The Norris Cotton Cancer Center received NCI Cancer Center designation
In 1978, the Norris Cotton Cancer Center in New Hampshire received National Cancer Institute (NCI) designated in recognition…

In 1978, the Norris Cotton Cancer Center in New Hampshire received National Cancer Institute (NCI) designated in recognition…

In 1978, Squibb formed ConvaTec as a separate division to develop adhesive skin barriers and products that could…
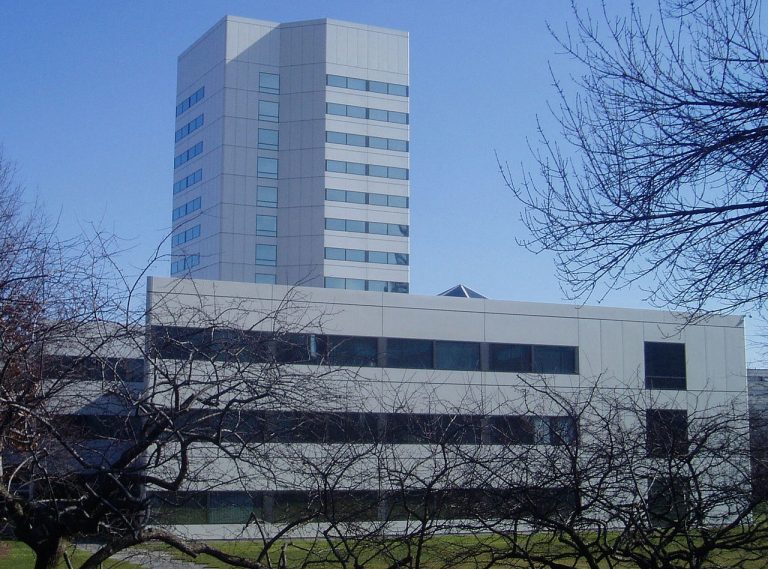

In 1978, Johnsonᅠ & ᅠJohnson announced plans to build their new World Headquarters in New Brunswick, New Jersey….
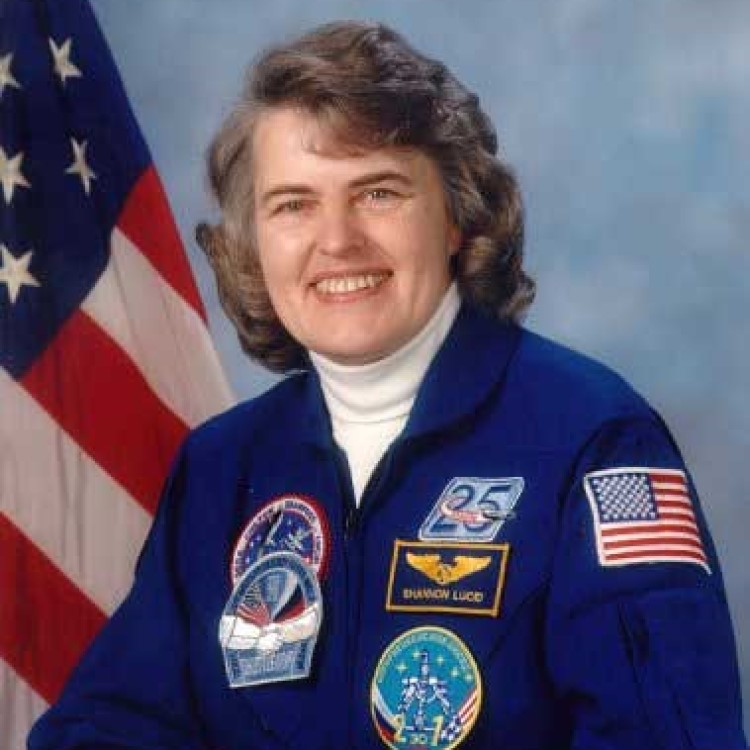

In 1978, Dr. Shannon Lucid, a researcher in the Biomembrane Research Laboratory, was selected by NASA as one…

