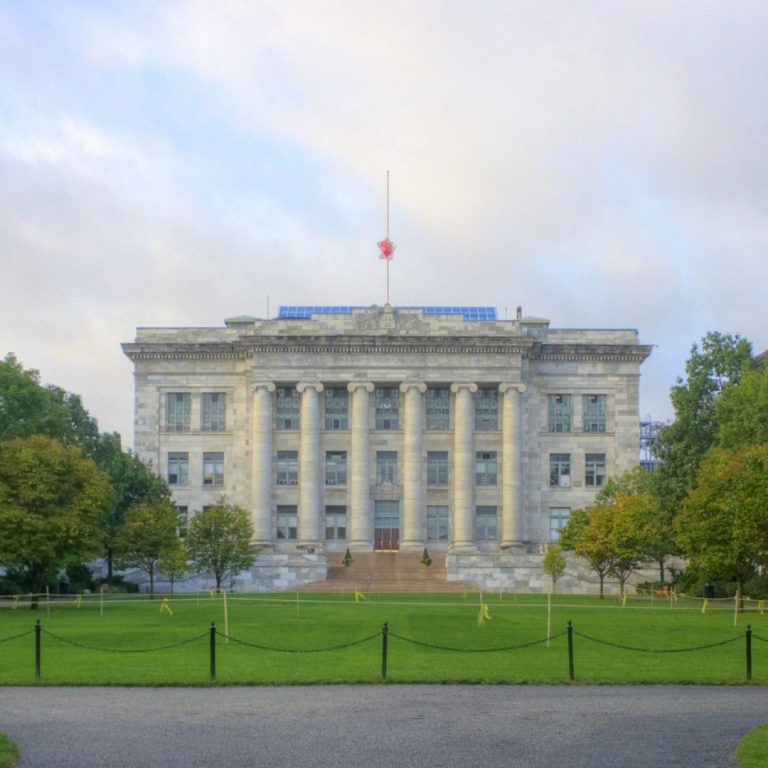

In 1922, the Public Health Service opened a Special Cancer Investigations Laboratory at Harvard Medical School.
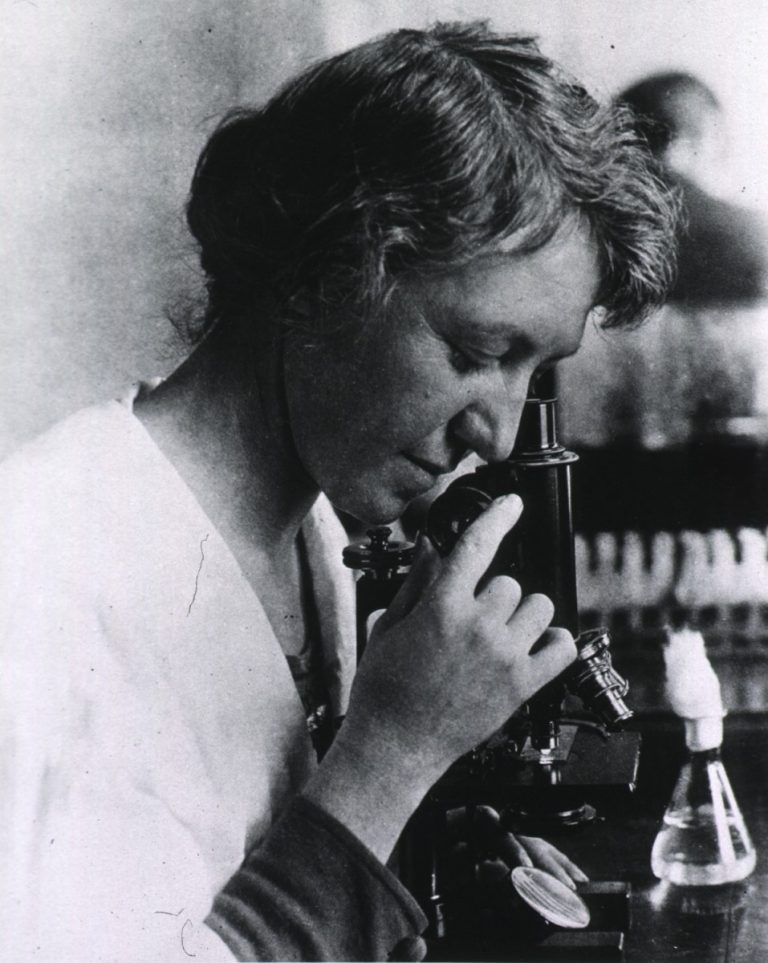

In 1922, Ida A. Bengtson discovered a new variety of Clostridium botulinum. This strain was designated as type…

In 1922, cod liver oil (vitamin D) was shown to prevent rickets in chicks improves poultry production.

In 1922, Wesley Memorial Hospital moved to a new building on the Emory’s Druid Hills campus. Three years…

In 1922, a maize breeding program was initiated at Iowa State University by Merrill Jenkins. The program came…

In 1922, Elliott Joslin, at Harvard Medical Center, introduced insulin to the United States and founded Joslin Diabetes…

In 1922, The Alaska Agricultural College and School of Mines was founded. The College grew quickly, and in…