NIH BRAIN Initiative tool helps researchers watch neural activity in 3D
On Apr. 13, 2020, an ultra-fast, 3D imaging technique called SCAPE microscopy, developed through the National Institutes of Health (NIH)メs Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Technologies (BRAIN) Initiative, allows a greater volume of tissue to be viewed in a way that is much less damaging to delicate networks of living cells.
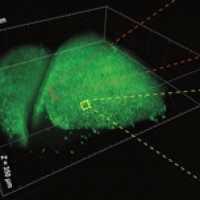
In a study published in Science, researchers used SCAPE to watch for the first time how the mouse olfactory epithelium ラ the part of the nervous system that directly perceives smells ラ reacted in real time to complex odors. They found that those nerve cells may play a larger and more complex role in interpreting smells than was previously understood.
Tags:
Source: National Institutes of Health
Credit: Image: Courtesy Hillman and Firestein labs, Using SCAPE, researchers can watch odor-sensing cells respond (turn green) to complex smells in real time.