In 1978, the Carbone Cancer Center Clinical Sciences Center was completed in January adding over 70,000 square feet…

In 1978, the University of Kentucky (UK) Markey Cancer Foundation, previously the Ephraim McDowell Cancer Research Foundation, was…
On Dec. 30, 1977, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Tamoxifen, an anti-estrogen drug, for the treatment…

On Nov. 23, 1977, the Saccharin Study and Labeling Act was enacted by the U.S. Congress to stop…
On Nov. 21, 1977, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed the first pneumococcal vaccine containing 14…
On Oct. 30, 1977, Ali Maow Maalin, a hospital cook in Merca, Somalia, was diagnosed with smallpox by…
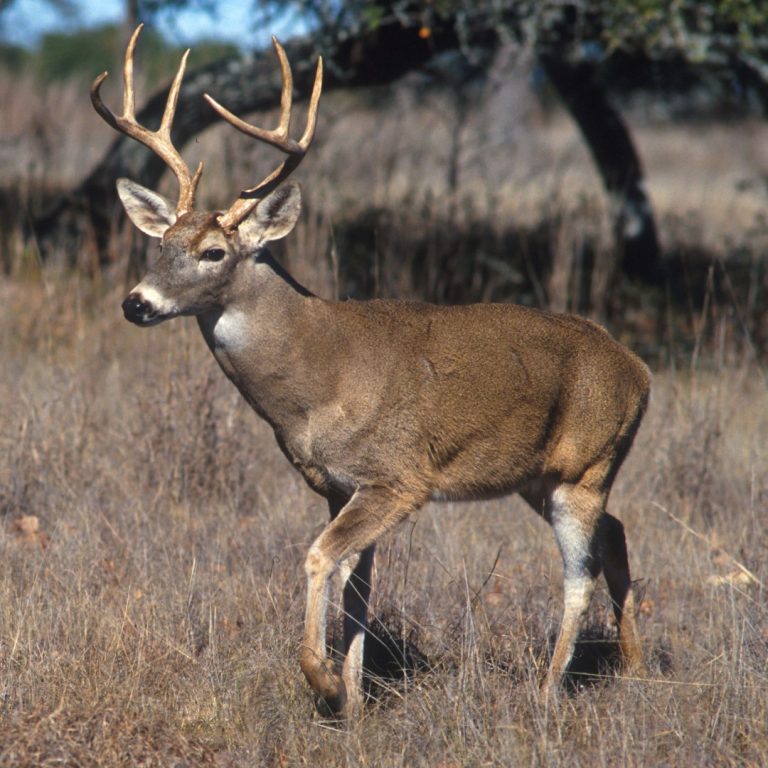

In 1967, chronic wasting disease (CWD) was first observed in a captive deer in Colorado where it was…

On Aug. 31, 1977, in recognition of the seriousness of lupus and America’s commitment to its control, the…
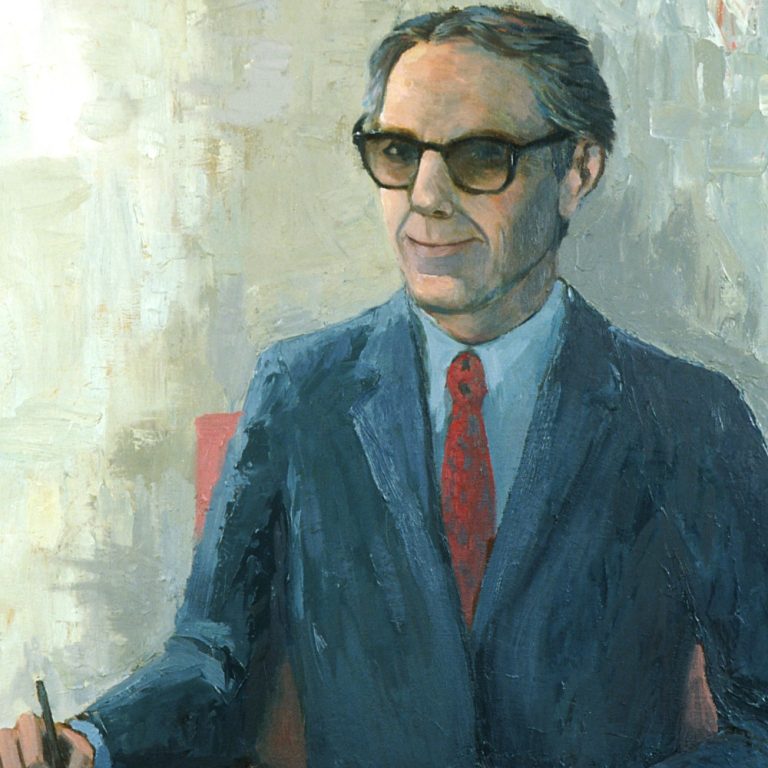

On Jul. 29, 1977, Arthur Canfield Upton, M.D. became the eighth director of the National Cancer Institute (NCI)…

On May 12, 1977, the Program for the Introduction and Adaptation of Contraceptive Technology (PIACT) was founded by…

On Apr. 6, 1977, the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (now Department of Health and Human Services)…

On Apr. 4, 1977, Donald Kennedy, Ph.D., became Commissioner of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Kennedy,…

In 1977, the Priestley Medal was awarded to Henry Gilman by the American Chemical Society “to recognize distinguished…
On Mar. 7, 1977, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Bristol-Myers’ BICNU (carmustine), for the treatment of…
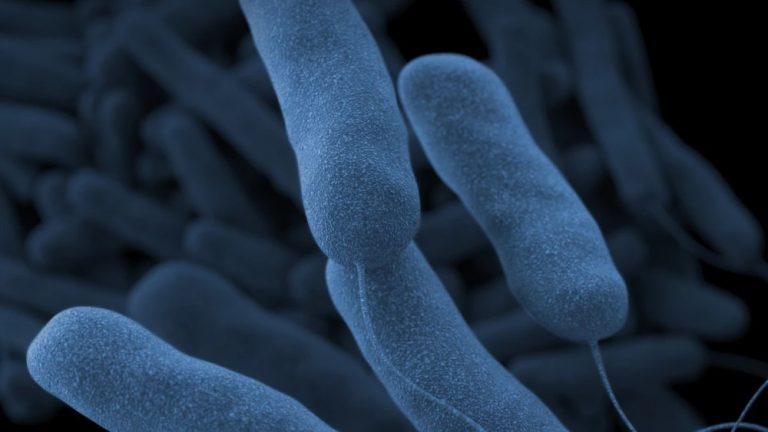
On Jan. 18, 1977, microbiologist Dr. Joseph McDade at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)…

In 1977, Rosalyn Yalow won a share of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the development…

In 1977, the multiple research programs that had developed were formally drawn together into the Research Institute of…
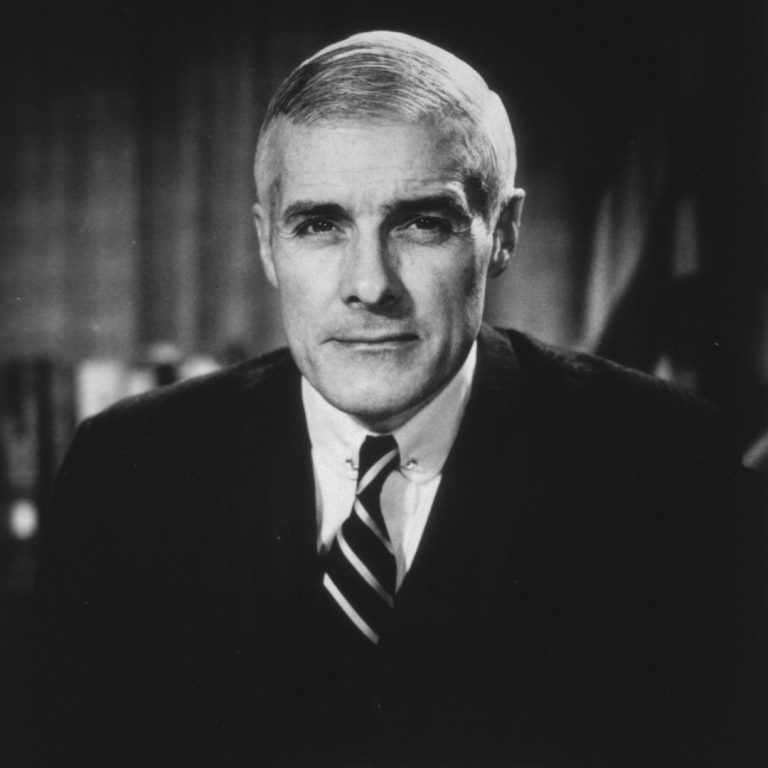

In 1977, Charles C. Edwards, formerly the nation’s top government health official, was named president and CEO of…

In 1977, Stanford Research Institute changed its name to SRI International. Stanford Research Institute, now known as the…
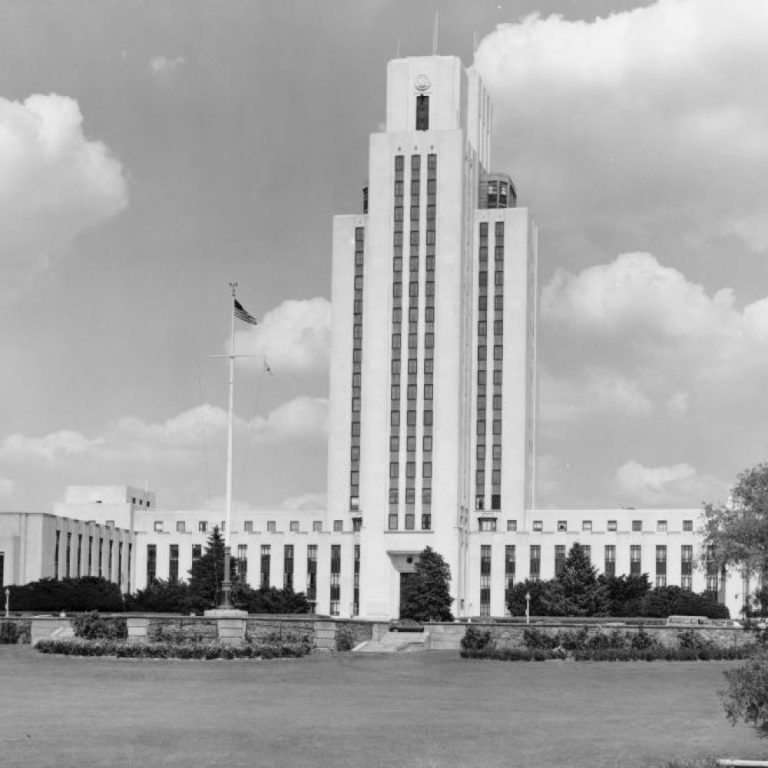

In 1977, the original Naval Medical Center tower was designated a historical landmark and entered into the Registry…
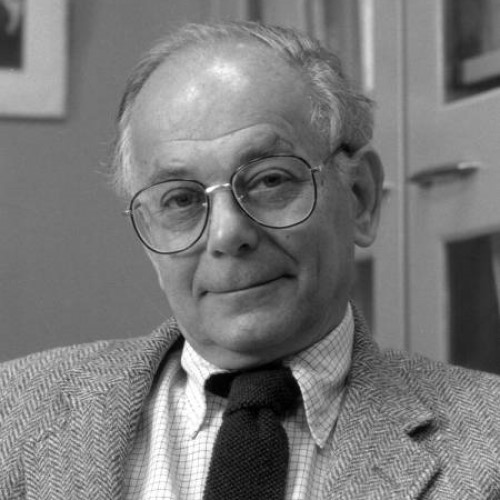

In 1977, Eugene Goldwasser published Purification of Human Erythropoietin (EPO) in the Journal of Biological Chemistry. Goldwasser spent…

In 1977, Dana-Farber (DF) received National Cancer Institute (NCI) Comprehensive Cancer Center designation one of the first in…
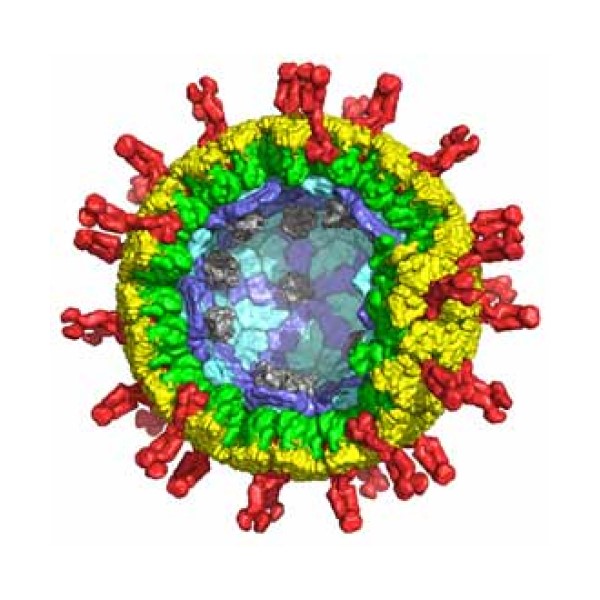
In 1977, Harvard Medical School researcher Stephen C. Harrison first determined the structure of an intact virus particle,…

In 1977, the Lineberger Foundation pledged $1 million to a building fund for a new cancer research center…
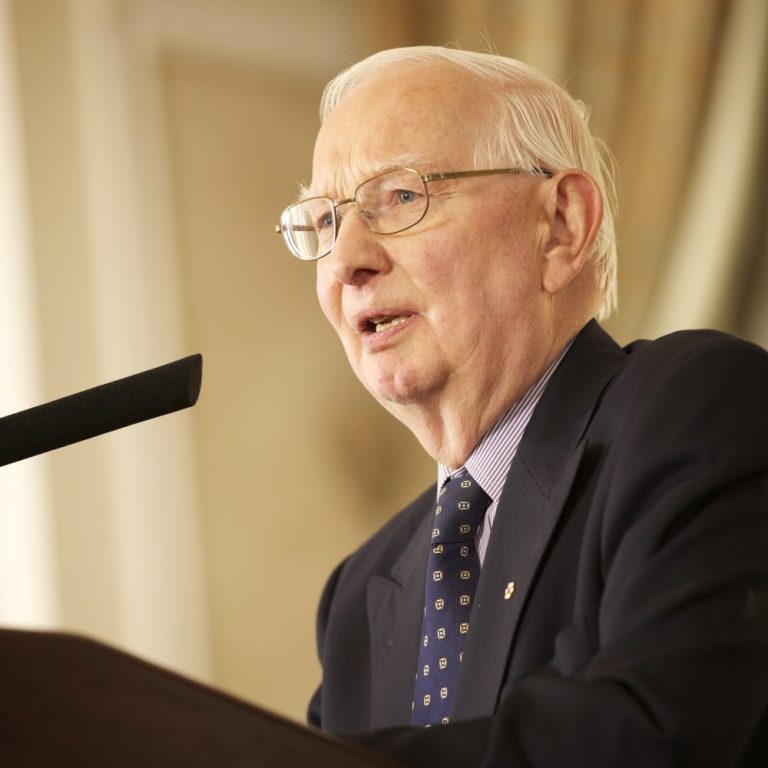

In 1977, Dr. Henry Friesen of McGill University discovered the hormone prolactin and defined its role as a…

In 1977, St.ᅠ Jude Children’s Research Hospital received National Cancer Institute designation. St.ᅠJude Children’s Research Hospital opened it’s…